* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 4 BASIC CIRCUIT DESIGN CONCEPTS
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
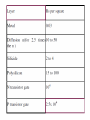
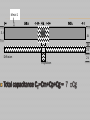
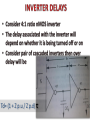
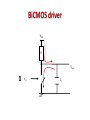
UNIT 4 BASIC CIRCUIT DESIGN CONCEPTS (Pucknell p:- 86-110) • Each of layers have their own characteristics like capacitance and resistances • Concepts such as sheet resistance Rs and a standard unit capacitance □Cg • Also delay associated with wiring, with inverters and with other circuitry may be evaluated in terms of a delay unit τ . • Consider a uniform slab of conduction material of resistivity ρ,of width W, thickness t, length between faces L • Consider the resistance between two opposite faces RAB= ρL/A Ω • Where area of the slab A=Wt. RAB= ρL/Wt Ω • Now, consider the case in witch L=W, that is a square of resistive material, then RAB= ρ/t =Rs • Where • Rs =ohm per square or sheet resistance • The table of values for a 5µm technology is listed below.5µm technology means minimum line width is 5µm and λ= 2.5µm. Capacitance Value in pF*10-4/µm2(relative values in brackets) Gate to channel 4 (1.0) Diffusion 1 (.25) Poly to sub 0.4 (.1) M1 to sub 0.3 (0.075) M2 to sub 0.2 (0.05) M2 to M1 0.4 (0.1) M2 to poly 0.3 (0.075) Relative value = specified value / gate to channel value for that technology W=3λ L = 20λ <- 100 λ -> I<- 4 λ -> I 3λ 4λ Metal 1λ 2λ Diffusion 2λ Polysilicon Metal 1 |<- 50 λ -> I<- 4 λ -> I <- 3λ 50 λ -> I 4λ 1λ 2λ Diffusion 2λ Polysilicon Td= (1 + Z p.u / Z p.d) τ Td= (1 + Z p.u / Z p.d) τ Estimation of CMOS inverter delay • The inverter either charges or discharges the load capacitance CL. • Raise-time and fall-time estimations obtained by following analysis • In this condition p-device stays in saturation for entire charging period of the load capacitance CL • the p device is in saturation current given by Idsp=ßp(Vgs-|Vtp|)2 /2 ----(1) • The above current charges the capacitance and it has a constant value. The output is the drop across the capacitance, given by • Vout =Idsp x t /CL ------(2) • Let t= τr ,Vout=Vdd, Vtp=0.2Vdd and Vgs=Vdd • We have τr = 3CL /ßpVdd Fall time estimation • Similar reasoning can be applied to the discharge of CL through the n- transistor • Making similar assumptions we may write for falltime : τf = 3CL /ßnVdd Summary of CMOS fall time and rise factors • Final expression we may deduce that: τr / τf = ßn / ßp • Raise time is slower by factor of 2.5 when both ‘n’ and ‘p’ are in same size • In order to achive symmetrical operation need to make Wp=2.5 Wn • The factors which affect rise-time and fall-time as follows: 1) τr and τf are proportional to 1/Vdd 2) τr and τf are proportional to CL 3) τr =2.5 τf for equal n and p transistor geometries • The problem of driving large capacitive loads arises when signals must travel outside the chip. • Usually it so happens that the capacitance outside the chip are higher. • To reduce the delay these loads must be driven by low resistance. • • Consider Vin=1 Inverter formed by T1 and T2 is turned on and thus the gate of T3 is pulled down to 0V but T4 is turned on and the output is pulled down • Consider Vin=0,then the gate of T3 is allowed to rise quickly to Vdd,T4 is turned off. • T3 is made to conduct with Vdd on its gate,i.e twice the average voltage that applied to gate • Super buffers are better solution for large capacitance load delay problems BiCMOS driver VDD R Vout 1 0 Vin CL GND BiCMOS driver • High current drive capabilities for small areas in silicon • Working of bipolar transistor depends on two main timing components: 1) Tin the time required to charge the base of the transistor which is large 2) TL the time take to charge output load capacitor which is less Delay T CMOS BiCMOS Tin CL(crit) Load Capacitance CL • Critical value of load capacitance CL(crit) below which the BiCMOS driver is slower than a comparable CMOS driver Cascaded inverters as drivers • N cascaded inverters, each one of which is larger than the preceding by a width factor f . • Now both f and N can be complementary. If f for each stage is large the number of stages N reduces but delay per stage increases. Therefore it becomes essential to optimize. 4: f 4: f2 4:1 1:1 CL 1: f 1: f2 GND • Fix N and find the minimum value of f. • For nMOS inverters • Delay per stage = fτ for ↑Vin • or = 4fτ for ↓Vin • The delay for a nMOS pair is 5 fτ • For N=even • Td=2.5 Neτ for nmos, • Td=3.5 Neτ for cmos • For N=odd nMOS CMOS Transition from 0 to 1 Td=[2.5(N-1)+1] eτ Td=[3.59N-1)+2]eτ Transition from1 to 0 Td=[2.5(N-1)+4]eτ Td=[3.5(N-1)+5]eτ Propagation delay • Cascaded pass transistors: delay introduced when the logic signals have to pass through a chain of pass transistors • The transistors could pose a RC product delay • Ex: the response at node V2 is given by C dV2/dt =(I1-I2)= [(V1-V2)(V2-V3)]/R • Lump all the R and C we have Rtotal=nrRs ….eq-1 Ctotal=ncロCg ….eq-2 Where r=relative resistance/section in terms of Rs c=relative capacitance/section in terms ofロCg • Overall delay τd for n sections is given by τd = n2rc Long wires may be a problem with slowly rising signals wiring capacitances • Fringing field: is due to parallel fine metal lines running across the chip for power connection. Total wire capacitance Cw=Carea+Cff • Interlayer capacitance: is due to different layers cross silicon area • Peripheral capacitance: is due to junction of two devices (regions) Total diffusion capacitance Ctotal = Carea + Cperi Choice of layer 1) Vdd and Vss lines must be distributed on metal lines due to low Rs value 2) Long lengths of poly must be avoided because they have large Rs 3) The resistance effects of the transistors are much larger, hence wiring effects due to voltage divider effects b/w wiring and transistor resistances 4) Diffusion areas must be carefully handled because they have larger capacitance to substrate.