* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skin Wounds Classification
Survey
Document related concepts
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
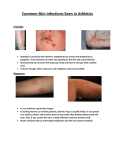
Objective 2: Identify soft tissue injuries and skin conditions o o o o Trauma that happens to the skin is visually exposed Categorized as a skin wound Defined as a break in the continuity of the soft parts of body structures caused by a trauma to these tissues Mechanical forces include: o Friction, scraping, compression, tearing, cutting, penetrating o o o Skin scraped against a rough surface Several layers of skin are torn loose or totally removed Usually more painful than a deeper cut b/c scraping of skin exposes millions of nerve endings o Wash wound to remove all dirt and debris o o o o o Soap and water or hydrogen peroxide Scrub wound if particles of dirt, rocks, or tar embedded Leave open to air, unless oozing of fluid or blood Apply antibiotic ointment to inhibit infections Scrapes scab over quickly o o o o Loose skin flaps form natural dressing; if flap dirty remove with clean nail clippers Check on date of last tetanus immunization Watch for signs of infection Seek medical attention if any of following: o o o o Pain increases after several days Redness/red streaks appear beyond edges of wound Swelling Drainage Flesh irregularly torn; cut or tear in the skin Minimal bleeding, minimal pain, & no numbness or tingling Cuts ≤ 0.25” (6mm) deep and 0.5” (1.3cm) long & have smooth, edges can be treated at home Deeper lacerations should be treated by physician (stitches) o o o o Cleaned with soap and water Irrigate with clean water to remove debris Do NOT use alcohol, iodine, or peroxide as it may cause further damage and slow healing process Stop bleeding o o Cover wound with sterile gauze Apply direct & constant pressure (15min+) o o o Once wound cleaned, antibiotic ointment may be applied to reduce risk of infection & aid healing Change sterile dressing daily as needed Bruising and swelling are normal o o Apply ice to site Elevate area above level of heart o Contact a physician if: o o o o o Laceration more than 0.25” (6mm) deep and 0.5” (1.3cm) long The wound is in area where wound by be opened by simple movement of body part Wound on face, eyelids, or lips Deep cuts on palm, finger, elbow or knee Loss of sensation or ROM of body part as result of cut STITCHES STERI-STRIPS® o o o Layers of skin torn off completely or only flap of skin remains Same mechanism as laceration, but to extent that tissue is completely ripped from it’s source May be considerable bleeding o o o o Clean wound with soap and water If flap of skin remains connected replace skin in its original position If deep avulsion, seek medical attention for stitches If large piece of skin torn off place in plastic bag and put on ice o o Skin should not get frozen or soaked in water Take skin in plastic bag to doctor; may be able to save and replace torn-off piece o o o o A blow compresses or crushes the skin surface and produces bleeding under the skin Does not break skin Bruising due to injury to blood vessels Most mild and respond well to RICE o o o Swelling Pain to touch Redness o Ecchymosis o o o o accumulation of blood in skin & subcutaneous tissue more than one cm in diameter General term=bruising Result of bleeding; clotting or bleeding disorders Bluish lesion at earliest stages of onset o o o o o o Careful monitoring Anti-inflammatory oral medications Compressive dressing Ice Modalities to ↓ ecchymosis, ↓ swelling, ↑ ROM Myositis ossificans: calcification that forms within muscle o Requires surgical intervention o Continuous rubbing over the surface of the skin causes a collection of fluid below or within the epidermal layer o o Wash area thoroughly Donut padding or moleskin covering o Prevention: o o o o Wear work gloves Break in new shoes Petroleum jelly/skin lube Adhesive bandage o o Skin has been sharply cut Surgical cut made in skin or flesh o o Remove bandage day after surgery; replace daily or as needed Normal for edges of healing incision to be slightly red o Call physician if: o redness increases/spreads more than half an inch o pus in incision o more than mildly tender or painful o o o o Keep incision clean & dry for several days after surgery Non-absorbable sutures or staples must be kept dry until doctor removes Steri-strips® should be kept dry 4-5 days On face, hands, arms: take showers or tub baths along as affected area stays dry Wash with soap and water Cover with sterile dressing Apply antibiotic ointment Apply Ice Never apply ice with snakebites Stimulates the spread of the venom Complications Poisonous Minimize movement Seek medical attention Infection Seek medical attention Treatment Look for stinger If stinger present scrape away from skin with finger nail or edge of a plastic card Never use tweezers to remove stinger- squeezing the stinger will release venom into body Wash area with soap water Cover with sterile dressing Apply Ice Watch for allergic reaction Caused by insect stings, food, other allergens Known as Anaphylactic shock Cause serious life-threatening breathing emergencies Air passages swell and restrict