* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reference Journal
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
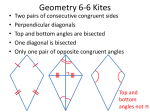
Reference Journal Your Name Table of Contents Chapter 1 – Review of Algebra…page 5 Chapter 2 – Word Problems… page Chapter 3 – Factoring …………page Chapter 4- Algebraic Fractions… page Chapter 5- Graphing Equations…page Chapter 6- Systems of Equations... Page Chapter 7- Radicals ……………….Page Chapter 8- Quadratic Equations…..Page Table of Contents Chapter 9 – Proofs Chaoter 10- Transformations Chapter 1- Algebra Review Evaluating Expressions Remember to put fractions in ( ) in calc Remember to put any negative numbers in ( ) in the calc… if there is an exponent that goes after the close ) Chapter 1 Algebra Review Order of Operations PEMDAS (x +y)2 … in order to solve this re-write twice and foil If there is a negative in front of ( ) make sure to multiply all terms by a negative –ex. 40 –(3x+2) = 40 -3x -2 When multiplying polynomials with exponents…add the exponents When dividing polynomials with exponents… subtract the exponents Chapter 1 Algebra Review Solving Equations Multiply on either side of the equation to get rid of the ( )… DO NOT write ( ) again! Combine like terms on each side of the equation separately Begin to move terms from one side of the equation to the other using inverse operations Chapter 2- Word Problems Number Word problems 5 less than twice a number… 2x-5 Product = *, Quotient = /, Sum = +, Difference= - Chapter 2 - Word Problems Consecutive Integer Problems Motion Problems Coin Problems Percent Problems Investment Age Chapter 3 Factoring LOOK FOR GCF!!!!!!!!!! Look for a Difference of 2 Perfect Squares (a + b) (a –b) Look for a trinomial and do factoring by grouping!!!! Factoring By Grouping Multiply first number (not variable) by the last number Look for factors of this new number that add to the center term Re-write trinomial splitting the center term into these two factors with the variable!!! Draw (), factor out GCF from each group If two binomials match, smile and write that binomial once and the other numbers and variables as the other binomial 71.(3y-2)(y-2) 87. (r-5s)(r+2s) 73.(2x+3)(x-1)89.(m+n)(5m-2n) 75.(3x+5)(x-1) 77.(5x-8)(x+1) 79.(2x-5)(2x-1) 81.(3x+4)(2x-1) 83.(x+5)(10x-1) 85.(x+2y)(x+y) 6. s(t-1)(t+1) 24. 4(5x+3y)(5x-3y) 8. 2(x-4)(x+4) 26. 3(x+1)(x+1) 10.2(3m-2)(3m+2) 28. x(x+5)(x+2) 12. 7(3c-1)(3c+1) 30. 2a(x-3)(x+2) 14.y(y-5)(y+5) 32. (z3-z)(z3+z) 16.a(2a+b)(2a-b) 34. (x2+2)(x+1)(x-1) 18.d(3b+1)(3b-1)36. (y+3)(y-3)(y-2)(y+2) 20 (x2+1)(x-1)(x+1) 22. 5(r+R)(r-R) Chapter 4- Algebraic Fractions Multiplication and Division of EXPRESSIONSFactor all numerators and denominators For division: flip the second fraction Cancel any like terms if one is in the top and one is in the bottom Multiply across (top times top and bottom times bottom) and simplify Adding and Subtracting EXPRESSIONS Find the lowest common denominator…sometimes you have to factor the bottoms to do this Multiply each fraction by the missing terms of the denominator Add the tops together…make sure to put in () and distribute if there is subtraction *DO NOT CANCEL BOTTOMS Algebraic Equations Follow the steps for adding and subtracting… except after you create like denominators you can cancel them away Finish solving the equation with only the tops Inequality Equations Follow steps for regular equations (with or without fractions) If you are multiplying or dividing by a negative number, you MUST flip the inequality sign Solving Equations with many Variables Always get all the terms that include an (x) on one side of the equation and all the other terms on the opposite side Usually you factor afterwards Chapter 5- Graphing Equations Y = mx + b … this is the form that all Linear equations should be in if you are going to graph them M = slope = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)= numerator is the amount you rise, the denominator is the amount you run (left) B= y-intercept- point at which the line crosses the y-axis To graph: 1) plot b 2) then use slope for rise and run Graphing in Calc: Press Y= Make sure the Y= menu is clear Type in the given equation in y=mx +b form Press graph to see the graph, if you don’t see the graph, press zoom and then hit # 6 zoom standard, then hit graph again…now u should see the graph Press 