* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download aka Subduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
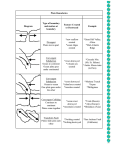
Plate Tectonics - theory stating that the Earth’s crust is made up of large, moving plates - the major force in geomorphology. Continental Drift - Idea developed by Alfred Wegener in 1915. - Proposed that the light continental crust “floated” on the dense oceanic crust. - Proposed the idea of “Pangea” - His theories were altered to create the modern view of plate tectonics. Boundaries -Three types of boundaries: - Convergent - Divergent - Transform Convergent Boundaries -Boundary where plates push together. - Three types: - Continent/Continent - creates non-volcanic mountains (Himalayas) Convergent Boundaries Convergent Boundaries -Boundary where plates push together. - Three types: - Continent/Continent - creates non-volcanic mountains (Himalayas) - Ocean/Continent - aka Subduction - creates volcanic mountains (Andes, Cascades) - Ocean/Ocean - creates volcanic islands (Indonesia) Divergent Boundaries -Boundary where plates pull away from each other. - Examples: - Mid-Atlantic Ridge (Iceland) - Great Rift Valley in Africa Divergent Boundaries Transform Boundaries -Boundary where plates slide parallel to each other. - Example: San Andreas Fault - major earthquakes Plate Tectonics Ring of Fire - Area of subduction around the Pacific Ocean known for volcanoes.