breathing S/S= rash, tightness in chest, swelling of face and tongue, dizzy, confused Use of Epi-pen is necessary treatment HITCH o o o Skin always has some amount of bacteria, fungus, and viruses living on it Skin infections occur when there are breaks in the skin and the organisms have uncontrolled growth It is more important to understand the potential for infection rather than placing a name on the skin problem o Bacteria—can be cured o Staphlococcus o Including MRSA & Impetigo o o Fungal—can be cured o o Streptococcus Ringworm Viral—cannot be cured, but can be treated o o Warts Eczema o o o o o Lesions with an irregular border Raised skin lesions “wet” or “moist” lesions Lesions that have different colors within the lesion Bright red colored lesions are more of a problem compared to faded lesions o o o o Lesions that are warmer compared to other skin Inflammation & irritation around skin lesion Prior history of infectious skin lesion Skin abrasions o Deeper or more traumatic break in skin, higher risk for subsequent infection o o o The right antibiotic is required to cure a specific bacterial skin infection Antibiotics for bacteria will not improve fungal or viral infections Bacterial infections can be the fastest growing infections o Thus the most easily spread among athletes o o o Infection caused by Staphylococcus bacteria About 25% of people normally carry staph in the nose, mouth, genitals, and anal areas Infection begins with a little cut gets infected with bacteria o o Range from a simple boil to antibioticresistant infections to flesh-eating infections Difference is: the strength of the infection o How deep it goes o How fast it spreads o How treatable it is with antibiotics o o o Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus Resistant to certain antibiotics most are skin infections o o Methicillin, oxacillin, penicillin, amoxicillin More severe or potentially life-threatening occur most frequently among patients in healthcare settings SKIN INFECTIONS o o o o o o o Appear as pustules or boils Red Swollen Painful Pus or other drainage First look like spider bites or bumps Occur at sites of visible skin trauma SEVERE INFECTIONS o Potentially life-threatening o o o o Blood stream infections Surgical site infections Pneumonia Signs & symptoms vary by type and stage of infections o o Spread by having contact with someone’s skin infection or personal items they’ve used Spread in places where people are in close contact o o o o o Close skin-to-skin contact Openings in the skin (cuts or abrasions) Contaminated items & surfaces Crowded living conditions Poor hygiene o o o o o Good hygiene Keep hands clean—wash with soap and water thoroughly Keep cuts and scrapes clean & covered with a bandage Avoid contact with other’s wounds/bandages Avoid sharing personal items i.e. towels, razors o Practice good personal hygiene o o o Do not share items that come in contact with your skin o o Towels & razors Ointments Take care of your skin Take precautions with common surfaces & equipment o o o o Keep hands clean Shower after exercise Do not share soap or towels Wash uniform & clothing o o Cover abrasions/cuts Change bandages regularly o Use barrier between skin & surface (towel, clothing) o o Antibiotic to drain infection DO NOT attempt to treat yourself! o o Includes popping, draining, using disinfectants on area If you think you have an infection: o o o Cover affected skin Wash hands Contact physician o o o o Mild itching & soreness Eruption of small vesicles and/or pustules that rupture to form honey-colored crusts Combo of 2 bacteria that spread rapidly when athletes in close contact with one another Responds rapidly to proper treatment o o Thorough cleansing of crusted area Application of topical antibacterial agent o o o o o Caused by streptococcus (strep) or staphylococcus (staph) bacteria MRSA becoming common cause May occur on skin where there is no visible break Most common in children, particularly unhealthy living conditions Infection carried in fluid that oozes from blisters o Single or many blisters filled with pus o o o Itching blister o o o o o Easy to pop When broken leave a reddish raw-looking base Filled with yellow or honey-colored fluid Oozing and crusting over Rash Skin lesions on face, lips, arms, or legs Swollen lymph nodes near infection o o o o Skin infection caused by fungus (not a worm ) Fungi thrive in warm, moist areas Often several patches at once Contagious o Symptoms: o o o o Itchy, red, raised scaly patches that may blister and ooze Patches often have sharply-defined edges Redder around outside; normal skin tone in center Skin appear unusually dark or light o o o o Body—tinea corporis Scalp—tinea capitis Groin—tinea cruris (jock itch) Feet—tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) Treatment Warts Verruca vulgaris Small tumors with dark centers May appear anywhere on body Cryosurgery Salicylic acid Develop on sole of foot Pinpoint black spots Can be protected with donutshaped pad to relieve pressure Itchy red rash Caused by Allergies Stress Temperature Drug reaction Scratching Sun exposure Treatment Corticosteroid Lotions and ointments Antihistamines Lotions to hydrate skin