* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soil
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Soil governance wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
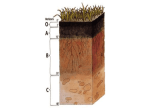
Soil Topic 2052 Anna Blight What is soil? • Soil is the product of the rocks from which it was derived after weathering • The top layer of the earth’s crust • Renewable natural resource that supports life What does soil do? • Storehouse for nutrients • Allows for aeration • Holds water • Anchors the plant Rhizoshpere • 24” of soil just below the earth’s surface • Living micro-organisms interact with plant life • Urban trees have 80% of their roots in the top 12” of soil • What happens to soil at this level is important for plant health Soil Quality • Plants need suitable biotic habitat for beneficial micro-organisms to live • Inhibit degradation by - not allowing compaction from heavy equipment - protect soil from run-off or flooding • Add organic matter to improve quality Mycorrhizae • A group of beneficial fungi associated with roots of plants in healthy soil • Aid roots in nutrient absorption from soil Soil Texture • • • • Percentage of sand, silt and clay SAND is the largest particle, course texture SILT is medium textured CLAY is the smallest particle and is very fine textured Soil texture affects: • • • • • Compaction Ease of tillage Drainage Water holding capacity Nutrient holding capacity Soil Structure • Particles group into aggregates • CLAY helps bind, but too much clay will form a barrier to drainage • SAND aids drainage and aeration, but too much sand causes water to drain too fast and makes soil dry out • Excessive tillage destroys structure Ideal soil composition • 45% sand, silt and clay mixture • Pore spaces 25% air and 25% water • 5% organic matter Soil and Water • Depending on soil type, it takes between 200-1000 pounds of water for formation of 1 pound dry matter of plant material • Amount of water passed through one acre of corn plants is equal to 16 inches of rain Soil in nature • Outdoors, soil is made up of organic matter, sand, silt and clay • Different proportions of each will form different soil textures • Ideal soil is not too sandy or too much clay Indoor Soil Mixtures • Soil less mixtures are usually a mix of peat, perlite, vermiculite and bark • Perlite is white and aids in drainage • Vermiculite is gold - copper color and looks like an accordion, which makes it useful in retaining water in the mix Resources • http://aged.ces.uga.edu/lessons/course01461.htm • Integrated Plant Health Management Training Program for Landscape Maintenance Providers, MSU Nursery and Landscape Team • http://hubcap.clemson.edu/~blpprt/bobweb/BOBWEB24.H TM • http://ltpwww.gsfc.nasa.gov/globe/index.htm