* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bacteria
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
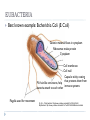
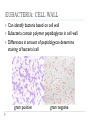
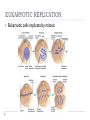
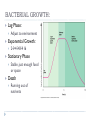
BACTERIA SBI 3C: OCTOBER 2010 BACTERIA CLASSIFICATION Can be classified into 2 kingdoms: Eubacteria Archaebacteria Similarities: Unicellular Prokaryotic Single chromosome Reproduce asexually by binary fission Thrive in moist environments Dr. Oz – Toilet bacteria: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CljhLb1Ar9U Mythbusters: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TeAOC3A0xJ8&feature=related CELL TYPES 2 TYPES OF CELLS: Eukaryotic: Has a true nucleus surrounded by nuclear membrane Ex. Plants and animal cells Prokaryotic: Does not have its chromosomes surrounded by nuclear membrane Ex. Bacterial cells PROPERTIES: NUCLEUS PROPERTY EUKARYOTES PROKARYOTES DNA •USUALLY 46 CHROMOSOMES •FOUND IN NUCLEUS •SINGLE CHROMOSOME •SINGLE LOOP TRUE NUCLEUS •PRESENT •ABSENT NUCLEAR MEMBRANE •PRESENT •ABSENT PROPERTIES: ORGANELLES PROPERTY EUKARYOTES PROKARYOTES INTERNAL ORGANELLES •COMPLEX •MANY •VERY FEW •SIMPLE ORGANELLES RIBOSOMES •LARGER •SMALLER CELL WALL •FOUND IN PLANTS, ALGAE AND FUNGI •PRESENT MITOCHONDRIA •PRESENT •ABSENT PLASTIDS •CHLOROPLASTS IN PLANTS AND ALGAE •ABSENT FLAGELLA •COMPLEX TAILS INVOLVED IN MOVEMENT, FEEDING AND SENSING •SIMPLE PROPERTIES: FUNCTIONS PROPERTY EUKARYOTES PROKARYOTES MOVEMENT •COMPLEX FLAGELLA, •SINGLE FLAGELLA CILIA, CYTOPLASMIC GLIDING STREAMING REPRODUCTION •MITOSIS •BINARY FISSION •CONJUGATION EVOLUTION •APPEARED 1.5 BILLION YEARS AGO •APPEARED 3.5 BILLION YEARS AGO METABOLISM •LOWER METABOLIC RATE, LOWER GROWTH RATE AND THUS GREATER GENERATION TIME •HIGHER METABOLIC RATE, HIGHER GROWTH RATE AND THUS A SHORTER GENERATION TIME PROPERTIES: SIZE AND EXAMPLES PROPERTY EUKARYOTES PROKARYOTES SIZE •USUALLY >2UM DIAMETER •USUALLY <2UM DIAMETER EXAMPLES •PLANTS •ANIMALS •PARAMECIUM •E COLI •BACILLUS ANTHRACIS ARCHAEBACTERIA Thrive under extreme conditions Three major groups: Thermophiles: Methanogens: Live in extremely hot environments (hot springs) Grow on carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas to produce methane Live in deep sea vents and intestines of mammals (ex. humans) Halophiles: Live in extremely salt environments (salt flats) EUBACTERIA Best known example: Escherichia Coli (E. Coli) Genetic material floats in cytoplasm Ribosomes: make protein Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Capsule: sticky coating Pili: hair-like structures, help that protects them from bacteria attach to each other immune systems Flagella: used for movement Dr. Oz – Toilet bacteria: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CljhLb1Ar9U Mythbusters: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TeAOC3A0xJ8&feature=related EUBACTERIA: CELL WALL Can identify bacteria based on cell wall Eubacteria contain polymer peptidoglycan in cell wall Differences in amount of peptidolgycan determine staining of bacterial cell gram positive gram negative STAINING THE CELL WALL BACTERIA Stained with crystal violet dye (purple) Fixed with Gram’s iodine Decolourized with ethanol Stained with safranin (red) Gram-positive bacteria retain crystal violet and appear purple Ex. Staph Gram-negative bacteria ethanol washes out crystal violet so they stain red with safranin and appear pinkish red Ex. E coli EUBACTERIA: SHAPE AND CONFIGURATION SHAPES: Spherical Rod Spherical Rod Spiral CONFIGURATION: Cocci (singular: coccus) Bacilli (singular: bacillus) Spirilla (singluar: spirillum) All form pairs, cluster colonies or chains of cells Spiral EUBACTERIA: NUTRITION AND RESPIRATION RESPIRATION: Some are aerobic (need oxygen to survive) Some are anaerobic (only grow without oxygen) Tetanus, botulism Some can grow with or without oxygen TB bacteria E Coli NUTRITION: Autotrophs: make their own food Photosynthetic (energy from sun), chemisynthetic (energy from chemical reactions) Heterotrophs: obtain nutrients from other organisms EUKARYOTIC REPLICATION: Eukaryotic cells replicate by mitosis PROKARYOTIC REPRODUCTION: Reproduce asexually by binary fission CONJUGATION: Donor and recipient bacteria make cell to cell contact by sex pilus Plasmids (genetic info) are exchanged resulting in altered characteristics BACTERIAL DISEASES NAME SYMPTOMS BACTERIAL SHAPE PNEUMONIA Clogs up lungs Cocci Salmonella (from food) Vomiting, diarrhea Bacillus Cholera (from water supply) Diarrhea, cramps Bacillus Tetanus Convulsions Motile bacillus Tuberculosis Infects lungs, fever, weight loss Bacillus Leprosy Skin lesions, decay of extremities Bacillus Gonorrhea Penal discharge, painful urination Diplococcus TREATMENT AND PREVENTION: Bacterial diseases can be treated using antibiotics Antibiotics are chemicals toxic to bacteria which are produced commonly by plants and fungi Eg. Penicillin (from the fungus penicillium) Bacterial diseases could be prevented using vaccines Substances which stimulate your body to produce antibodies to the bacterium even though you are not infected BACTERIAL GROWTH: Lag Phase: Exponential Growth: 24816 Stationary Phase Adjust to environment Stable, just enough food or space Death Running out of nutrients