* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
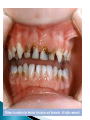
MOST OF US ARE AWARE SUGAR NEEDS TO BE CONSUMED IN MODERATION. BUT MANY OF US ARE CONSUMING FAR MORE THAN WE THINK. THERE'S SUGAR 'HIDING' IN FOOD AND DRINK THAT MIGHT SURPRISE US. MANUFACTURERS OFTEN ADD EXTRA SUGAR TO FOOD BECAUSE IT MAKES IT TASTE BETTER. WHEN FAT IS REMOVED FROM A PROCESSED MEAL, FOR EXAMPLE, SUGAR IS OFTEN ADDED TO HELP DISGUISE THE BLANDER TASTE. BECAUSE OF THIS, MANY FOODS WE THINK OF AS WHOLESOME - LIKE YOGURT, GRANOLA BARS, LOW-FAT SNACKS AND FRUIT-FLAVOURED WATER - MAY ACTUALLY CONTAIN MUCH MORE SUGAR THAN WE REALISE. SUGAR IS NOT INHERENTLY BAD FOR YOU - IT'S THE AMOUNT AND HOW FREQUENTLY YOU EAT IT THAT MATTERS. WHEN WE EAT FOOD, THE SUGARS ARE BROKEN DOWN INTO GLUCOSE AND FRUCTOSE, WHICH ARE ABSORBED INTO THE BLOODSTREAM. HOWEVER FRUCTOSE MUST THEN BE CONVERTED INTO GLUCOSE IN THE LIVER. IF WE CONSUME MORE SUGAR THAN WE BURN THROUGH ACTIVITY OUR LIVER CONVERTS THE EXCESS GLUCOSE INTO FAT. SOME OF THIS FAT STAYS IN THE LIVER BUT THE REST IS STORED IN FATTY TISSUES AROUND THE BODY. THIS IS WHY REPEATEDLY EATING TOO MUCH SUGAR CAN LEAD TO WEIGHT GAIN, AND EVEN OBESITY, WHEN COMBINED WITH A SEDENTARY LIFESTYLE. HERE ARE SOME OTHER HEALTH PROBLEMS THAT CAN BE CAUSED BY EATING TOO MUCH SUGAR: Diabetes: Consuming too much sugar in your diet can lead to obesity, which increases your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Those with this condition don't produce enough insulin and aren't sensitive enough to what's produced. Blood sugar levels aren't regulated properly leading to thirst and tiredness in the short-term and damage to blood vessels, nerves and organs if left untreated. Heart disease: Obesity also raises blood pressure and 'bad' cholesterol levels while lowering levels of 'good' cholesterol. These all contribute to raising the risk of heart disease. Fatty liver disease: Excess sugar can be stored as fat in the liver. The condition has been linked to an increased risk of diabetes and even liver cancer. Tooth decay: When we eat sugary foods, bacteria in our mouths break down the carbohydrates and produce acids that dissolve minerals in our tooth enamel. The longer the sugar is in contact with teeth, the more damage bacteria can cause. Left untreated this can cause pain, infection, and tooth loss. Bad mood: Sugary foods like chocolate, cake and biscuits have been labelled 'bad mood food'. They can give you a quick burst of energy by causing a sharp increase in blood sugar, but when levels fall this can make your mood dip. This cycle can make you feel irritable, anxious, and tired. WORKING OUT HOW MUCH SUGAR IS IN YOUR FOOD OR DRINK CAN BE CONFUSING AS IT APPEARS UNDER MANY DIFFERENT DISGUISES, SUCH AS SUCROSE, GLUCOSE, FRUCTOSE AND HONEY. FOOD MANUFACTURERS ARE NOT REQUIRED BY LAW TO SEPARATE ADDED SUGARS FROM NATURALLY OCCURRING SUGARS ON A NUTRITION LABEL, BUT YOU CAN FIND OUT HOW MUCH TOTAL SUGAR IS IN A PRODUCT BY LOOKING FOR THE 'CARBOHYDRATES (OF WHICH SUGARS)' FIGURE. MORE THAN 15G OF TOTAL SUGARS PER 100G MEANS IT HAS A HIGH SUGAR CONTENT, 5G OF TOTAL SUGARS OR LESS PER 100G MEANS IT HAS A LOW SUGAR CONTENT.