* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physiology - Cloudfront.net
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
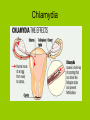
Physiology STDs and Teens Standards: • BI10. c. Students know how vaccination protects an individual from infectious diseases. • BI10. d. Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication, the body’s primary defenses against bacterial and viral infections, and effective treatments of these infections. • BI10. e. Students know why an individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Objectives: • Explain how different organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis. • Understand the importance of maintaining a stable internal environment in the human body. • Explain the various ways your body protects itself from pathogens. • Understand the role of antibodies in protecting your body against infection. • Explain how a vaccination protects an individual from infectious diseases. • Understand how HIV weakens and individuals immune system causing AIDS. • Understand how sexually transmitted diseases are passed between individuals. Sexually Transmitted Disease Myths • Can only get STDs by having “sex” • You can look at someone and tell they have an STD • People with STDs show symptoms immediately • You can be tested for all types of STDs • Condoms provide 100% protection from STDs STD Facts • Unprotected sex and sex with multiple partners greatly increases your chances of getting a STD • STDs are contracted by 12 million people per year, the majority are teens • 10,000 teens get a STD per day • 1 out of 4 female teens has a STD • Some STDs can show few or no symptoms Viral vs. Bacterial STD Infections Viral • Ex.-HPV, HIV, Herpes, Hepatitis Bacterial • Chlmyadia, Syphilis, Gonorrhea • No cure • Cured with antibiotics (drug-resistant bacteria) Common STDs Chlamydia • Bacteria passed through sexual contact, can be passed from pregnant mother to the baby • 1-3 weeks before symptoms occur • Pain and discharge during urination and sex, infertility, swelling of testicles • 2.3 mil infections per year in the US (13-39) • Because the cervix (opening to the uterus) of teenage girls and young women is not fully matured and is probably more susceptible to infection, they are at particularly high risk for infection if sexually active. Gonorrhea • Bacteria passed through sexual contact, can be passed from pregnant mother to the baby • Can grow in mucus membranes • Pain and discharge during urination, genital sores, bladder infections, sometimes no symptoms • 700,000 per year • The highest reported rates of infection are among sexually active teenagers, young adults, and African Americans. Chlamydia HIV/AIDS Facts • 1 million Americans have HIV/AIDS • 40,000 new cases of HIV/AIDS diagnosed per year in US • 100s of teens are diagnosed with HIV/AIDS per year • 40 million people have HIV/AIDS worldwide • 3 million people die per year worldwide from AIDS • Cannot catch HIV/AIDS from casual contact • Prevention-If sexually active-testing, abstinence, latex condoms, avoiding contact with body fluids from sex Effect of HIV on the Body Prevention of STDs • Abstinence-no “sex” • Protection-latex condoms, not 100% • Monogamous relationships with one partner that has been tested (how do you know?-not the best option for teens) Summary Questions: • What are the differences between bacterial and viral STD infections? • What are some common myths of STDs and why are they incorrect? • What are some of the symptoms of one of the STDs discussed today? • Which groups of people are at the highest risk of getting an STD?