* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5 The Market Equilibrium
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
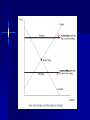
The Market Equilibrium (One More Time) ■ Market demand and supply ■ Bring together suppliers and demanders ■ Equilibrium Market Demand Is the Sum of All Individual Demands At each price, sum the individual quantities demanded, Da, Db … Dn, to get market quantity demanded (Dm) + Da = Db Dm = ∑ Da + Db + . . . Dn Dm Market Supply Is the Sum of All Individual Suppliers At each price, sum the individual quantities supplied to get market quantity supplied (Sm) Sm = ∑ Sa + Sb … Sn Sb Sa + = Sm Competition ■ Demanders compete with each other to get goods. Their efforts push price up, enriching suppliers. ■ Suppliers compete with each other to attract customers. Their efforts push price down, enriching demanders. ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! They are bargaining: Each party tries to convince the other of the powerful competition faced by alternatives. Equilibrium: Competition means mutually beneficial cooperation At “equilibrium” no one has an incentive to change behavior: Price S P* D Q* Q/time Adjustments to equilibrium ■ Price above P* ► Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded: excess supply, or “surplus” ► Frustrated suppliers compete for business, lowering prices (“buyers’ market”) ► Price falls until market clears ■ Price below P* ► Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied: excess demand, or “shortage” ► Frustrated demanders compete for product, raising prices (“sellers’ market”) ► Price rises until market clears Adjustment process What if the price is NOT right? ■Competition forces push price toward equilibrium: Price P high P low Excess Supply Excess Demand S D Q/time Minimum Wage: A Price Floor Legal minimum on wage: Wm – If greater than W* excess supply of labor Winners: – Those who keep their jobs Losers – Firms (& their customers) who pay – Those who lose their jobs $ S Wm W* D 0 Ld L* Ls Labor Data Confirming Theory Rent Controls: A Price Ceiling on Apartments Legal maximum on allowable rent: Pm less than P* excess demand for space Winners: – Those who keep apartments Losers – Landlords – Those who can’t get in $ S P* Pm D 0 Qs Q* Qd Quantity Questions How do each of these events influence the equilibrium (i) price of airline tickets and (ii) quantity of airline trips taken 1. Rise in price of jet fuel 2. Depression in the economy 3. Threat of war 4. Government regulations making air travel safer



















![[A, 8-9]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006655537_1-7e8069f13791f08c2f696cc5adb95462-150x150.png)


