* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.344 Directed Evolution: Engineering Biocatalysts
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
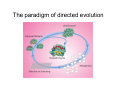
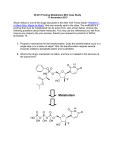
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 7.344 Directed Evolution: Engineering Biocatalysts Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 7.344 Directed Evolution: Engineering Biocatalysts Kerry Love (Instructor) Feb 7th class overview • • • • • • Introductions Class day/time How to read a scientific journal article? Directed evolution overview Concepts for next week Handout papers / website The paradigm of directed evolution Directed evolution • Why do we want to evolve enzymes? • What are the two main steps in the evolution process? • Which of these steps is more challenging/important? Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Image of PCR scheme removed due to copyright restrictions. • Transitions versus transversions Molecular cloning Image removed due to copyright restrictions. Please see http://www.accessexcellence. org/RC/VL/GG/plasmid.php 1. PCR amplify gene of interest (insert restriction sites) 2. Digest bacterial vector (plasmid DNA) and gene of interest 3. Ligate digested DNA and vector 4. Transform bacteria with vector 5. Select for bacteria containing gene of interest