* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
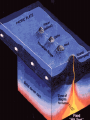
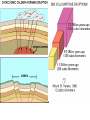
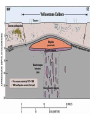
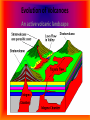
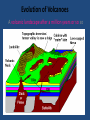
1. What is a volcano? a. Types of lava A-a, Hawaiian term for lava flows that have a rough rubbly surface composed of broken lava blocks. Sharp clinker block, slower moving and cool in temp. pahoehoe • Pahoehoe is a Hawaiian term for basaltic lava that has a smooth, hummocky, or ropy surface. A pahoehoe flow typically advances as a series of small lobes and toes that continually break out from a cooled crust. The surface texture of pahoehoe displaying all kinds of bizarre shapes often referred to as lava sculpture The Ring Of FIRE • Borders plate edges • Mainly in Pacific Ocean as that is where subduction is occurring the most • Most volcano’s are at DIVERGING BOUDARIES OR CONVERGING • Some are HOT SPOTS Tuff Ring: Diamond Head, Hawaii Divergent boundary volcano’s • Mostly underwater • Emit gasses and pillow lava • do break surface in Iceland and east Africa Divergent usually are rift eruptions or cinder cones Convergent Boundaries • Due to subduction and crust recycling • We get more gas and silica • More explosive cones • Form Island arc’s- Sumatra Island arc system ocean-ocean plate collisions forms volcanic island arc shape chain of islands Japan, Aleutians in Alaska Hot spot volcanoes • Can be EXPLOSIVE like convergent boundaries (yellowstone) • Or VERY mild like Hawaii • Hotspot is an area that has excess heat, the plate moves over it and creates volcano’s Usually for Shield Cones Section 3-2 VOLCANIC ACTIVITY 1. How Magma reaches the Surface • • • • • Less Dense than surroundings Low density RISES Still hot so find weak spot melts thru Pressure builds As pressure rises TEMP rises (BOYLE’s LAW) • Eruption!! . Eruption • Magma is now lava–Flows and projectiles • Ash into atmosphere • Gasses ejected –WATER,N, O , C, S, Hydrogen sulfide others –Early atmosphere??? Inside the volcano • Magma chamber is the pocket of magma • Vent is escape route. Main is largest side are lateral vents • Pipe is neck to chamber • Crater is top of vent • Magma is liquid rocks and hot gasses Draw pg 95 • Batholith-large body of igneous rock formed beneath the Earth’s surface by the intrusion and solidification of magma) with a surface exposure of 100 square km (40 square miles) or larger. • Stock-is a discordant igneous intrusion having a surface exposure of less than 40 sq mi (100 km2), differing from batholiths only in being smaller. FLAT BASE Laccolith • a type of igneous intrusion that has split apart two strata, resulting in a domelike structure; the floor of the structure is usually horizontal. A laccolith is often smaller than a stock Dike runs up and down Sill runs ---- Batholith Evolution of Volcanoes An active volcanic landscape Evolution of Volcanoes A volcanic landscape after a million years or so so Types of volcanic eruptions • Quiet- mainly slow flow lava, some gas • Pahoe-hoe and a-a lava • Lava Tubes- cooled and hard on top but still flowing below Explosive eruptions • • • • Thick, high silica magma Lots of gas Pressure builds Explosion produces ash and BOMBS Pyroclastic Flows • Ash, gas and cinders thrown with force, flows like a river, DEADLY Products of Eruptions Lava Flows Pyroclastic Debris • Bombs • Lapilli • Ash Mudflows Landslides Gases • Steam • Carbon Dioxide • H2S • SO2 • HCl • HF Types of Volcano’s • Extinct- Not active • Dormant-Sleeping, not active in recent history • Active- Live has erupted, will erupt Other activity • Geothermal- as magma or REMNANT heat heats water it rises (that density thing again) it can then form hot springs and geysers • Geyser is when it is forced out when the water reaches Boiling point. • This energy can be used for electricity Caldera Formation