* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islamic Art - Lakeland Regional High School
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Islamic influences on Western art wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Women as imams wikipedia , lookup
Al-Aqsa Mosque wikipedia , lookup
Umayyad Mosque wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
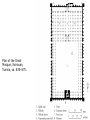
Islamic Art “art beyond the European tradition” “There is only one God, and Muhammad is his prophet.” Chapter 13 Islam • In Arabic Islam means “to submit” • The religious faith of Muslims, based on the words and religious system founded by the prophet Muhammad and taught by the Koran, the basic principle of which is absolute submission to a unique and personal god, Allah. Five Pillars of Islam • Belief in Allah; Qur’an (Koran), Muhammad • Muslims believe that faith alone is meaningless unless backed by action in everyday life. • These actions (pillars) are characterized: faith, prayer, fasting, pilgrimage and charity. Five Pillars of Islam • 1) There is only 1 God – the prophet Muhammad (Faith) • 2) Muslims should pray 5 times a day (Prayer) • 3) Provide for the poor (Charity) • 4) Fast during the month of Ramadan (Fast) • 5) Muslims who are physically and economically able to make pilgrimage to Mecca, the holiest site in Islam (Pilgrimage) Art Historically…. • Pillars 1 and 2 are most important… • Exert a huge influence on Islamic art and architecture. • Worshipping other gods was forbidden – much like Christianity and Judaism….HENCE…. • Forbade images of humans and animals – which could represent gods in sacred buildings. • Therefore, the art of Islamic sacred places lacks figural representation, HOWEVER elaborate abstract designs were created. Koran and Calligraphy Figure 13-16 Koran page with beginning of surah 18, al-Kahf (The Cave), ninth or early tenth century. Ink and gold Koran • The holy book of Islam • Divided into 14 suras (chapters) • Details the many visions and revelations given to Muhammad by Allah through the angel Gabriel. • Reading the Koran is important, because it establishes faith (1st pillar). • All the writing provided a major form of artistic expression, CALLIGRAPHY, decorative writing. • Decorative and didactic instructs the religion’s followers. Arabesque Designs Complex interweaving of plant motifs and geometric pattern. Arabesque Designs • “Arab-like” • Verses in the Koran describe paradise as a place of lush gardens, verdant groves of trees and flowing streams. • The mosaics helped the Muslim faithful to visualize the beauty that awaits them. • The arabesque is distinctive feature of Islamic Art. Mosques • A place of worship for Muslims • Aid in the fulfilling of the 1st and 2nd pillars 1) only one God (Allah) 2) prayer (5 times a day) • Form of the mosque follows its Function! -minaret, qibla wall (prayer hall, hypostyle), mihrab, minbar Mosque (place of worship) The Great Mosque Aleppo, Syria Mosque Architecture • Minaret (tower) - a Muslim crier climbs to the top to call prayer • Recall Hagia Sophia – had 4 minarets • During prayer the faithful face Mecca – a qibla wall – points in the direction of Mecca. • The qibla is part of a prayer hall –often designed as a hypostyle, a room of columns, Muslims gathered in the prayer hall and prayed toward the qibla. • The qibla contained a niche (usually in the center), called a mihrab, the purpose is unclear. Considered decorative. Mosque Architecture • A mosque usually has a dome in the roof marking where the mihrab is located. • The interior of the dome is usually very ornate. • The exterior the mihrab dome is useful in recognizing the mosque • A mosque has podium or minbar – where a religious teacher reads verses from Koran • Before and after worship the faithful gather in forecourt, a large courtyard, of the mosque complex. • Encourages community, and fellowship Plan of the Great Mosque, Kairouan, Tunisia, ca. 836–875. Mihrab from the Madrasa Imami, Isfahan, Iran, ca. 1354. Glazed mosaic tilework, 11’ 3” X 7’ 6”. Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. Dome of the Rock Dome of the Rock • Built has a holy platform from which Muhammad ascended, climbing the golden ladder, into heaven to meet Allah. • Located in Jerusalem • A pilgrimage site—NOT a mosque. • Excellent example of Islamic art and architecture. • Interior of dome covered in tiles with arabesques and calligraphy. • NO people or animal images. • Exterior BLUE and GOLD calligraphic panels of verses from the Koran. Dome of the Rock • Octagonal structure with a dome… • Dome 75’ high • 60’ wide • Shows the influence of Byzantine buildings…..such as San Vitale, in Ravenna Figure 13-2 Interior of the Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, 687–692. Figure 13-11 Prayer hall of the Great Mosque, Córdoba, Spain, eighth to tenth centuries. Great Mosque in Cordoba, Spain • One of the most famous features of the space is the hypostyle prayer hall. • Red and white pattered double arches that rest on 36 piers and 514 columns • The columns were taken from Roman buildings in the region and were too small to provide ample space, SO the architects created a 2-tierd arch system, with the lowest arch having a horseshoe shape. • The numbers of columns and the double arches of the prayer hall make the GM in Cordoba one of the most famous in the world. Figure 13-11 Alternate View Interior of the Mosque with some of the 36 piers and 514 columns Figure 13-13 Dome in front of the mihrab of the Great Mosque, Córdoba, Spain, 961–965. Taj Mahal, India Taj Mahal • The TM is a tomb – NOT a mosque • Elaborate funeral monument • Its height (not including the minarets) is the same as its width, the distance from the base of the dome is equal to the height of its facade. • Four minarets, with a reflecting pool and gardens. • Shah Jahan built the TM in honor of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal. • After 19 years of marriage, his wife died giving birth to their 14th child. • The tomb was ordered to be built “as beautiful as she was beautiful”. • For 22 years, 20,000 workers labored on Shah Jahan’s last gift to his queen. • The effect is to appear weightless, with a white marbled monument that could float toward the heavens. Islamic Art- Closure • Lacks figural representation in holy buildings • Adorned their religious structures with calligraphy and arabesques. • Know and explain the functions of the Islamic mosques. • Form follows function! • Parts of the mosque reflects the requirements set forth by the Five Pillars of Islam – especially 1 and 2!! • Holy buildings: Dome of the Rock, Great Mosque in Cordoba, Spain. Do Now! What is the role of art and architecture in the Islamic world? What do you think are the most impressive visual qualities of Islamic art?