* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Perfect Competition: Short Run and Long Run
Economics of digitization wikipedia , lookup
Schools of economic thought wikipedia , lookup
History of macroeconomic thought wikipedia , lookup
History of economic thought wikipedia , lookup
Icarus paradox wikipedia , lookup
Marginalism wikipedia , lookup
Chicago school of economics wikipedia , lookup
Macroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brander–Spencer model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of the firm wikipedia , lookup
Supply and demand wikipedia , lookup
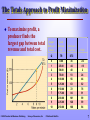
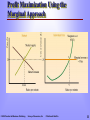
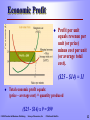
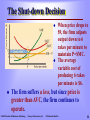
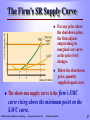
CHAPTER 5 Perfect Competition: Short Run and Long Run Prepared by: Jamal Husein © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin Perfectly Competitive Market A perfectly Competitive market is characterized by: 1. There are many firms. 2. The product is standardized, or homogeneous. 3. Firms can freely enter or leave the market in the long run. 4. Each firm takes the market price as given. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 2 The Short-run Output Decision The firm’s objective is to produce the level of output that will maximize profit. Economic profit = total revenue (TR) minus total economic cost (TC). revenue = price × quantity sold. The cost structure of the business firm is the same as the one we studied earlier. Total © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 3 The Firm’s TC Structure (Revisited) The shape of the total cost curve comes from diminishing returns in the short run. STC TFC STVC Short-run Short-run Total Fixed = Cost + Total Variable Total Cost Cost © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin Output: Rakes per Minute Fixed Cost Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 FC 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 Total Sh Variable Short-run Ma Cost Total Cost TVC 0 8 12 15 20 27 36 48 65 90 130 STC 36 44 48 51 56 63 72 84 101 126 166 S 4 The Revenue Structure of the Competitive Business Firm The perfectly competitive firm is a price-taking firm. This means that the firm takes the price from the market. As long as the market remains in equilibrium, the firm faces only one price—the equilibrium market price. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 5 Computing the Total Revenue of a Price-taker Price ($) Total Revenue ($) C o s t in $ Output: Rakes per Minute Total Revenue 250 200 150 Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 P 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing TR 0.00 25.00 50.00 75.00 100.00 125.00 150.00 175.00 200.00 225.00 250.00 100 50 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Output: Rakes per minute Since the perfectly competitive firm faces a constant price, the shape of its total revenue is an upward-sloping line. Total revenue changes only with changes in the quantity sold. Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 6 The Totals Approach to Profit Maximization To maximize profit, a producer finds the largest gap between total revenue and total cost. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e Output: Rakes per Minute Total Revenue ($) Short-run Total Cost Profit Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TR 0.00 25.00 50.00 75.00 100.00 125.00 150.00 175.00 200.00 225.00 250.00 STC 36 44 48 51 56 63 72 84 101 126 166 -36 -19 2 24 44 62 78 91 99 99 84 O’Sullivan & Sheffrin P 7 The Marginal Approach The other way to decide how much output to produce involves the marginal principle. Marginal PRINCIPLE Increase the level of an activity if its marginal benefit exceeds its marginal cost, but reduce the level if the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit. If possible, pick the level at which the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 8 Marginal Revenue The benefit of producing and selling rakes is the revenue the firm collects. If the firm sells one more rake, total revenue increases by $25. Marginal benefit = marginal revenue = market price © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 9 The Marginal Rule for Profit Maximization A firm maximizes profit in accordance with the marginal principle—by setting marginal revenue (or market price) equal to marginal cost. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e Output: Rakes per Minute Marginal Revenue = Price ($) Short-run Marginal Cost Profit Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 P 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 SMC 8 4 3 5 7 9 12 17 25 40 -36 -19 2 24 44 62 78 91 99 99 84 O’Sullivan & Sheffrin Ou Rak Mi 1 10 Profit Maximization Using the Marginal Approach © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 11 Economic Profit Profit per unit equals revenue per unit (or price) minus cost per unit (or average total cost). ($25 - $14) = 11 Total economic profit equals: (price – average cost) × quantity produced ($25 - $14) x 9 = $99 © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 12 Shut-down Decision The firm should continue to operate if the benefit of operating (total revenue) exceeds the cost of operating, or total variable cost. TR = (P × Q) must be greater than STVC = SAVC × Q, therefore, If P > SAVC, the firm should continue to operate If P < SAVC, the firm should shut down © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 13 The Shut-down Decision When price drops to $9, the firm adjusts output down to 6 rakes per minute to maintain P=SMC. The average variable cost of producing 6 rakes per minute is $6. The firm suffers a loss, but since price is greater than AVC, the firm continues to operate. