* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Radioactive Decay & Convection Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
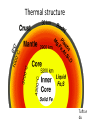
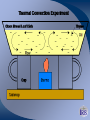
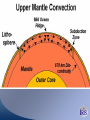
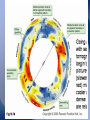
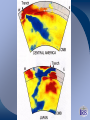
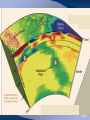
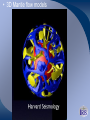
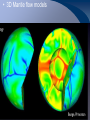
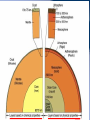
Radioactive Decay and Thermal Convection Thermal structure of the Earth: Heat is a driver for seismological processes Starting with student experiences What evidence do they have for Earth’s internal temperature? Starting with their experiences Earth’s heat and the age of the Earth • Uniformitarianism (Lyell’s Principles of Geology) – same geological processes occurring today have existed throughout geologic time • Darwin (Origin of Species) estimated that it took 300 million years to erode a chalk deposit in southern England • Lord Kelvin - estimate time from molten state to solidification via cooling – temperature at Earth's core = melting point of rocks – temperature gradient with regard to depth below the surface (1 degree/50’) – thermal decrease through conductivity of rocks* – Estimate of 20 myo to 400 myo) Challenges to Kelvin’s model • Assumption of a solid Earth • Some argued that the Earth had never been a molten sphere; rather Earth had formed from the slow accumulation of solid material like asteroids. • Some attacked Kelvin's assumption about a closed system of dwindling initial heat • Others offerred the possibility that the then-unknown internal structure of atoms could contain massive amounts of potential energy Where does the heat come from? • 20% Residual heat from accretion and gravitational collapse • 80% Radioactive decay – Uranium-238 (4.47 × 109) – Uranium-235 (7.04 × 108) – Thorium-232 (1.40 × 1010) – Potassium-40 (1.25 × 109) Average 25oC/km Thermal structure Tufts.e du Earth’s Energy Budget • Solar Radiation - (99.978%, or nearly 174 petawatts; or about 340 W m-2) • Geothermal Energy - (0.013%, or about 23 terawatts; or about 0.045 W m-2) • Tidal Energy – (0.002%, or about 3 terawatts; or about 0.0059 W m-2). • Waste Heat - (about 0.007%, or about 13 terawatts; or about 0.025 W m-2) How is Earth’s heat released? • Conduction • Convection • Sketch expected convection in pan How to best model mantle material • Obleck? – Cornstarch and water • Silly putty? • What are important criteria for choosing? Convection and Earth’s interior • 3D Mantle flow models • 3D Mantle flow models • Mantle convection – Can be imaged using seismic waves – Complex – Sometimes both upper and lower mantle together – Some subduction zones can be imaged to base of mantle Reflection on Earth’s interior • First by yourself, and then with your table, consider 1, 2 or all 3 of the following questions: – What is the difference between the crust and the mantle? – What is the difference between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere? – Why are both sets of terms used, and which would be simplest for your students to understand?