* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Free preview of PowerPoint and Teacher Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
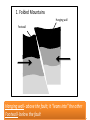
How Mountains Form III. I. Earth’s core is hot. I. hot! II. This causes the magma in the mantle to spin slowly (convection). II. III. At Earth’s surface, tectonic plates, floating on the spinning magma, forms mountains 3 different ways: 1. Folded mountains 2. 3. Cause (fault?) Stress Result 3 Examples Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com 1. Folded Mountains Hanging wall Footwall Hanging wall- above the fault; it “leans into” the other Footwall- below the fault Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com How Mountains Form III. I. Earth’s core is hot. I. hot! II. This causes the magma in the mantle to spin slowly (convection). II. III. At Earth’s surface, tectonic plates, floating on the spinning magma, forms mountains 3 different ways: 1. Folded mountains Footwall Cause (fault?) Stress Result 3 Examples 2. Fault-block mountains 3. Hanging wall Folded mountains occur along a reverse fault. Compression squeezes the rock together. This causes rock in the hanging wall to go up, or “fold”. 3 examples are the Appalachians, Himalayas, and Alps Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com 2. Fault-block Mountains Foot wall Hanging wall Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com How Mountains Form III. I. Earth’s core is hot. II. This causes the magma in the mantle to spin slowly (convection). I. hot! II. III. At Earth’s surface, tectonic plates, floating on the spinning magma, forms mountains 3 different ways: 1. Folded mountains Footwall Hanging wall Cause (fault?) Folded mountains occur along a reverse fault. Stress Compression squeezes the rock together. Result This causes rock in the hanging wall to go up, or “fold”. 3 Examples 3 examples are the Appalachians, Himalayas, and Alps 2. Fault-block mountains 3. Volcanic Mountains Footwall Hanging wall Now fill these in Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com (removed for preview) Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com (removed for preview) Copyright © InteractiveScienceTeacher.com Come back and visit InteractiveScienceTeacher.com for everything you need for every lesson: Videos- where I show you how to present each lesson Teacher Notes PowerPoints Student Handouts