* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jupiter Versus the Earth: Composition & Structure
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
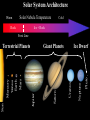
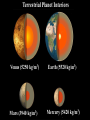
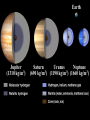
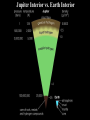
JUPITER VERSUS THE EARTH: COMPOSITION & STRUCTURE Randy Gladstone Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio TX 78238 NASA Space Science Workshop Explore! Jupiter’s Family Secrets May 4-5, 2010 Springfield, MO Solar System Architecture Warm Solar Nebula Temperature Rock Cold Ice + Rock Frost Line Pluto Neptune Ice Dwarf Uranus Saturn Giant Planets Jupiter Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Terrestrial Planets How Do We Know What’s Inside a Planet? • For planets other than Earth, there are only a few ways to determine what’s inside • From the mean density (the total mass divided by the total volume) it is possible to constrain the internal structure based on models of likely composition • From the gravity field (determined by watching how satellites orbit) it is possible to tell more about how the mass inside a planet is distributed (e.g., whether it has a core, etc.) • For Earth, most of our knowledge of the interior come from the study of seismic waves (as are generated by large earthquakes) Terrestrial Planet Interiors Venus (5250 kg/m3) Mars (3940 kg/m3) Earth (5520 kg/m3) Mercury (5420 kg/m3) Earthquake Waves Probe Earth’s Interior Inside Earth The major regions in the Earth are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core: • The outer crust is relatively thin (~30 km thick in the continents and ~5 km thick in the oceans) • The mantle is ~3000 km thick (almost halfway to the center of the Earth) and is made of a dense rock called peridotite; it has plastic-like properties and its slow overturning drags along the crust, causing plate tectonics (i.e., continental drift) • The liquid outer core is 2300 km thick and is a mixture of iron (90%) and nickel (10%); motions in the liquid give rise to the Earth’s magnetic field • The solid inner core at Earth’s center has a 1200 km radius and is made of iron (90%) and nickel (10%); the temperature at the Earth’s core is ~5700 K and the pressure there is ~3.6 million atmospheres Earth Jupiter (1310 kg/m3) Saturn Uranus Neptune (690 kg/m3) (1190 kg/m3) (1660 kg/m3) Jupiter Interior vs. Earth Interior Inside Jupiter Jupiter is still cooling off (and contracting) from its formation 4.5 billion years ago (it emits 1.7 times as much energy as it receives from the Sun)! • The atmosphere (the outermost ~5000 km at <1 atmosphere) is mostly molecular hydrogen and helium); heavier elements are generally enriched by ~3 times compared to the Sun • The deep atmosphere continues down another ~15000 km to a point where the pressure increases above a few million atmospheres and hydrogen becomes metallic; helium may be raining out near this boundary • The metallic hydrogen layer is ~50,000 km thick and motions in the fluid give rise to Jupiter’s strong magnetic field • The rocky inner core at Jupiter’s center contains between zero and 20 Earth masses; the temperature at the Jupiter’s core is ~20,000 K and the pressure there is ~40 million atmospheres