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 14 The Shut-down Decision The firm’s shutdown price is the price at which the firm is indifferent between operating and shutting down. At $5, P = SAVC. Above this price, the firm is better off continuing to produce at a loss. Below this price, the firm is better off shutting down because it could not recover its operating cost. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 15 Short-run Supply Curve The firm’s short-run supply curve shows the relationship between the market price and the quantity supplied by the firm over a period of time during which one input—the production facility—cannot be changed. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 16 The Firm’s SR Supply Curve For any price above the shut-down price, the firm adjusts output along its marginal cost curve as the price level changes. Below the shut-down price, quantity supplied equals zero. The short-run supply curve is the firm’s SMC curve rising above the minimum point on the SAVC curve. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 17 The Market Supply Curve The short-run market supply curve shows the relationship between the market price and the quantity supplied by all firms in the short run. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 18 A Market in Long-run Equilibrium A market reaches a long-run equilibrium when three conditions hold: 1. The quantity of the product supplied equals the quantity demanded 2. Each firm in the market maximizes its profit, given the market price 3. Each firm in the market earns zero economic profit, so there is no incentive for other firms to enter the market © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 19 A Market in Long-run Equilibrium In short-run equilibrium, quantity supplied equals quantity demanded and each firm in the market maximizes profit. In addition to the conditions above, in long-run equilibrium the typical firm earns zero economic profit so there is no further incentive for firms to enter the market. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 20 A Market in Long-run Equilibrium In long-run equilibrium, price = marginal cost (the profit-maximizing rule), and price = short-run average total cost (zero economic profit). © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 21 The LR Supply Curve for an Increasing-cost Industry An increasing-cost industry is an industry in which the average cost of production increases as the total output of the industry increases. The average cost increases as the industry grows for two reasons: Increasing input prices Less productive inputs © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 22 Industry Output and Average Production Cost Number of Firms Industry Output Rakes per Firm 50 100 150 350 700 1,050 7 7 7 Typical Cost for Typical Firm $70 84 96 Average Cost per Rake $10 12 14 The rake industry is an increasing-cost industry because the average cost of production increases as the total output of the industry increases. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 23 Drawing the Long-run Market Supply Curve © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e Each point on the long-run supply curve shows the quantity of rakes supplied at a particular price (i.e., at a price of $12, 100 firms produce 700 rakes). The long-run industry supply curve is positively-sloped for an increasing cost industry. O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 24 SR Increase in Demand and the Incentive to Enter An increase in market demand puts upward pressure on price. As price increases, there is an opportunity to earn profit in the short run, and the industry attracts new firms. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 25 The Long-run Effects of an Increase in Demand © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e In the short-run, firms respond to the increase in demand by adjusting output in their existing production facilities, and the price adjusts from $12 to $17. O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 26 The Long-run Effects of an Increase in Demand © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e In the long run, after new firms enter, equilibrium settles at $14. The new price is a higher price than the price before the increase in demand (increasing cost industry). O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 27 Long-run Supply Curve for an Constant-cost Industry In a constant-cost industry, firms continue to buy inputs at the same prices. The long-run supply curve is horizontal at the constant average cost of production. After the industry expands, the industry settles at the same long-run equilibrium price as before. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 28 Long-run Supply Curve for the Ice Industry © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Survey of Economics, 2/e An increase in the demand for ice increases the price of ice to $5 per bag. In the long-run, the price of ice returns to its original level. O’Sullivan & Sheffrin 29