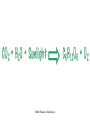* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download H - Granbury ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
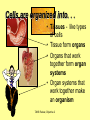
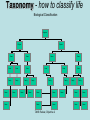
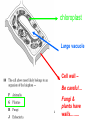
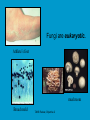
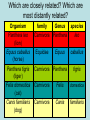
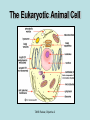
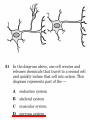
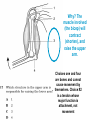
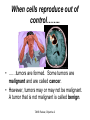
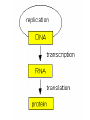
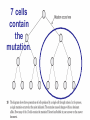
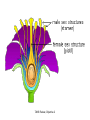
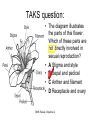
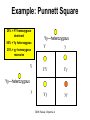
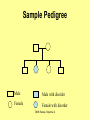
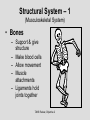
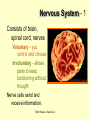
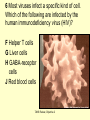
The student will demonstrate an understanding of the organization of living systems. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Living things are . . . • Made of cells • Grow and develop • Respond to the environment • Use energy • Reproduce TAKS Review, Objective 2 Cells are organized into. . . • Tissues - like types of cells • Tissue form organs • Organs that work together form organ systems • Organ systems that work together make an organism TAKS Review, Objective 2 Hydrochloric acid is produced by the lining of the stomach. What is its function? Calories are how the energy contained in food is measured. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. ‘Lipids’ is the name for fats and oils. TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 Taxonomy - how to classify life Biological Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Genus Genus Class Order Order Family Family Genus Phylum Class Order Family Genus Order Family Genus Class Order Family Family Genus Genus Genus Genus TAKS Review, Objective 2 Genus Order Family Family Genus Genus Genus Genus The taxonomy divisions from largest to smallest are: 49 Which of these classifications Kingdom (6) is most specific? Phylum A Family B Genus C Phylum D Order Class Order Family Genus TAKS Review, Objective 2 species TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Six Kingdoms – the largest groupings of living things Plantae Fungi Animalia Protista Eubacteria TAKS Review, Objective 2 Archaebacteria Animal Kingdom (Animalia) • Multicellular • Heterotrophic • Includes all vertebrates (one major phylum) and invertebrates (several phyla) • Insects, jellyfish, people…… all are animals TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 Kingdom Plantae Multicellular & Autotrophic ~ all plants perform photosynthesis Examples: mosses, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants (grasses, trees, shrubs, most garden plants, wildflowers) TAKS Review, Objective 2 chloroplast Large vacuole Cell wall – Be careful… TAKS Review, Objective 2 Fungi & plants have walls…….. Kingdom Fungi • Multicellular & some single-celled • Most of these organisms are decomposers • Includes mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and infections like athlete's foot TAKS Review, Objective 2 Fungi are eukaryotic. Athlete’s foot mushroom Bread mold TAKS Review, Objective 2 So, how do they DIFFER from animals? TAKS Review, Objective 2 Kingdoms of Single-Celled Organisms • Protista • Eubacteria • Archaebacteria TAKS Review, Objective 2 WHY?? TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 Kingdom Protista Largest source of food and oxygen for the entire planet. Includes plankton, amoeba, and ciliates (like the paramecium) Described as – unicellular eukaryotes • What is the significance of “A?” • How do you know that this is not a prokaryotic organism? What are the clues? TAKS Review, Objective 2 Prokaryotic Kingdoms - Cells without membrane-bound organelles 1. Kingdom Eubacteria: Unicellular prokaryotes, often decomposers 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria: Unicellular prokaryotes from extreme environments TAKS Review, Objective 2 8 Some bacteria benefit mammals by helping with — F growth G defense H digestion J respiration • Kingdom of Bacteria has beneficial and harmful members • The best answer here is H, since digestive systems of mammals contain many bacteria. • Bacteria found in the respiratory system usually result in illness, which would trigger the defenses; not help the organism TAKS Review, Objective 2 Binomial Classification • Living things are given a two-part scientific name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized. The second part is the species name, which is never capitalized. • Scientific names are used because the same plant or animal in different places may have different common names. • Man’s scientific name is Homo sapiens TAKS Review, Objective 2 12 The bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, is most closely related to the F spotted chorus frog, Pseudacris clarki G Asian flying frog, Polypedates leucomystax H northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens J African bullfrog, Pyxicephalus adspersus TAKS Review, Objective 2 Which are closely related? Which are most distantly related? Organism family Genus species Panthera leo (lion) Equus caballus (horse) Carnivora Panthera Panthera tigris (tiger) Carnivora Panthera Felis domestica (cat) Carnivora Felis domestica Canis familiaris (dog) Carnivora Canis familiaris Equidae Equus TAKS Review, Objective 2 leo caballus tigris Related (in biological terms) means family, genus, species. F spotted chorus frog, Pseudacris clarki G Asian flying frog, Polypedates leucomystax H northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens J African bullfrog, Pyxicephalus adspersus • Genus is always a capital letter, species is lower case. • Most closely related would be in the same genus, Rana. • ANSWER? • H TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Cell Theory Matthias Schleiden, Robert Virchow, and Robert Brown all contributed to the formation of the cell theory, which states: – 1. All living things are composed of cells. – 2. Cells are the smallest working units of living things. – 3. All cells come from preexisting cells by cell division. TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Eukaryotic Plant Cell TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Eukaryotic Animal Cell TAKS Review, Objective 2 Cell Part Function Cell membrane Nucleus Chromosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Controls what enters and leaves the cell Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus Control center of the cell Genetic information in the nucleus Transport system in cell Ribosome Golgi Body Organelle makes proteins Organelle packages proteins Vacuole Stores water and/or waste Nuclear membrane Lysosome Mitochondria Breaks down old cell parts Organelle for cellular respiration – TAKS Review, Objective 2 provides energy TAKS Review, Objective 2 The cell membrane has many roles including maintaining homeostasis: structure, regulating transport of nutrients and wastes into and out of the cell, and basic protection of the cell. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Be familiar with the structure and function of parts of cells including bacteria. In biology….always consider FORM & FUNCTION!! TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 Why? The muscle involved (the bicep) will contract (shorten), and raise the upper arm. Choices one and four are bones and cannot cause movement by themselves. Choice #2 is a tendon whose major function is attachment, not TAKS Review, Objective 2 movement Viruses are different from cells and have different properties and functions. TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 This is the only answer that makes sense…. Why are A, B and D not good choices? TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 Plant cells have….. but animal cells don’t • Chloroplasts – organelle responsible for photosynthesis • Cell Walls – a structure outside of the membrane to provide support • Large vacuoles to store extra water TAKS Review, Objective 2 This is a typical plant cell • It contains a cell wall, chloroplasts, a very large vacuole. • Why do plants need large vacuoles? •ANSWER: This is where food and water are stored. TAKS Review, Objective 2 52 Compared to annual rings of trees that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — These 3 F be softer would G grow at a faster rate indicate more water, H be thinner not less J photosynthesize at a faster rate TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS question Which structure regulates gas exchange during the processes of photosynthesis and respiration? • AQ • BR • CS • D T = stomata TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Temperate Forest TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Desert TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Tundra TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Taiga TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Tropical Rain Forest TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Grasslands TAKS Review, Objective 2 Mechanisms of Seed Dispersal • By animal • By wind • Floating in water TAKS Review, Objective 2 Animal Dispersal Some animals bury seeds and Barbs get tangled in animal they grow into new plants. fur and carried to new places. Animals eat fruit, and after digestion theTAKS seeds are dropped in new places. Review, Objective 2 More barbs and hooks… TAKS Review, Objective 2 Dispersal by wind…. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Floating on water….. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Explosive dispersal TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS question Which of the following characteristics could help short plants survive in areas with limited sunlight? F Broad leaf surfaces G Brightly colored flowers H Thick stems J Shallow roots TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS question #4 Which of these characteristics might help a plant species survive in an area with limited sunlight? • F Bright flowers • G Large leaves • H Short stems • J Thick cuticles TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS question This seed is best dispersed by — • A water • B birds • C wind • D insects TAKS Review, Objective 2 Cell Reproduction • The Cell Cycle is the life cycle of a cell. It has two parts. Mitosis is the process of nuclear division. What is interphase? • During mitosis the nucleus separates into two new identical sister nuclei. TAKS Review, Objective 2 26 If a cat has 38 chromosomes in each of its body cells, how many chromosomes will be in each daughter cell after mitosis? • • • • F 11 G 19 H 38 J 76 H Mitosis is the normal division of any cell nucleus, so the chromosomes replicate exactly and then separate into two identical cells. So the answer is TAKS Review, Objective 2 When cells reproduce out of control…….. • ……tumors are formed. Some tumors are malignant and are called cancer. • However, tumors may or may not be malignant. A tumor that is not malignant is called benign. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Transporting into Cells Diffusion Osmosis is the diffusion of H2O • Passive movement - from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is diffusion. • The diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Why? Because this means that water is moving from high concentration (of water) to lower concentration (of water) TAKS Review, Objective 2 across the membrane. What is active transport? Energy is used to move selected molecules into a cell, even if they are at a low concentration (that is….fromTAKS low to high concentration) Review, Objective 2 Ways to Maintain Homeostasis • Passive transport – no ATP used – Diffusion – Osmosis – Facilitated diffusion • Carrier proteins • Ion channels • Active transport – ATP used – Carrier proteins • Cell membrane pumps (sodium-potassium) – Endocytosis – Exocytosis TAKS Review, Objective 2 34 When a sea urchin egg is removed from the ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells and bursts. Which of these causes water to enter the egg? F Coagulation Means to clump together – Incorrect G Sodium pump Sodium is not being moved – Incorrect H Active transport The egg would not use energy to do this since it kills the cell. J Osmosis This is the movement of water from an area of high concentration (the fresh water) to low concentration (inside TAKS Review, Objective 2 the Egg) SUNLIGHT 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon dioxide plus Water Produces Glucose This is photosynthesis: TAKS Review, Objective 2 and Oxygen TAKS Review, Objective 2 Plants carry out photosynthesis and cellular respiration. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Cellular Respiration • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • Occurs in ALL living things (In mitochondria of eukaryotes) TAKS Review, Objective 2 The • Genetic Code All of the information to make a new cell/organism is contained in the chromosomes of the cell. • Chromosomes are made of tightly coiled DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid. • Chromosomes contain genes, each of which codes for a single protein. There may be hundreds/thousands of genes on each chromosome. TAKS Review, Objective 2 DNA is formed of nucleotides, which have 3 parts; a sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base. The 4 different nitrogen bases of DNA are: o o o o DNA Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine The process of copying DNA is called replication A REPLICA of each side of the strand of DNA is made. TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 The Code of Life • The structure of DNA is called a double helix. • The base Guanine always pairs to Cytosine. Adenine pairs to Thymine • Apples in Trees, Cars in Garages • Mutations are caused when these pairings are not made. TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 38 In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? F Amount of adenine G Number of sugars H Sequence nitrogen Adenine isofonly one bases Every base is of thenitrogen 4 nitrogen J Strengthto ofahydrogen attached sugar so, bases; it can’t code G bonds is not correct. for anything by itself. Hydrogen bonds strength does not change enough to code for trait changes. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Transcription . . . • messenger RNA reads the DNA in the nucleus and then leaves the nucleus to take the information to the ribosome. • the DNA then wraps back up until next time. TAKS Review, Objective 2 RNA vs. DNA Characteristic RNA DNA Strands 1 2 Sugar molecule Bases Ribose Deoxyribose A, U, C, G A, T, C, G Nucleus and cytoplasm Nucleus only Nucleotide Nucleotide Where Found Building block TAKS Review, Objective 2 Kinds of RNA There is only one kind of DNA, but there are 3 kinds of RNA. –Messenger RNA (mRNA) –Transfer RNA (tRNA) –Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) TAKS Review, Objective 2 Translation . . . code into words • mRNA takes the code from the nucleus to the ribosome where it pairs with transfer RNA to put amino acids into chains called