* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 1 - UniMAP Portal
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Phone connector (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Rotary encoder wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
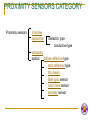
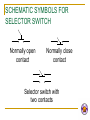
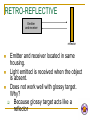
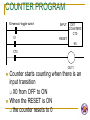
CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL CONTROLLER EQUIPMENT BY: Salsabila Ahmad ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT BASIC 4 ELECTRICAL BASICS POWER SUPPLY INPUT DEVICE Input Controller Equipment CONDUCTOR OUTPUT DEVICE Output Controller Equipment POWER SUPPLY Definition: A device which supplies energy needed to create an electrical current INPUT DEVICE DEFINITION 2 TYPES OF INPUT DEVICE Mechanical input device Solid state proximity device ELECTRICAL SWITCHING Basic Principle of Electrical Switching Types of Contacts How do These Contacts Work? DEFINITION: A device which allows/ controls the flow of current in a circuit These devices are known as “ELECTRICAL CONTROLLER EQUIPMENTS” Provides Electrical Switching MECHANICAL INPUT DEVICES Definition: An input device with a mechanical contact SOLID STATE PROXIMITY DEVICES Definition: An electronic input device which needs power to be able to operate EG Various types of sensors EXAMPLE OF MECHANICAL INPUT DEVICES Contact Relay Push button Limit Switch Selector Switch Toggle Switch Temperature Switch Pressure Switch Solenoid Switch Induction Motor Controller PROXIMITY SENSORS CATEGORY Proximity sensors inductive capacitive dielectric type conductive type ultrasonic optical diffuse reflective type retro reflective type thru beam fiber optic sensor color mark sensor encoder sensor RELAY 2 TYPES OF RELAY: EMR SSR ELECTROMAGNETIC RELAY (EMR) Definition: An EMR is an electromagnetic device composed of a frame/core, electromagnet coil and contacts (move and fixed) Based on simple electromagnetic principle SOLID STATE RELAY (SSR) HOW IT OPERATES? Operates similarly to EMR, but with no mechanical contact. Employ semiconductor switching elements such as thryristors, triacs, diodes and transistors. Employ optical semiconductors called photo couplers to isolate input and output signals. Photo couplers change electrical to optical signals and relay the signal through space. CHARACTERISTICS OF EMR AND SSR EMR slow speed wears out easily Noisy Cheap SSR high speed, high frequency for switching operations no failure due to wear out, since no mechanical contacts little noise Expensive RELAY SYMBOLS Most common relay symbols used in electrical machine diagram Normally open (NO) Normally close (NC) Coil BASIC PRINCIPLE OF ELECTRICAL SWITCHING A situation of breaking and open an electrical circuit Or to direct current from one conductor to another. The PLC is the solution to today’s electrical switching requirements where it is able to solve complex switching requirements. 2 TYPES OF CONTACT NO NC HOW DO THESE CONTACTS WORK? Once coil is energized, the contact will change state NO NC NC NO SOLENOID SWITCH Use concept of magnetic flux for armature/plunger to move Produces linear mechanical motion PUSH BUTTON DEFINITION pushbutton-type operator Have one set or more contact/spring Mostly have a set of normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contact CONCEPTS OF OPERATION Pushing the operator causes the contacts to change state Spring causes switch operator to automatically return to it’s natural state when it is released. NO NC NC NO natural state change state NO NC automatic return a switch with this return spring action, is called a momentary switch. APPLICATIONS Frequently used in industrial applications to control functions such as starting and stopping the machine’s operation With a safety nature. Why? SCHEMATIC SYMBOLS FOR PUSH BUTTON Normally Open Contact Normally Closed Contact SELECTOR SWITCH Similarly to pushbutton, but instead of pushing, you rotate a knob may be designed to stay in a selected position or may have a momentary action selector switch that stays in a certain position is called a maintained switch. APPLICATION Widely used in industrial applications for switching mode of operation to turn the main power on and off to select between AC or DC output. Some requires key (authorized person) to turn on for safety reason. SCHEMATIC SYMBOLS FOR SELECTOR SWITCH Normally open contact Normally close contact Selector switch with two contacts TOGGLE SWITCH Toggle switch is a maintained switch INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER Commonly used micro-controllers PROXIMITY SENSORS INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR Sense only metallic objects e.g. steel, iron, aluminum, tin, copper etc Has limited sensing range