2nd, then hit graph, this shows the table for your given equation Types of Slopes Positive –rises from left to right (m is pos) Negative- falls from left to right (m is neg) Zero slope – horizontal line… y=? Undefined slope or No slope – vertical line… x = ? Parallel lines have the same slope Given two Points: Write the equation of a line Plug the two points into the slope formula Plug the slope into y = mx +b, for m Plug in one of the two given points into the equation with the slope, solve for b Then plug the slope and y-intercept into y = mx+ b Absolute Value Graphs Y = |x|… this graph is a v that has its center point on the origin Y = |x| + a … this moves the v up or down on the y-axis Y = |x + a|… this moves the v left or right… it moves in the opposite direction of a Y = a|x|…this makes the v wider or thinner, if a is a fraction =wider, if a is a number greater than 1 = thinner Absolute Value Graphs Continued Y = -|x|…v flips upside down For the Calculator: Press y=, press MATH, press right arrow to NUM, press #1 abs, put the part of the equation that is inside the bars inside (), put all other parts outside the ()… Y = 2|x-3|+4… the x-3 goes inside the () x = |y|… sideways in the 1st and 4th quadrant Graphing Inequalities Put the equation in y = mx + b form, remember if you are dividing or multiplying by a negative you must flip the inequality sign < or > then the line is dashed ≥ or ≤ then the line is solid To see shading on the calc: Press y=, move cursor to the far left so that the line next to Y1 is blinking, then press ENT either 3 or 4 times, 3 times for greater than, 4 times for less than Chapter 6- Systems of Equations Consistent SystemInconsistent SystemDependent SystemThe 3 methods of solving a system Graphically Addition Method Substitution Method Word Problems Chapter 7 – Radicals How do I add or subtract radicals? How do I multiply radicals? Monomial*monomial Binomial *binomial How do I divide with radicals? How do I solve Radical Equations? How do I add/subtract with Radicals? Simplify all radicals List the factor sets for the number under the radical sign and break the number into the factor set that has the largest perfect square Then take the square root of the perfect square and write it on the outside of the radical sign Variables- even exponents divide by 2 and write the variable with that exponent on the outside of the radical sign Odd exponents- subtract one from the exponent and leave this on the inside of the radical, then divide the even exponent by 2 and write on the outside of the radical sign ONLY ADD/SUB if numbers/variables under the radical are exactly the same!!! How do I multiply/divide radicals? Multiply/divide the numbers/variables outside the radical sign by other numbers/variables outside the radical sign and only multiply/divide interior numbers/variables by interior numbers/variables Ex. (3√5)(4 √6) = 12 √30 Ex. 2 * √5= 2 √5 FOIL FOR BINOMIAL*BINOMIAL Ex. (3√5 + 2)(4 √6 + 4)= 12 √30+12 √5+8√6+8 Rationalizing a Fraction NEVER leave a radical in the denominator of a fraction Multiply the numerator and denominator of the fraction by the radical number… this will make the radical go away in the denominator because you are squaring it Ex. (3√5)/(4 √6)…multiply by√6/√6…answer is √30/8 Perfect Squares to 15 and 20 4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121,144, 169,196,225…400 Solving Radical Equations Isolate the Radical portion of the equation Square both sides of the equation If a binomial is being squared, make sure to write twice and FOIL Now the radical should have disappeared… solve like a regular equation…you should always check your answers…you can get an erroneous answer Chapter 8- Quadratic Equations How do I solve for the Roots of an equation? (find the zeros of the equation) Using the calculator: Using Factoring: Put equation in standard form so that it is equal to zero When taking the square root of both sides of an equation you get a positive and negative answer See chapter 3 for factoring steps Using the Quadratic Formula: X= -b +/- √b2 – 4ac 2a Using the Calculator: TO find the Roots: Type equation into Y= Press zoom, press zoom standard Press 2nd, trace, #2 for Zero Use cursor to go to the left side of the first root, press ENT Use cursor to go to the right side of the first root, press ENT Press ENT again…answer appears