proteins. • mRNA pairs to tRNA in the ribosomes This protein building is called TRANSLATION. TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 What does this chart represent? It says codons, and has U instead of T, so it must be mRNA. How would you find the amino acid coded by GAC? TAKS Review, Objective 2 Mutations are changes in the sequence of base pairs in the DNA molecule. There is no guarantee that mutations will be dominant or recessive. In fact, the term “homozygous recessive” refers to what would happen if two copies of a mutated gene were present in a cell. In a skin cell where the mutation occurred, this is not the case. Mutations effect DNA, not RNA. However, mutations must occur with the DNA coding region for mRNA codons to affect the skin cell. They would not affect offspring unless they were passed on in a gamete (sex cell). Offspring don’t get their parent’s skin cells; only their gametes. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Following the base pairing rules for DNA (A-T and G-C), AATCGC would have the complement TTAGCG, and run from 5’ to 3’. Uracil (U) is not found in DNA – only in RNA This does not follow the base-pairing rule TAKS Review, Objective 2 53 The table shows a comparison of some amino acids found in cytochrome c. The two organisms in the table that are most closely related are — A Q and T B R and S C Q and R D 2Q and S TAKS Review, Objective To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the levels are the same and differ in the other 2 by a smaller percent. Answer: TAKS Review, Objective 2 Not A Not B Not D C Transcription and Translation TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 What is the DNA base pair rule (Chargaff’s Rule)? 24 If the template of a strand of DNA is 5' AGATGCATC 3', the complementary strand will be — F 3' TCTACGTAG 5' G 5' CTACGTAGA 3' H 3' AGATGCATC 5' J 5' AGACGTCTA 3' TAKS Review, Objective 2 In DNA A to T and T to A, C to G and G to C 5' AGATGCATC 3‘ TCTACGTAG • Base pair each letter by the above rule. • So the answer is: • F TAKS Review, Objective 2 Nothing wrong here………….. answer TAKS Review,The Objective 2 is D! 7 cells contain the mutation. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Genetics – How traits are inherited….. • Father of Genetics is Gregor Mendel. • Dominant traits always are visible, and are represented by capital letters. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Genetics Recessive traits are hidden unless both alleles are the recessive one (know ~ homozygous v. heterozygous) At least one pair of alleles determines the trait in genetic inheritance. TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS question: • The diagram illustrates the parts of this flower. Which of these parts are not directly involved in sexual reproduction? • A Stigma and style • B Sepal and pedicel • C Anther and filament • D Receptacle and ovary TAKS Review, Objective 2 Example: Punnett Square 25% = YY homozygous dominant 50% = Yy heterozygous 25% = yy homozygous recessive Y Yy—heterozygous Y y YY Yy Yy yy Yy—heterozygous y TAKS Review, Objective 2 Punnett Squares D d d Heterzygous D Dd & Dd Homozygous Recessive d dd dd D d DHeterzoygous DD Dd& dHeterozygous Dd dd d D Homozygous Dominant D DD Dd & Heterozygous D DD Dd D Homozygous Recessive & d Dd Dd Homozygous Dominant d Dd Dd TAKS Review, Objective 2 The homozygous tall parent is TT for height and the short parent is tt for height. This will give each offspring a Tt genotype for height. Both parents are wrinkled making them ss for this trait. This will give each off spring a genotype of ss for the wrinkled trait. This make 100% of the offspring Ttss. These percentages are not possible. To get this genotype percentage one of the parents would need to be homozygous smooth and the other parent would need to be wrinkled. TAKS Review, Objective 2 gg is not possible! Half will inherit long beak from the male (Ll) and half will be short beak (ll) Why? All the offspring must have green feathers Half, not all will be short beak. because all children receive the G gene from the male. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Phenotype is what is seen….. • Phenotype refers to what is visible – the dominant trait or the recessive trait. • How do you know the phenotype? • LOOK!! TAKS Review, Objective 2 Genotype – actual combination of alleles • Only 3 possibilities • BB = Homozygous Dominant • Bb = Heterozygous • bb = Homozygous recessive • How do you know? Must look at inheritance pattern to find out. