* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virus PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
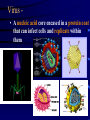
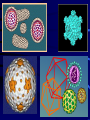
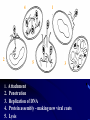
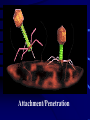
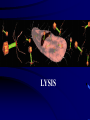
Viruses • Non-living - does not grow, eat, release waste, or breathe. • Is able to reproduce, but only when inside a host (the cell that a virus enters) • 100 times smaller than bacteria Virus • A nucleic acid core encased in a protein coat that can infect cells and replicate within them Structure of a Virus • Capsid (protein coat) • Nucleic Acid (DNA) • Tail • Tail Fibers REPRODUCTION 1. Viruses cannot reproduce on their own 2. They need a host cell to do all the work 3. It is a five step process called the Lytic Cycle that ends in the host cells death. Viral Reproduction - Lytic Cycle 1. Attachment - Virus attaches to the Host cell 2. Penetration - Virus injects its RNA or DNA 3. Replication - Host cell makes many copies of the viral RNA or DNA 4. Assembly - Host cell builds new viruses 5. Lysis - New viruses breaks out of host cell -killing it – to attack other hosts 4 2 1 5 3 1. Attachment 2. 3. 4. 5. Penetration Replication of DNA Protein assembly - making new viral coats Lysis Attachment/Penetration LYSIS MOBILITY • Viruses do NOT move on their own • Transferred by water, air, food, human contact MOVEMENT VIRAL DISEASES Pathogenic (disease causing) • Flu • Hepatitis C • Mumps • Measles • Ebola • Polio Polio • HIV How are viruses treated? • Antibiotics/medicines do NOT work on viruses • About the only treatment is to drink plenty of fluids and bed rest. Some medicines may improve symptoms such as aspirin for fever. What are vaccines? • Vaccinations (can be live, dead or weakened) • Vaccinations prevent you from getting that particular virus • The flu virus mutates so rapidly that vaccines are a challenge • HIV virus attacks the immune system mutates VERY rapidly - vaccine difficult