Repeat for second root on right Also you can use these steps to find a minimum or maximum Using the Calculator: TO Graph a parabola with the vertex: To find the vertex without the calc…….x= -b/2a Enter the equation in Y=, press graph Press 2nd, Graph for Table Look for symmetry in the y chart The number in the center of the symmetry is your vertex Plot those 7 points on your graph! Word Problems Consecutive Integer, Even and Odd X, x+1, x+2 Even/odd- x, x+2, x+4 Rectangle Problems: Perimeter = 2L +2w Area= L*W Remember to always put a binomial variable in () in an equation Ex. The sum of the squares of two consecutive integers… X2 + (x+1)2 Proofs Addition and Subtraction Proofs Partition… a part + a part = whole Substitution… the two pieces you are trying to prove congruent Use addition if you have 4 small pieces or 3 small pieces (then you need reflexive) Use subtraction if you have 2 big pieces and 2 small pieces or 2 big pieces and 1 small piece (then you need reflexive) List of Theorems Definition of Midpoint: a line has only one midpt which cuts it in half Definition of a Angle Bisector: it is a line that cuts an ANGLE in half Definition of a Line Bisector: it is a line that goes to the MIDPT Definition of a Median: a line drawn from a vertex of a triangle to the midpt of a side Definition of Altitude: a line drawn from a vertex that is perpendicular to the side (makes right angles) List of Theorems Perpendicular lines form right angles All right angles are congruent Vertical angles are congruent Definition of Supplementary Angles Supplements of congruent angles are congruent If two angles are congruent and supplementary then they are right angles Definition of Complementary angles Complements of congruent angles are congruent List of Theorems Isos. Triangle Theorem: if 2 base angles are congruent, then 2 sides are congruent In an isos. Triangle, if the line drawn from the vertex angle is an altitude then it is also the median and angle bisector Definition of an Equilateral Triangle: all sides and angles are congruent Perpendicular Bisector Theorem: if given a picture that looks like a kite with the 2 top sides congruent and 2 bottom sides congruent, then there is a perp. Bis. Proving Triangles SAS, ASA, SSS CPCTC… use this after you prove 2 triangles congruent to prove other sides or angles congruent If you are given 2 sets of lines or angles that are cut in half and you want to prove that half of one line is congruent to half of the other line then …. Use Division, or halves of equal quantities are equal or multiplication Reflexive: a side or angle is congruent to itself All right angles are 90 All straight lines are 180 degrees Chapter 10- Transformations Line Reflection… r name of the line you reflect over Point Reflection… Ro for origin or another point (x,y) Rotation… Rdegrees Dilation… Dnumber that you multiply the preimage by Translation…T(x,y) that you add to the preimage Glide Reflection… composition of translation and reflection Line Symmetry Point Symmetry Orientation, Direct Isometry and Opposite Isometry Line and Point Reflections r x-axis…(x,y) …(x, -y) r y-axis…(x,y)…(-x,y) r y=x …(x,y) …(y,x) r y=-x…(x,y)…(-y,-x) Ro…reflect over origin (x,y)…(-x,-y) Count the boxes to the origin and then go that distance from the origin in the other direction Rotations R90=R-270…(x,y)…(-y,x) R180=R-180…(x,y)…(-x,-y) R270=R-90…(x,y)…(y,-x) Count the distance that the preimage is from the x-axis and make the image this distance from the y-axis in the correct quadrant. Count the distance the preimage is from the y-axis and make the image this distance from the x-axis. Dilation and Translation Dilation – Da...(x,y)…(ax,ay) Translation-T(a,b)…(x,y)…(x+a,y+b) Glide Reflection… either T(x,y) ◦ r y=x Or ry=x ◦ T(x,y) ◦….then… but you work from RIGHT to LEFT Defintions: Orientation- the letters going around a figure from right to left or left to right Direct Isometry- is a transformation that preserves distance and orientation…translation, rotation, point reflection Opposite Isometry- preserves distance but not orientation…line reflection Dilation – DOES NOT PRESERVE DISTANCE Definitions Line Symmetry- you can cut it in half in a direction or you can fold the figure on top of itself perfectly in some direction Point Symmetry- turn your piece of paper 180 degrees and the picture should look the same!!!