* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cladogram ppt Intro to cladograms
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
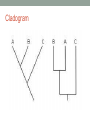
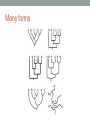
INTRO TO CLADOGRAMS • Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that are widely distributed today. • These provide evidence that all organisms (living and extinct) are linked by common ancestry. Shared across domains • Domains: Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya 1. DNA and RNA as carriers of genetic material 2. A universal genetic code 3. Many metabolic pathways Shared among Eukaryotes 1. Cytoskeleton 2. Nucleus 3. Membrane-bound organelles 4. Linear chromosomes 5. Endomembrane systems • Presence of these conserved elements provides evidence that they were present in a universal ancestor and that present life evolved from a universal ancestor Phylogenetic trees Phylogenetic trees and cladograms • Graphically model evolutionary history. • Represent both genetically acquired traits and those lost during evolution. • Illustrate relatedness of groups of organisms based on based on how recently they had a common ancestor Phylogenetic trees and cladograms • Can be based on • Morphological • DNA and protein similarities • Sophisticated computer programs. • Can be used to determine the evolutionary history of both living organisms and fossils. • Are DYNAMIC! Phylogenetic trees Cladogram Many forms