* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes - Sonoma Valley High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
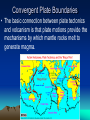
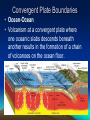
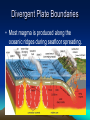
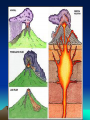
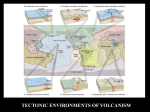
Volcanoes Types of Eruptions • Violent and explosive • Quiet and flowing – Depends on trapped gases and magma composition http://news Trapped Gases • Water vapor and carbon dioxide are trapped in magma • At low pressure, they escape quietly when they reach the surface • At high pressure, they escape violently when they reach the surface Magma Composition • Two types: – Basaltic – less silica and very fluid; produces quiet eruptions – Granitic – lots of silica, high water vapor content, and very thick; produces very violent eruptions Forms of Volcanoes • Three forms: – Shield – Cinder Cone – Composite Shield Volcano • Formed by quiet eruptions • Basaltic lava builds up in flat layers • Gently sloping sides • Ex: Hawaiian Islands Cinder Cone Volcano • Caused by explosive eruptions • Granitic lava thrown high into the air • Lava cools into different sizes of volcanic material called tephra • Steep-sided, loose slopes Composite Volcano • A mix of the other two types • Quiet or violent • Basaltic or granitic • Steep or gentle slopes • Layered or tephra Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity • Most of the volcanoes on Earth occur along the margins of the ocean basins, within the circum-Pacific, known as the Ring of Fire. • 2nd group is found in the deep-ocean basins, Hawaii and Iceland. • 3rd group is composed of volcanic structures that are irregularly distributed in the interior of the continents. Convergent Plate Boundaries • The basic connection between plate tectonics and volcanism is that plate motions provide the mechanisms by which mantle rocks melt to generate magma. Convergent Plate Boundaries • Ocean-Ocean • Volcanism at a convergent plate where one oceanic slabs descends beneath another results in the formation of a chain of volcanoes on the ocean floor. Convergent Plate Boundaries • Ocean-Continent • Develop where slabs of oceanic lithosphere are subducted under continental lithosphere to produce a continental volcanic arc. Divergent Plate Boundaries • Most magma is produced along the oceanic ridges during seafloor spreading. Intraplate Igneous Activity • Occurs within a plate, not at a plate boundary. • Yellowstone National Park • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called mantle plume rises toward the surface. • Caused by hot mantle plumes rising up from the core mantle-boundary, causing decompression melting and forming small areas of volcanic activity on the surface. Review • How are the locations of volcanoes related to the plate boundaries? • What causes intraplate volcanism? • Where is most of the magma produced on Earth on a yearly basis? • What is the ring of fire?