* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
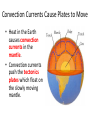
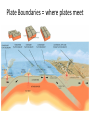
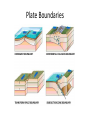
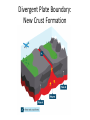
The Structure of the Earth Learning Objectives: 1. Describe the layers of the structure of the Earth. 2. Describe the theory of continental drift. 3. Describe the theory of plate tectonics. 4. Explain how earthquakes and volcanoes form. Structure of the Earth • Crust = thin, rocky outer layer • Mantle = properties of solid but flows slowly • Outer core = liquid nickel and iron • Inner core = solid liquid and iron Continental Drift • 1912 Alfred Wegner came up with the theory of crustal movement or continental drift. • Theory of Continental Drift = continents were once joined together and gradually moved apart • Wegener’s ideas were not accepted at the time. Evidence Supporting Continental Drift • Apparent fit of the continents = continents fit like puzzle pieces • Fossil Correlation = identical fossils have been found on either side of the ocean • Rock and Mountain correlation = identical rocks and mountain structures have been found on either side of the ocean • Paleoclimate Data – coal found in cold regions and glacial evidence found in warm regions Plate Tectonics • Theory of Plate Tectonics = the Earth’s crust is broken up into pieces called tectonic plates which float on top of the mantle Convection Currents Cause Plates to Move • Heat in the Earth causes convection currents in the mantle. • Convection currents push the tectonics plates which float on the slowly moving mantle. Plate Boundaries = where plates meet Plate Boundaries Divergent Plate Boundary: New Crust Formation Continental Collision Boundary: Mountain Ranges Transform Boundaries: Earthquakes • Earthquakes can occur at all moving plate boundaries. • Plates do not move smoothly due to friction. • Pressure builds up and plates “slip” suddenly Subduction Zone Boundaries: Volcanoes • When one plate is pushed under another, oceanic crust is pushed into the Earth. • Melting crust releases gases which can get pushed upwards creating a volcano.