range affected by the type of metal sense CAPACITIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR sense all material with mass. operation for both dielectric and conductive type are the same The dielectric type works best for high density material Low density material (e.g. paper, foam etc) do not cause a detectable change in dielectric. The conductive type works best on electrically conductive material e.g. metal or water-based material) ULTRASONIC SENSOR Use ultrasonic technology How does it works? CONCEPTS OF ULTRASONIC SENSOR Use an ultrasonic “ping” sent from sensor to target Sensing area is a funnel shape area Therefore, target must be located directly in front of sensor When echo is returned, sensor detects target by measuring time delay between transmitted ping and returned echo sensor calculate distance between sensor and target Do not work well on cloth, foam rubber since good absorber of sound waves Works best on high density material where sound waves reflects best DIFFUSE REFLECTIVE Emitter and receiver Emitter and receiver located in same housing Light emitted is received when the object is present Works well on glossy target but not transparent RETRO-REFLECTIVE Emitter and receiver reflector Emitter and receiver located in same housing. Light emitted is received when the object is absent. Does not work well with glossy target. Why? Because glossy target acts like a reflector THRU-BEAM emitter receiver Emitter and receiver is located in different housing Sense the object’s present when it passes through between emitter and receiver where it stops the light from hitting receiver FIBER OPTIC Thru-beam Reflector object Use plastic and glass fibers to carry lights Available in both thru beam and reflective COLOR MARK A special type of diffuse reflective optical sensor that can differentiate between colors some can detect contrast between colors. Typically used to check labels and sort packages by color mark. ENCODER Used for position feedback and some for velocity feedback Two main types Incremental absolute CONDUCTOR Definition: A medium that connects all the components and allows current to flow. Examples: copper wire bread board OUTPUT DEVICE DEFINITION A component that will produce a desired output. It is also referred to as a load. COIL Can represents various forms of output including Motor Light Pump Counter Timer Relay TIMER most common symbol for displaying timer function is in block diagram uses a box shape to display the timer function Sometimes, timer is displayed in coil format symbol CHARACTERISTICS OF TIMER Timers typically have one or two input Timer with one input has functions as a timer enable input. When input ‘high’, the timer begins timing A timer with 2 inputs has additional functions which is used to reset the timer accumulated time to zero when the second input is ‘high’ Every timer has a time base Typically; 1 sec, 0.1 sec and 0.01sec. HOW TIMERS ARE IDENTIFIED? Each timer will have number to identify it There are two parameters for timer timer number Used to identify timer e.g. Timer 0, Timer 2. Preset value Is the delay time set for the timer TIMER’S PROGRAM There are still many similarities in the way the timers are programmed even when PLC are different brand Let say the time base of a timer is 0.1 second Therefore, if a programmer entered 50 for the number of delay increments What is the timer’s delay? the timer would have a 5-second delay. 50 x 0.1 sec = 5 sec TMR Has one input Timer enabled if the input logic is ON Timer reset if the input logic is OFF Maximum value 9999 TMR INPUT TIMER0 T0 K40 TMRA Has two inputs Timer starts timing when ENABLE is ON Timer stops when ENABLE is OFF without resetting the current value to 0 ENABLE TMRA TIMER2 T2 RESET K50 The timer resets when RESET is ON The timer is enabled to start when RESET is OFF What is it? What is it characteristics? How does it works? Testing your understanding….. Testing your imagination….. COUNTER used to capture and store number of occurrence CHARACTERISTICS set to some preset number value when this value of input pulses has been received, it will operate its contacts Let say the counter is set for 10 pulses, then when 10 pulse impulses have been received, the counter contacts will close When there is a input transition for X0 from OFF to ON, counter starts counting When the RESET is ON, the counter resets to 0 COUNTER PROGRAM X0=sensor/ toggle switch X1 INPUT CNT COUNTER0 CT0 RESET K5 CT0 OUT1 Counter starts counting when there is an input transition X0 from OFF to ON When the RESET is ON the counter resets to 0 MOTOR In PLC, motor can only be controlled for power (ON/OFF) direction (CCW/CW) preset speed TYPES OF MOTOR DC motor type wound field permanent magnet electronics commutation dc motors AC motor type induction motors synchronous motor