* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Populations
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
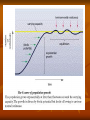
Animal Population Diversity and Structure Species diversity – number of different species a community contains combined with the abundance of individuals within those species. Community niche structure – how ecological niches vary and differ. Niche – a species role in the community Most diverse or species rich environments are the tropical rain forests and some coral reefs. Species types Native Species – normally live in and thrive in a particularly area 1. 1. Nonnative Species – accidentally or deliberately introduced to an area 2. 1. 3. White Tailed Deer, Bald Eagle, Opossum Horses Invasive Species/Alien Species – wreak havoc on the environment. No natural predators Invasive Species Asian Carp Mississippi River No natural predators Eats all the plankton Kudzu Vine South United States 7 million acres Grows 1 ft per day Kudzu bug (also invasive) started eating all of the soybean crop. 4. Indicator Species – a species that serves as early warnings of danger to an area Ex – Butterflies, trout, frogs ButterfliesThey have brief life cycles and are affected by climate change and pesticides. Birds plan their breeding season around when the caterpillers are most abundant TroutHealthy stream=abundant trout They need clean water, a specific temperature, protection, unsilted gravel to spawn and an abundant food supply. Indicator Species What about the frogs? Well… Vulnerable because different life cycles involve different habitats Tadpoles – live in water and eat plants Adults – live on land and eat insects that can be exposed to pesticides Eggs – have no protective shell so are vulnerable to increased UV rays or pollution Hundreds of species have vanished since 1980 ¼ of all amphibian species are extinct, endangered or vulnerable Why should we care? Their death indicates that there is some deterioration of the environment Large part of the ecological pyramid – they are predator and prey Secretions in the skin - Can be used in the pharmaceutical industry for medication 5. Keystone Species – species that have a significant role in the community Examples: A.Pollinators such as bees, humming birds, bats B. Top predators such as wolves, lions, alligators, and sharks C. Decomposers such as beetles A loss of these types of species leads to population crashes and extinctions 6. Foundation species – species that shape communities by creating and enhancing their habitats in ways that benefit others Ex – Elephants, beavers Energy in an Ecosystem Energy is the most important factor in determining how many and what kinds of organisms live in an ecosystem. Trophic Levels 1st Level Producers: take in energy from their surroundings and store it in complex molecules. Also called autotrophs/ photosynthetic Use the sun to power the production of food. 2nd Level Primary Consumers Obtain energy by consuming Autotrophs. Also called heterotrophs. 3rd Level Secondary consumers Obtain energy by consuming both producers and primary consumers Tertiary Level Apex predators Top of the food chain Will consume anything from all of the previous levels Decomposers Consumers that obtain energy by consuming organic wastes (feces, urine, leaves, dead plants) and dead bodies. Recyclers of nutrients. Food Chain Single pathway of feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem that results in energy transfer. Example: grass mice snake hawk Food Web Multiple food chains in a ecosystem Many consumers eat more than one kind of food. More than one species may eat the same organism. Species interaction 5 Basic types of interaction 1. Interspecific competition – competition between species for shared resources such as space and food 2. Predation – one species (predator) directly feeds on another (prey) Ex – lions eat gazelle 3. Parasitism - when one species (parasite) feeds on part of another organism (host) Ex – Ticks, Tapeworm 4. Mutualism – two species interact in a way that benefits both. Ex – Oxpeckers and Rhinos Clown fish and sea anemones 5. Commensalism – one species benefits and the other is not effected Ex – Epiphytes and tropical trees Remora Fish and the Shark Avoiding Predation 1. Camouflage – uses shape or color to hide 2. Chemical warfare – examples are poisons, irritants (stingers), Foul smells (skunk), tasting bad (monarch butterfly) 3. Warning colors – bright colors indicate an organism is poisonous 4. Mimicry – looking and acting like another animal Limits on Population Growth Environmental resistance – factors that act to limit the growth of a population Examples: disease, predators, natural events, humans Logistic growth – involves exponential growth followed by a steady decrease in population growth with time until the population size levels off. Human Impacts We Have: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Reduced biodiversity Used, wasted, or destroyed net primary productivity that supports all consumers Strengthened some populations of pests and bacteria Eliminated some predators Introduced nonnative species in communities Interfere with chemical cycles and energy flow