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Inheritance of Traits • Pedigree—family history that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations. – Helps identify carriers of genetic disorders • Carriers—individuals who are heterozygous for a genetic disorder but do not show symptoms—can pass the mutant allele to their offspring TAKS Review, Objective 2 Sample Pedigree Male Male with disorder Female Female with disorder TAKS Review, Objective 2 Pedigree Shows the Family Tree Colorblindness Inheritance P = Father has colorblindness; Mother is a carrier Male Parent Male Colorblind Male Male Female Parent Carrier Male Normal Female Female ? Male Female Male Colorblind Female TAKS Review, Objective 2 Pedigree Shows the Family Tree Colorblindness Inheritance P = Father has colorblindness; Mother is a carrier XcY XcY Male Male XCXc XCY Female XX ? Male Female XCY Female TAKS Review, Objective 2 TAKS Review, Objective 2 Homeostasis • … is the maintenance of the normal operating conditions of an organism • …control of body temperature, pulse rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, urine output, digestive absorption, metabolism rate, growth rate and hormone levels all need to be maintained…..a “steady state.” TAKS Review, Objective 2 Structural System – 1 (Musculoskeletal System) • Bones – Support & give structure – Make blood cells – Allow movement – Muscle attachments – Ligaments hold joints together TAKS Review, Objective 2 Structural System – 2 • • • 3 types of muscles – Smooth, involuntary – Striated, voluntary – Cardiac, heart muscle somewhat like both above Allow for movement Attached by tendons above and below joints TAKS Review, Objective 2 17 Which structure in the upper arm is responsible for raising the lower arm? A1 B2 C3 D4 In order to raise it, it must be attached, so its not 1 or 2. 4 is a bone not a muscle, so its answer: TAKS Review, Objective 2 Nervous System - 1 Consists of brain, spinal cord, nerves Voluntary - you control and choose Involuntary - allows parts to keep functioning without thought Nerve cells send and receive information. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Nervous System - 2 Main parts of nerve cell: TAKS Review, Objective 2 – Axon: sends signal – Cell Body: controls cell functions – Dendrite: receives signal from another – Synapse: space between cells Nervous System - 3 • Involuntary is controlled by the medulla oblongata of the brain. • This is how you keep breathing while sleeping and digest food without thinking about it. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Circulatory System - 1 This system helps to connect many other systems as it provides the transport of substances from one organ to another. Every cell must touch a blood vessel to take in what it needs and get rid of waste. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry it back to the heart. The heart pumps the blood TAKS Review, Objective 2 Circulatory System - 2 • The top parts of the heart receive blood – Atrium/atria • The bottom two are very muscular and pump the blood – Ventricle/ventricles • Two contractions, right ventricle pumps to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps to the body and brain. TAKS Review, Objective 2 29 Nutrients from digested food move from the digestive system directly into the — Endocrine system does not transport. So . . . A circulatory system B integumentary Excretory system gets rid of waste system CO2 and H2O, not food. So . . C excretory Integumentary system system holds D endocrine organs and tissues in place. The Circulatory system So. . . System carries TAKS Review, Objective 2 everything to every 25 The medulla, part of the brain stem, reacts quickly to increased levels of CO2 in the blood and stimulates a response from the — A excretory system B immune system C respiratory system D integumentary system Increased respiration gets rid of excess CO2. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Immune System - 1 • • • The immune system Could also be called first protects from infections line defense. and illness 1st Order Non-specific: includes skin, mucous membranes, cilia of trachea and bronchi, stomach acid, tears 2nd Order: includes the inflammatory response (swelling, redness due to histamine release), fever, white blood cells Could also be called such as phagocytes and second line defense. macrophages destroying the pathogens and TAKS Review, Objective 2 infected tissue cells. Immune System - 2 Two main types of immunity: • ACTIVE – body makes its own antibodies after being sick - permanent OR a vaccination to help your body make antibodies • PASSIVE – injection with antibodies, or transferred from mother to unborn baby TAKS Review, Objective 2 6 Most viruses infect a specific kind of cell. Which of the following are infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)? F Helper T cells G Liver cells H GABA-receptor cells J Red blood cells TAKS Review, Objective 2 Ask yourself: which cell type deals with immunity? F Helper T cells G Liver cells H GABAreceptor cells J Red blood cells • Answer? Helper T cells. • All the rest are body cells with specific jobs that do not relate to immunity. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Plant Systems There are 3 main plant systems: • Reproductive – this is the flower structure (in flowering plants) • Transport – this is the stem and roots and their xylem and phloem • Energy – this is the leaf and other areas of photosynthesis. TAKS Review, Objective 2 Leaf Tissue – What happens where? TAKS Review, Objective 2 NEXT – Ecology and the Environment TAKS Review, Objective 2