* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
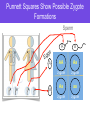
Punnett Squares Objective • SWBAT predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic make up of the parents DO NOW: Look at this picture. What do you think it is saying? What’s the word…? 1. Rats have one allele from its mother that is R and one from its father that is r, what term would describe it’s genotype? 2. aa can be described as this ____________ while AA can be described as ______________. 3. Different forms of genes are called ________________ (like brown or blonde hair) 4. A section of DNA coding for a specific trait Some Vocabulary • Heterozygous: Has two different forms of an allele • Example: Bb • Homozygous: Contains the same form of an allele • Example: bb, BB • Homozygous Dominant: • Homozygous Recessive: Practice A man is heterozygous for the hair color gene, and he has black hair. He marries a woman who is homozygous recessive and has blonde hair. Write the genotype and phenotype for each person AND tell me what the dominant and recessive traits are. Man Genotype Phenotype Woman Dominant Trait = Recessive Trait = Can we predict phenotypes of children? Mendel’s Experiment • Mendel bred a green pea plant with a yellow pea plant (Parental Generation). He found that all of the offspring (F1 generation) were also green. • When he bred these offspring together though, he got 3 green pea plants and one yellow plant. (F2 generation) How can we test this ourselves? • Mendel realized that there was a mathematical way to predict the genotype and phenotype of an offspring • This mathematical technique is known as a punnett square Punnett Squares Show Possible Zygote Formations Sperm A A a a AA Aa zygote zygote Aa aa zygote zygote Mendel’s Punnett Squares • In Mendel’s first experiment, he crossed: a GG (green pea plant) and a gg (yellow pea plant) together G G g g Gg Gg Parents: GG and gg Offspring: Gg Genotypes: all Gg Phenotypes: all Green Gg Then he took 2 of the offspring from the F1 generation and mated them together G G g • Parents’ Genotypes: Gg, Gg GG Gg • Parents’ Phenotype: Green • Offspring’s Genotypes: GG, Gg, gg g Gg gg • Offspring’s Phenotypes: Green and Yellow Now YOU try Understanding G G GG G GG Check for Understanding • Parents: • Genotypes GG and Gg • Phenotypes all green • Offspring: g Gg Gg G = green g = yellow • Genotypes: GG and Gg • Phenotypes: all green Determining Probability • Use the information from your last punnett square to answer the questions. • What is the probability that the offspring will have green peas? • • What is the probability that the offspring will have yellow peas? • • 4/ 4 = 100% 0 /4 = 0 % What is the ratio of green peas to yellow peas? 4:0 More Vocab • Genotypic Ratio: Number of times a genotype would appear in the offspring after a test cross • Example: 2 GG: 2 Gg • Phenotypic Ratio: Number of times a phenotype would appear in the offspring after a test cross • Example: 4 green: 0 yellow More Practice - Check for Understanding A woman homozygous dominant for a BIG tongue mates with heterozygous man. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring? B B B BB BB B = Big tongue b = Small tongue • Parents: BB and Bb • Offspring: b Bb Bb • Genotypes: BB and Bb • Phenotypes: all BIG Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disorder. Symptoms appear in mid- adulthood and cause neurological cell death. Using the following Punnett square, determine the chance that someone with Huntington’s disease will have children with the disease if mated with a homozygous recessive individual. H H h Hh Hh h Hh Hh H = Huntington’s Disease h = No disease What’s the probability that one of her children will have Huntington’s Disease? 100% Practice SpongeBob’s aunt is famous around town for her itty, bitty stubby nose! She recently met a cute squarepants fellow who also has a stubby nose, which is a recessive trait. Would it be possible for them to have a child with a regular long nose? Why or why not? Create a Punnett square to help you answer this question. l l ll l ll Recessive = stubby nose = l Dominant = long nose = L • Parents: ll and ll • Offspring: l ll ll • Genotypes: all ll • Phenotypes: all stubby nose Do Now 1. The genetic makeup of a cell is known as _______________________. 2. The physical characteristic of something (like having dimples) 3. Green colored skin is more likely to be expressed over red skin. The green colored skin is known as a _______________ allele. 4. If my alien had red skin (see #4), it would be expressing the ________________ trait. Law of Segregation • If a person is heterozygous (Rr), what are the possible alleles that his/her gametes will have? • Either R OR r • Think- Pair- Share: what does this have to do with meiosis? • Because the two alleles are on homologous chromosomes and they will separate in meiosis Law of Independent Assortment • Occurs because chromosomes go through “random segregation” when they make gametes • Mother and father chromosomes DO NOT need to move together into new cells • Example: if my dad has blonde hair (bb) and dimples (dd), what gametes can he possibly make? • Example: If my mom is heterozygous for brown hair (Bb) and dimples (Dd), what gametes can she possibly make?