* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT-IV-LIC
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
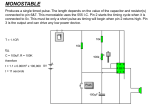
UNIT – IV SPECIAL ICs PREPARED BY V.SANDHIYA LECT/ ECE Integrated Circuits History • tubes and valves • transistor - 1947 Bell Labs, Holmdel, NJ IC Families How logic gates are configured… • TTL • CMOS IC Families • TTL - Transistor-Transistor Logic • CMOS - Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor IC Families TTL - Transistor-Transistor Logic • 74xx designation, i.e., 7447,7490, etc. digital devices • Requires 5 volt supply (max. 5.5 volts) • moderately high current draw • Includes 74Lxx & 74LSxx designations (74L47, 74LS47) that have significantly lower current requirements IC Families CMOS - Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor • 4000 designation, i.e., 4001, 4511, 4517, etc. • Works within a range of voltage: 3-15 volts • Low current requirements • slightly higher cost than TTL • very sensitive to static charges (it ruins them) 555 • Introduced in 1972 • Can accurately time from 0.0000011 seconds to 11,000 seconds (just over 3 hours) • Uses external capacitor and 1 or 2 resistors to control timing • Output is always a digital signal (on-off square wave) • Contains 28 transistors, 12 resistors • Requires 4.5 - 18 volts • Will switch 200mA 555 Timer DIP chip Dual In-Line Pins 1 8 2 7 3 555 4 6 5 top view 555 Timer Ground (-) 1 8 +5 to +15VDC 2 7 3 555 4 6 5 top view • High state output is always 1.7V less than supply • Output is 7.3V @ 9V supply Ground (-) Output 555 Timer 1 8 +5 to +15VDC 2 7 3 555 4 6 5 top view 555 Monostable timing • “One shot” timing • One stable state (off) • Switches on for duration of time then goes back to stable (off) state 555 Astable timing • No stable state (keeps flip-flopping between states) • On time called “mark” • Off time called “space” • Mark-space timing can be adjusted with external capacitor and two resistors Monostable circuit +9VDC R1 = 470K R2 = 1K 7 6 2 8 555 1 4 3 LED C1 = 47mf R3 = 330 Monostable circuit +9VDC +9VDC R1 = 470K R2 = 1K 7 6 2 R2 = 1K 8 555 4 3 1 R1 = 470K 1 8 2 555 7 3 6 4 5 LED C1 = 47mf R3 = 330 C1 = 47mf LED R3 = 330 Monostable circuit +9VDC Timing Control Components R1 = 470K R2 = 1K 7 6 2 8 555 1 4 3 LED C1 = 47mf R3 = 330 Monostable circuit +9VDC Output Components R1 = 470K R2 = 1K 7 6 2 8 555 1 4 3 LED C1 = 47mf R3 = 330 Monostable circuit +9VDC R1 = 470K R2 = 1K 7 6 2 LED 8 555 1 C1 = 47mf 4 R3 = 330 3 Note LED polarity