* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Probability and Heredity 2013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
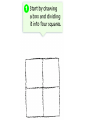
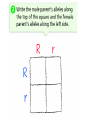
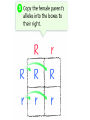
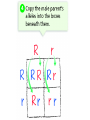
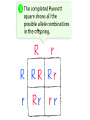
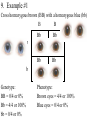
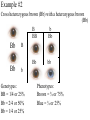
Probability and Heredity EQ: How does probability affect the way traits are inherited? Previously, in life science… • You learned that alleles for traits are inherited according to definite patterns. Now, you will discover the mathematical foundation for these patterns. 1. What is Probability? • The likelihood that a particular event will occur. • Coin Toss (20X) H T prediction actual • Probability predicts what is LIKELY TO OCCUR…Not necessarily what will occur • Each event occurs INDEPENDENTLY What is probability? A number that describes how likely it is that a certain event will occur 2. What are Punnett Squares? • Chart used to show possible allele combination What is a Punnett square? A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. 3. How do you use Punnett squares? Show possible combination 1. Draw a square. Divide it into 4 sections. 2. One parent’s alleles on the top 3. One parent’s alleles on the side 4. Cross alleles (like multiplication!) What is the probability that an offspring will have white fur? 0% ! What is the probability that an offspring will have black fur? 100% ! 4. What is phenotype? • An organism’s appearance, or visible traits. • Example: Purple or white flowers 5. What is genotype? • An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele combinations. • Example: PP or Pp or pp 6. What is homozygous? • having 2 identical alleles example: PP or pp 7. What is heterozygous? • having 2 different alleles example: Pp 8. Make a chart showing the genotypes and phenotypes B = Brown; b = blue genotype phenotype Homozygous or Heterozygous? 8. Make a chart showing the genotypes and phenotypes B = Brown; b = blue genotype BB B___ b ___ phenotype Homozygous or Heterozygous? How many genotypes are there for the smooth-pod phenotype? Two! 9. Cross homozygous brown (BB) with a homozygous blue (bb) 9. Example #1 Cross homozygous brown (BB) with a homozygous blue (bb) B B b b Genotype: BB = Bb = bb = Phenotype: Brown eyes = Blue eyes = 9. Example #1 Cross homozygous brown (BB) with a homozygous blue (bb) B B Bb Bb Bb Bb b b Genotype: BB = 0/4 or 0% Bb = 4/4 or 100% bb = 0/4 or 0% Phenotype: Brown eyes = 4/4 or 100% Blue eyes = 0/4 or 0% 10. Cross heterozygous brown (Bb) with a heterozygous brown (Bb) Example #2 Cross heterozygous brown (Bb) with a heterozygous brown (Bb) B b BB Bb Bb B Bb Bb bb b Genotypes: BB = 1/4 or 25% Bb = 2/4 or 50% Bb = 1/4 or 25% Phenotypes: Brown = ¾ or 75% Blue = ¼ or 25% 11. How is probability related to genetics? • Mendel discovered that probability can be used to predict the results of genetic crosses! • Probability is used to PREDICT the RESULTS of a genetic cross 12. What is codominance? • Neither allele is dominant or recessive, both alleles are expressed in the offspring. Will the offspring be heterozygous or homozygous? heterozygous! They have alleles for white and black feathers. DISCLAIMER: ROOSTER NEED TO MATE WITH A CHICKEN NOT ANOTHER ROOSTER!