* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prices and Markets
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
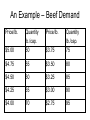
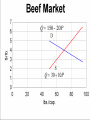
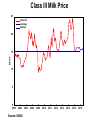
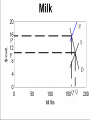
Prices and Markets AG BM 102 Introduction • Prices change all the time • The reason is because of changes in supply and/or demand • This happens in a market • A market is many things, but essentially it is where suppliers and demanders meet Market – the context of transactions between buyers and sellers of the same good or service A Market • Where the prices are determined • Where the terms of trade are negotiated • May be defined as a place, a time, a group of buyers or sellers, a level of the marketing system Equilibrium • Occurs where supply and demand curves meet • Defines a price and a quantity that clears market • Sends message to those in the market about preferences An Example – Beef Demand Price/lb. Price/lb. $5.00 Quantity lb./cap. 50 $3.75 Quantity lb./cap. 75 $4.75 55 $3.50 80 $4.50 60 $3.25 85 $4.25 65 $3.00 90 $4.00 70 $2.75 95 An Example – Beef Supply Price Quantity Price Quantity 3.00 60 4.25 72.5 3.25 62.5 4.50 75 3.50 65 4.75 77.5 3.75 67.5 5.00 80 4.00 70 5.25 82.5 Q 150 20 P Q 30 10 P Demand Q 150 20 P Supply Q 30 10 P Demand = Supply 150 20 P 30 10 P 120 30 P P 4 and Q 70 Why is it stable? • If P is too low, quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied and price is bid up • If P is too high, quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded and price falls Class III Milk Price 25 Class III average futures 20 $/cwt. 15 10 5 0 2005 2006 Source: USDA 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Why does this happen? • Why does a small shift in supply cause the price to change by so much? • Demand is so inelastic! • The only way to absorb the additional milk is to torpedo the price What happens when a line moves? • • • • • • • In this graph, the milk supply decreased Supply curve shifts New equilibrium at a higher price Sometimes the demand curve shifts Same idea – move a line, new equilibrium Increase in demand – higher price Decrease – lower price What changed? • If demand increases – the line moves • It crosses supply at a new point • An increase in demand causes an increase in QUANTITY SUPPLIED • In general, one line moves & you move along the other line to the new equilibrium Kinds of changes • • • • • • Input price rises Competing good goes on sale Income falls Health news New production technique Etc. Efficient Markets • Present price incorporates all known information • Who will sell you 100 shares Coca Cola when you want to buy? • Winner’s Curse Winner’s Curse Concluding Comments • Market defines price and quantity • Sends message to everyone about conditions • Regulates decisions • Becomes interesting when a line moves





























![[A, 8-9]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006655537_1-7e8069f13791f08c2f696cc5adb95462-150x150.png)


