* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plate tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
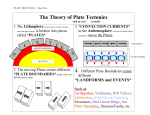
Pangaea Colliding Plates • Objectives – Explain how plate tectonics accounts for the movement of continents – Compare and contrast divergent, convergent and transform plate boundaries. – Explain how convection currents inside Earth might be the cause of plate tectonics • Key Terms – plate tectonics, lithosphere, divergent boundary – Convergent boundary, transform fault boundary Plate Tectonics • Tectonic plates – Think of the hypotheses of continental drift and sea-floor spreading as clues to a mystery. – How can the two hypotheses be explained? • In the 1960’s, geologists developed a new theory to explain the apparent movement of the continents. • The theory of plate tectonics suggests that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates (that move). • But, what are they made of and how do they move?? • We already know that the Earth’s crust is a layer of solid rock. • The uppermost portion of the mantle is also solid – Together, these two areas are known as the lithosphere • We also know that there is an area in the mantle that is less solid. Here, the material acts more like a putty; it’s a solid that can flow. – This putty-like layer is called the asthenosphere Plates • Divergent Boundaries – The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other • Magma is forced upward between the two plates, creating a new crust, thus making…. • Mid-ocean ridges are divergent boundaries Divergent Boundary Learning Check • The theory that suggests that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates (that move) is known as… – plate tectonics • Together, the Earth’s crust is a layer of solid rock and the uppermost portion of the mantle is also solid are known as – Lithosphere • The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other is known as… – Divergent boundary • Convergent Boundaries – Crustal material can be destroyed where 2 plates meet head on. – This type of boundary is called a convergent boundary – What do you think happens when two plates containing continental crust collide? • The two plates crumple forming mountain ranges! • The Himalaya Mountains formed when the Indian Plate collided with the southern part of the Eurasia plate. Himalayas Convergent Boundaries • There are three styles of convergent plate boundaries – Continent-continent collision – Continent-oceanic crust collision – Ocean-ocean collision Convergent Boundary • Transform Fault Boundaries – A third type of boundary that is formed when two plates slide past one another in opposite directions. • Think about the San Andreas Fault in California – This is where the North America and the Pacific plate slide past one another! • Along this boundary, the Pacific plate moves NW relative to the North American plate at an average rate of 2 cm per year. Transform Fault Boundary Transform Fault Bound. Cause Earthquakes! • Causes of Plate Tectonics – How does the theory of plate tectonics explain the cause of plate movements? • The driving force behind this movement is HEAT! • A material that is hot is less dense than the same material that is cold • This is because the same mass takes up more volume (space) when the material is heated. • This helps us explain the process of convection currents… Convection Currents in the Earth • Convection Currents – C.C.’s within the Mantle cause the various plates in Earth’s lithosphere to move around. – As the plates bump into each other, boundaries form! – Plates move in different directions because there are many conv. cells within the Mantle! Learning Check! • A type of boundary that is formed when two plates slide past one another in opposite directions is known as – Transform Fault Boundary • Boundary where crustal material can be destroyed where 2 plates meet head on is – Convergent Boundary • Mountain Ranges – Convergent • Earthquakes – Transform Fault Convergent Boundaries Continent-Continent Collision • Forms mountains, e.g. European Alps, Himalayas Continent-Oceanic Crust Collision • Called SUBDUCTION Subduction • Oceanic lithosphere subducts underneath the continental lithosphere • Oceanic lithosphere heats and dehydrates as it subsides • The melt rises forming volcanism • E.g. The Andes Ocean-Ocean Plate Collision • When two oceanic plates collide, one runs over the other which causes it to sink into the mantle forming a subduction zone. • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The worlds deepest parts of the ocean are found along trenches. – E.g. The Mariana Trench is 11 km deep! Convergent Boundary