* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plosky tolbachik volcano in kamchatka erupts after 40 years
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
David A. Johnston wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
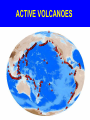
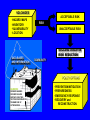
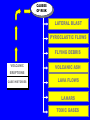
PLOSKY TOLBACHIK VOLCANO IN KAMCHATKA ERUPTS AFTER 40 YEARS January 6, 2013 Walter Hays, Global Alliance for Disaster Reduction, Vienna, Virginia, USA PLOSKY TOLBACHIK SPEWS ASH 4 KM: JAN. 6, 2013 The Plosky Tolbachik volcano, which emitted lava, poisonous gases, and ash, is located in Kamchatka peninsula, hundreds of miles (km) from the nearest residential areas. Tourists rushing to the area to view the once-in-40 years spectacle have been warned about the toxic gases. Until the lava-spewing fissure that occurred on November 27, 2012, and the current eruption phase, Plosky Tolbachik had been dormant since 1976. The current eruption, which is expected to continue for some time, has not yet forced any changes in the airline flight patterns over this part of Russia. This type of eruption, known as a strombolian eruption, is usually moderate. BACKGROUND VOLCANOES are awesome manifestations of heat flowing at hot spots (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) and in subduction zones (e.g., along almost the entire Pacific Rim). GLOBAL DISTRIBUTION OF 1,500 ACTIVE VOLCANOES ACTIVE VOLCANOES VOLCANOES •HAZARD MAPS •INVENTORY •VULNERABILITY •LOCATION ACCEPTABLE RISK RISK UNACCEPTABLE RISK VOLCANO DISASTER RISK REDUCTION DATA BASES AND INFORMATION COMMUNITY POLICY OPTIONS HAZARDS: GROUND SHAKING GROUND FAILURE SURFACE FAULTING TECTONIC DEFORMATION TSUNAMI RUN UP AFTERSHOCKS •PREVENTION/MITIGATION •PREPAREDNESS •EMERGENCY RESPONSE •RECOVERY and RECONSTRUCTION VOLCANO HAZARDS (AKA POTENTIAL DISASTER AGENTS) • • • • VERTICAL PLUME ASH AND TEPHRA LATERAL BLAST PYROCLASTIC FLOWS VOLCANO HAZARDS (AKA POTENTIAL DISASTER AGENTS) • LAVA FLOWS AND TOXIC GASES • LAHARS • EARTHQUAKES (related to the movement of lava) • “VOLCANIC WINTER” CAUSES OF RISK LATERAL BLAST PYROCLASTIC FLOWS FLYING DEBRIS VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS CASE HISTORIES VOLCANIC ASH LAVA FLOWS LAHARS TOXIC GASES ELEMENTS OF VOLCANO RISK HAZARDS EXPOSURE RISK VULNERABILITY LOCATION VOLCANOES CAUSING MAJOR LOSS OF LIFE Three past volcanic eruptions caused major loss of life: 1) Krakatoa, Indonesia, where 32,000 were killed in 1883; 2) Mt. Pelee, Martinique, where 29,000 were killed in 1902; and 3) Nevada del Ruiz, Colombia, where 23,000 were killed in 1985. EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES FOR VOLCANOES • FORECASTS OF ERUPTIONS • MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES (E.G., DEFORMATION, SEISMICITY, GAS EMISSIONS, REMOTE SENSING, WINDS) • WARNING SYSTEMS • DATABASES FOR EACH VOLCANO • COMPUTER MODELS OF VOLCANOES • MAPS • DISASTER SCENARIOS • HAZARD ASSESSMENT • RISK ASSESSMENT MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES .