* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13.2 Angles of Rotation
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation matrix wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation group SO(3) wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
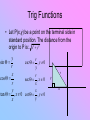
13.2 Angles of Rotation Unit Circle Quiz: May 11 Ch. 13 Test: May 13 Do you recall… • In geometry, an angle is defined by two rays that have a common endpoint. • In trig, an angle is defined by a ray that is rotated around the endpoint…this is called ANGLE OF ROTATION. – The Greek letter theta, Θ, is commonly used to name an angle of rotation. • The starting position is the Initial Side and the final position is the TERMINAL SIDE. • When the endpoint is at the origin, it is called STANDARD POSITION. What else? • If rotated COUNTERCLOCKWISE- the angle has a positive measure • If rotated CLOCKWISE-the angle has a negative measure • The most common unit for angle measure is the degree. • A complete rotation is 360 degrees, so 45 degrees is 1/8th of a complete rotation. – (hint…divide) COTERMINAL • Two angles are co-terminal if they have the same terminal side. – What is co-terminal with 230 degrees? • You can find the co-terminal angles by adding or subtracting integer multiples of 360o. Example: • Find the coterminal angle, θ, for each angle below such that -360o<θ<360o. 180o -27o Reference Angles • For an angle in standard position, the reference angle, Θref , is the positive acute angle formed by the terminal side and the x-axis. Example: • Find the reference angle for: 94 degrees 245 degrees 290 degrees -110 degrees Trig Functions • Let P(x,y) be a point on the terminal side in standard position. The distance from the origin to P is: x 2 y 2 y r sin csc , y 0 r y x r cos sec , x 0 r x x y tan , x 0 cot , y 0 y x r y x Example: • Let P(-2,-3) by a point on the terminal side in standard position. Find the exact values of the 6 trig functions. Let’s make you think… • The terminal side of Θ in standard form is in Quadrant II and cos Θ = -3/5. Find the exact values of the 6 trig functions. Practicing Helps You Remember • P. 841 #9 – 63 odd