* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why Carbohydrates - Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
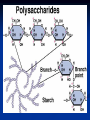
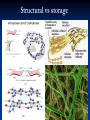
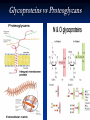
DS/ Reducing vs non-reducing Sucrose α (D) glucopyranosyl 1 fructofuranoside Lactose 2 β (D) galactopyranosyl 1 4 glucopyranose cellulose Amylose amylopectin glycogen DS that are formed by the linkage of sugars derivatives Polysaccharides Definition and properties: *They are composed of many sugar residues. *All are nonreducing. PS/Different classification. 1- Branched vs linear polysaccharides. Example: amylose, inulin, and amylopectin, glycogen 2- Sturctural vs storage polysaccharides. Example: Cellulose, pectin and glycogen, inulin. 3- Homo vs hetero polysaccharides. Example: Amylon, cellulose and glycosaminoglycanes. PS/ linear vs Branched Amylose linear Amylopectin / Glycogen Branched Structural vs storage Other Structural Polysaccharides Alginates - Ca-binding polymers in algae Agarose and agaropectin - galactose polymers Glycosaminoglycans - repeating disaccharides with amino sugars and negative charges Dextrans If you change the main linkages between glucose from alpha(1,4) to alpha(1,6), you get a new family of polysaccharides - dextrans Branches can be (1,2), (1,3), or (1,4) Dextrans formed by bacteria are components of dental plaque Cross-linked dextrans are used as "Sephadex" gels in column chromatography These gels are up to 98% water! PS/Homo vs Heteropolysaccharide Amylose, inulin, and amylopectin, glycogen, Cellulose Chitin - exoskeletons of crustaceans, insects and spiders, and cell walls of fungi Similar to cellulose, but C-2s are Nacetyl Cellulose strands are parallel, chitins can be parallel or antiparallel Hetero PS (Glycosaminoglucans) (GAG+ peptide) Glycoproteins vs Proteoglycans Two main classes of ECM molecules: a) Glycosaminoglycans mostly proteoglycans polysaccharide chains - glycosaminoglycans, GAGs, covalently bound to proteins highly hydrated, porous, gels b) fibrous proteins (embedded in the above gel) structural (collagen, elastin) strengthen the ECM adhesive (fibronectin, laminin) attach cells to the appropriate part of ECM Polysaccharides/ Peptidoglycanes Gram Negative bacteria Gram positive bacteria Glycoproteins Glycolipids Vs Lipopolysaccharides Glycolipids (Crebroside, Ganglioside) Relative swetness & Artificial sweetners Relative sweetness of sugar Sucrose: Glc: 70 Fru:170 Mal: 30 Lac: 16 100 Relative sweetness of Artificial sweetners • Cyclamate: 3, 000 • Aspartam: 20, 000 • Saccarin: 40, 000 • Monilin: 400, 000 Different ways for qualitative and quantitative identification of sugars Crystal formation(Osazones) Furfral and hydroxy furfural reaction with cyclic alcohol. Iodine Enzymatic Glucokinase Hexokinase Oxidative and reductive reactions: Benedict Benedict: An assay for sugars Cu2+ Cu+