* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 17.2 Seafloor Spreading
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
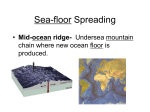
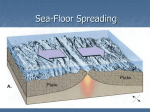
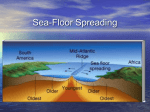
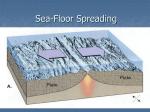
Chapter 17 Plate Tectonics Section 17.2 Sea-Floor Spreading Vocabulary Subduction: Sea-flooring spreading: The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary. The process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor. Deep-ocean trench: A deep valley along the ocean floor through which oceanic crust slowly sinks towards the mantle. Vocabulary Mid-ocean ridge: The undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary. Sonar: A device that determines the distance of an object under water by recording echoes of sound waves. Mapping the Mid-Ocean Ridge Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the mid-ocean ridge. A. The mid-ocean ridge is the longest chain of mountains in the world. B. The mid-ocean ridge is found only below the Pacific Ocean. C. The mid-ocean ridge lies completely under water. D. The top of the mid-ocean ridge is split by a steep-sided valley. Mapping the Mid-Ocean Ridge A device that bounces sound waves off sonar underwater objects is called __________. What is sonar used for? Sonar is used to determine the distance to an object. It has been used to map the mid-ocean ridge. Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called sea-floor spreading ________________. Molten rock erupts through cracks. Molten rock cools to form strip of rock. Older rock is pushed aside. Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading Three types of evidence for sea-floor spreading: Molten material Magnetic stripes Drilling samples Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about Earth’s magnetism. A. At times in the past, a compass needle on Earth would have pointed south. B. Rock that makes up the ocean floor lies in a pattern of magnetized stripes. C. The pattern of stripes is different on both sides of the mid-ocean ridge. D. Rocks that harden at the same time have the same “magnetic memory.” Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading How did drilling samples show that sea-floor spreading really has taken place? The farther away from the ridge that the samples were taken, the older they were, and the youngest samples were always in the center of the ridge. Subduction at Deep-Ocean Trenches Deep underwater canyons are called deep-ocean trenches ________________. True or False: At deep-ocean trenches, conduction allows oceanic crust to sink back into the mantle. False Subduction and Earth’s Oceans True or False: The Pacific Ocean is shrinking. True Why is the Atlantic Ocean expanding? The Atlantic Ocean is expanding because it has only a few short deep-ocean trenches, so the spreading ocean floor has virtually nowhere to go.