* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pricing Strategy
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Congestion pricing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Transfer pricing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
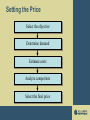
Pricing Decisions Jeremy Kees, Ph.D. Pricing Overview • Price: the exchange value of a good or service • Robinson-Patman Act – Federal legislation prohibiting price discrimination that is not based on a cost differential • Fair Trade Laws – Allow manufacturers to stipulate minimum prices for their products and force retailers to adhere to them The Importance of Pricing… • Prices, and the resulting sales, determine how much revenue a company receives • Prices thus influence a firm’s profits • Prices also influence the firm’s employment of the factors of production: – – – – Natural resources Capital Human Resources Entrepreneurship Just a few strategic issues… • How much focus should be on costs? • Should we always strive for the industry’s traditional margins • How often should we revise price? (often enough to capitalize on market changes) • Should pricing decisions happen independently or as an intrinsic element of market-positioning strategy? • How much should we vary price for different products, segments, channels, and purchase occasions? Strategies • “Freemium” strategy —giving some offering away for free while profiting from extras that are priced appropriately – Skype – Ryanair • parody Consumer Psychology and Pricing • Reference Prices – Internal – External • Price-Quality Inferences – Moderated by category/product knowledge • Price Cues – “Psychological Pricing” • Odd Pricing • Unit Pricing Setting the Price Select the objective Determine demand Estimate costs Analyze competitors Select the final price Objective Purpose Example Profitability Objectives Profit Maximization Target Return Low introductory interest rates on credit cards with high standard rates after 6 months. Market Share Objectives Sales Maximization Market Share Dell’s low-priced PCs increase market share and sales of services Value Objectives Value Pricing Per-song charges for music downloads Prestige Objectives Lifestyle Image High-priced luxury autos such as BMW and watches by Piaget NFP Objectives Cost Recovery Market Incentives Market Suppression High prices for tobacco and alcohol to reduce consumption Determining Demand • Price sensitivity – Implications for branding!! • Estimating demand curves – Done primarily through marketing research • Price elasticity of demand – Elastic vs. Inelastic Estimating Costs • Types of Costs – – – – Fixed Variable Total Average Competitive Analysis • Only after we determine market demand and company costs • We need to examine… – Product features – Perceived value Select Pricing Method • “3 Cs” – Customer Demand – Cost Function – Competitors Prices Pricing Strategies • Skimming – High-End Products – Introduction Stage of the PLC – Adidas / Fathead • Penetration Pricing – Generates Trials Pricing Strategies • Value Pricing - EDLP – Wal-Mart • Competitive Pricing – Compete on other product attributes Select Pricing Method • • • • • Markup pricing (cost-plus) Target-return pricing (breakeven analysis) Perceived-value pricing Going-rate pricing (customary) Auction-type pricing Select Final Price • Factors to consider: – – – – Impact of other marketing activities Company pricing policies Gain-and-risk sharing pricing Impact of price on other parties Adapting the Price • By geographic area • Discounts and Allowances – – – – – Cash Discount Trade Discount Quantity Discount Allowances Rebates • Promotional Pricing – Loss Leaders • Differentiated Pricing • Product Mix Pricing (Product-Line Pricing) – Bundling Risks of Making Price Adjustments • Customers assume quality is low • A low price buys market share but not loyalty (remember relationship marketing?) • Higher-priced competitors match the lower prices but have longer staying power because of deeper cash reserves • Trigger a price war Responding to Low-Price Competitors