* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Boundary Types (1) PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
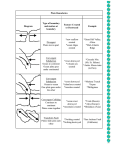
Theory of Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift The Theory of Plate Tectonics starts with another idea… Continental Drift. The Earth once had a single land mass called Pangaea that broke apart into pieces that drifted away to become the major continents of today. Pangaea Evidence that supports Continental Drift • Identical types of fossils found in Africa and South America • Continents can “piece”together with the same rock formations • Glacial deposits left by same sheet of ice Africa-South America The continents are moving because of sea floor spreading. • Running down the middle of the oceans are long mountain chains with valleys in the middle called mid ocean ridges. Lava erupts from the center of the valley and pushes the ocean floor away on the other side. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is separating at approximately 4 cms per year. More evidence… • Rocks are younger by the mid ocean ridge than farther away • Magnetic stripes match up on either side of the ridge as the poles reverse themselves Magnetic Stripes Why doesn’t the Earth keep getting bigger?…Subduction Zones • The ocean floor is also being destroyed • Parts of the ocean floor are going back down into the mantle at subduction zones. These trenches are the deepest part of the ocean.(Ex: Marianas Trench) Subduction Zone The Theory of Plate Tectonics explains the formation, movements, collisions, and destruction of the Earth’s crust. Areas of Sea Floor Spreading Key Subduction Zones How do the plates move? • One hypothesis is that large convection currents within the mantle move the plates. • Movement is caused by differences in temperature causing a rising and sinking cycle. Convection Currents The lithosphere is divided into 7 major and minor plates. Plates move at different speeds in different directions. Plate boundaries are where two plates meet. Major Plates Three Types of Plate Boundaries: • Divergent—Boundary where plates move apart (ex: Great Rift Valley—Africa; Mid ocean Ridges) • Convergent—Boundary where plates come together (ex: Himalayan mountains, Japan, and Philippines) • Transform—Boundary where two plates slide along side each other (ex: San Andreas Fault— San Francisco) Divergent Boundaries occur where plates move apart. There are two types of divergent or constructive boundaries: **Mid-Ocean Ridge **Rift Valley Divergent Boundary Mid- Ocean Ridge- New ocean floor, mountains, earthquakes and volcanic action occur when an ocean plate spreads apart (Mid-Atlantic Ridge: largest mountain range in world.) Mid-Ocean Ridge Mid-Atlantic Ridge Rift Valley- Continent starts to split apart forming a rift valley and eventually a seaway and then an ocean. Volcanic activity and earthquakes occur in these areas. (Ex: African Rift Valley) Rift Valley The Great African Rift Valley Three Types of Plate Boundaries: • Divergent—Boundary where plates move apart (ex: Great Rift Valley—Africa; Mid ocean Ridges) • Convergent—Boundary where plates come together (ex: Himalayan mountains, Alps) • Transform—Boundary where two plates slide along side each other (ex: San Andreas Fault— San Francisco) Convergent Boundaries form when two tectonic plates come towards each other. There are three types of convergent boundaries or destructive boundaries. **continent - continent **ocean – ocean **continent – ocean Continent -Continent: Mountains form and earthquakes occur when continental plates run into each other and fold upwards. (Ex: Himalayas and Alps) Continent to continent The summit of Mt. Everest is made of marine limestone. Ocean Plate-Ocean Plate: Volcanic island arcs, trenches & earthquakes occur when older ocean plate subducts under a younger ocean plate. (Ex: Japan, Aleutian Islands-off Alaska, Philippines, Tonga Islands, Marianas Trench). Ocean to Ocean Boundary Earth Observatory Center: Japan Ocean Plate-Continent Plate: Mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes occur as an ocean plate subducts under a continental plate. The Oceanic plate melts; less dense-magma rises to form volcanoes. (Ex: Andes, Cascade Range, Sierra Nevada) Ocean to Continent Boundary Goddard Space Flight Center Ocean to Ocean and Ocean to continent are destructive boundaries Three Types of Plate Boundaries: • Divergent—Boundary where plates move apart (ex: Great Rift Valley—Africa; Mid ocean Ridges) • Convergent—Boundary where plates come together (ex: Himalayan mountains, • Transform—Boundary where two plates slide along side each other (ex: San Andreas Fault—San Francisco) Strike-slip or transform boundaries occur where two plates slide along side each other. Earthquakes occur in these areas (Ex: San Andreas Fault in California). Transform Boundary San Andreas Plate Movements Hot Spots The Hawaiian Islands do not occur by a plate boundary. These islands form as the Pacific plate moves over a hot spot in the mantle. Hot spot or Mantle Plume Earth Observatory What will the Earth look like in the future? Present Day Earth