* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cenozoic 1 - E. R. Greenman
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
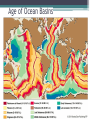
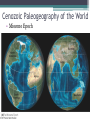
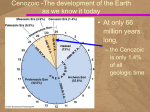
Cenozoic Era Geologic Time • Eons: • Hadean ▫ 4.5-3.8 bya • Archaean ▫ 3.8-2.5 bya • Proterozoic ▫ 2.5 bya – 543 mya • Phanerozoic • 543 myapresent Geologic Time in 24-hours • At only 66 million years long, the Cenozoic is only 1.4% of all geologic time ▫ or only 20 minutes on our hypothetical 24hour clock for geologic time Cenozoic Events • When the Cenozoic began, semitropical (angiosperm) forests covered much of North America, and many mammals dwelled in these forests • Many event that began during the Cenozoic continue to the present, including ▫ the ongoing erosion of the Himalayas in Asia and the Andes in South America, ▫ the origin and evolution of the San Andreas fault, ▫ and the origin of the volcanoes that make the Cascade Range. Neogene and Paleogene • Geologists divide the Cenozoic Era into two periods of unequal duration ▫ The Paleogene Period 66 to 23 million years ago includes Paleocene, Eocene, and the Oligocene epochs ▫ The Neogene Period 23 million years to the present Includes Miocene, Pliocene, Pleistocene, Holocene epochs • Older system: ▫ Tertiary and Quaternary periods Cenozoic Rocks Are Accessible • Vast exposures of Cenozoic sedimentary and igneous rocks in western North America ▫ record the presence of a shallow sea in the continental interior, ▫ terrestrial depositional environments, ▫ lava flows, ▫ and volcanism on a huge scale in the Pacific Northwest. Paleocene Fort Union Formation, Montana Wasatch Formation, Bryce Canyon Miocene Lovejoy Basalt, California Cenozoic Plate Tectonics • The progressive fragmentation of Pangaea accounts for the present distribution of Earth's landmasses • Because the geographic locations of continents profoundly influence the atmosphere and hydrosphere, moving plates also directly affect the biosphere Paleogeography of the World • During the Triassic Period Paleogeography of the World • During the Jurassic Period Paleogeography of the World • During the Late Cretaceous Period Spreading Ridges • Spreading ridges such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and East Pacific Rise were established, along which new oceanic crust formed and continues to form • However, the age of the oceanic crust in the Pacific is very asymmetric, because much of the crust in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin has been subducted beneath the westerly moving North and South America plates Age of Ocean Basins Cenozoic Paleogeography of the World • Eocene Epoch Cenozoic Paleogeography of the World • Miocene Epoch Cenozoic Paleogeography of the World • Present Day End of the Tethys • Another important plate tectonic event ▫ Northward movement of the Indian plate and its eventual collision with Asia • Simultaneous northward movement of the African plate ▫ Caused the closure of the Tethys Sea ▫ Causes tectonic activity that currently takes place int an east–west zone from the Mediterranean through northern India Americas Move West • North and South America continued their westerly movement as the Atlantic Ocean basin widened • Subduction zones bounded both continents on their western margins ▫ Situation changed in North America as it moved over the northerly extension of the East Pacific Rise and it now has a transform plate boundary