* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angles - Humble ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
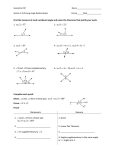
Angles Angle An object that has two rays (called sides) with a common endpoint (called the vertex). Example 1 Name each of the following: A B Sides:_____________________ Vertex:_________ Name:_____________________ C Interior of an Angle the space between the rays that create an angle. Exterior of an Angle the space that is outside of the rays Example 2 How does the diagram in EXAMPLE 1 differ from the diagram in this example? R Q S P Example 3 A) Name a point in the interior of QPS R in EXAMPLE 2. Q S P B) Name a point in the exterior of QPR in EXAMPLE 2. Adjacent To be next to. SHARING a side. Angle Addition Postulate The sum of two adjacent angles is equal to the largest angle. ANGLE ADDITION POSTULATE: If R is in the interior of QPS, then mQPR + mRPS = mQPS. R Q S If mQPR + mRPS = mQPS, then R is in the interior of QPS. P ANGLE ADDITION POSTULATE: If R is in the interior of QPS, then mQPR + mRPS = mQPS. R Q S If mQPR + mRPS = mQPS, then R is in the interior of QPS. P Example 4 If mPQS = 77 and mPQR = 32, then find mRQS. P R Q S Example 5 If mAOC = 70, mAOB =(x + 10), and mBOC =x, find: A x = __________ B O mBOC = _______________ mAOB = _______________ C Acute Angle An angle measuring less than 90° Right Angle An angle whose measure is exactly 90° Obtuse Angle An angle measuring greater than 90° but less than 180° Straight Angle An angle measuring exactly 180° For each of the following angles A) Name it. B) Tell whether its measure is <90, >90, =90, or = 180. C) Classify it. Y L 125 35 F I NAME:_________ OR ______ MEASURE:________ CLASSIFICATION___________ T C NAME:_________ OR ______ MEASURE:________ CLASSIFICATION___________ R T S NAME:_________ OR ______ MEASURE:________ CLASSIFICATION___________ N X S NAME:_________ OR ______ MEASURE:________ CLASSIFICATION___________ Congruent to be the same shape and same size. Angle Bisector a line, ray, or segment that divides an angle into two congruent angles. Example 7 If XZ is an angle bisector of WXY, name the two congruent angles that it forms. W X Z Y Example 8 FG bisects EFH. Find the value of x. m EFG = (5x – 10); E G m GFH = (3x + 25) I F H Example 9 FG bisects EFH. Find the value of x. m GFH = (3x + 20); E G m EFH = (4x + 80) I F H