* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Chpt. 24 Evolutn Show 5 Origin Species
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
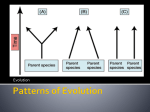
Mom, Dad… There’s something you need to know… I’m a MAMMAL! Origin of Species Chpt. 24 “That mystery of mysteries…” Darwin never actually tackled how new species arose… Both in space and time, we seem to be brought somewhat near to that great fact —that mystery of mysteries— the first appearance of new beings on this Earth. Macroevolution macroevoluti macroevolu macroevo speciation speciati specia spec speciation - origin of a new species KEY TO MACROEVOLUTION!! Anagenesis = one species transforming into one other species No biological diversity created speciation = origin of a new species Cladogenesis = one species transforming into more species Biological diversity created speciation = origin of a new species potential to interbreed produce viable offspring So…what is a species? Biological species concept defined by Ernst Mayr population whose members can interbreed & produce viable, fertile offspring reproductively compatible Distinct species: songs & behaviors are different enough to prevent interbreeding Eastern Meadowlark Western Meadowlark Question How many species of African Violets are here? What factors/ barriers can isolate gene pools? mixing What factors isolate gene pools? What factors isolate gene pools? What factors isolate gene pools? Habitat Isolation allopatric geographic separation What factors isolate gene pools? Temporal Isolation Temporal isolation Species that breed during different times of day, different seasons, or different years cannot mix gametes sympatric reproductive separation Eastern spotted skunk (L) & western spotted skunk (R) overlap in range but eastern mates in late winter & western mates in late summer What factors isolate gene pools? Behavioral Isolation Blue footed boobies mate only after a courtship display unique to their species reproductive isolation What factors isolate gene pools? Behavioral Isolation QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. reproductive isolation What factors isolate gene pools? Mechanical Isolation sympatric speciation? Even in closely related species of plants, the flowers often have distinct appearances that attract different pollinators. These 2 species of monkey flower differ greatly in shape & color, therefore cross-pollination does not happen. Plants What Animals factors isolate For many insects, male & gene female sex organs of closely related species do fit together, preventing pools? not sperm transfer sympatric speciation? QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Mechanical Isolation lack of “fit” between sexual organs: hard to imagine for us… but a big issue for insects with different shaped genitals! What factors isolate gene pools? Gametic Isolation sympatric speciation Gametic isolation Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize eggs of another species mechanisms biochemical barrier so sperm cannot penetrate egg receptor recognition: lock & key between egg & sperm chemical incompatibility sperm cannot survive in female reproductive tract Sea urchins release sperm & eggs into surrounding waters where they fuse & form zygotes. Gametes of different species— red & purple —are unable to fuse. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. What factors isolate gene pools? Reduced Hybrid Viability What factors isolate gene pools? Reduced Hybrid ex. mules Fertility Reduced hybrid fertility Even if hybrids are vigorous they may be sterile chromosomes of parents may differ in number or structure & meiosis in hybrids may fail to produce normal gametes Mules are vigorous, but sterile Horses have 64 chromosomes (32 pairs) Donkeys have 62 chromosomes Mules have 63 chromosomes! (31 pairs) What factors isolate gene pools? Hybrid F1 fine, subsequent… no good breakdown Hybrid breakdown sympatric speciation? Hybrids may be fertile & viable in first generation, but when they mate offspring are feeble or sterile In strains of cultivated rice, hybrids are vigorous but plants in next generation are small & sterile. On path to separate species. =Allopatric Speciation ex. Adaptive radiation ex. Adaptive radiation ex. Adaptive radiation ex. Adaptive radiation ex. Adaptive radiation ex. Adaptive radiation ex. Adaptive radiation Polyploidy 2N TEMPO 4N of evolutio n =Sympatric Speciation Polyploidy 2N BIG changes occur b/c of 4N the accumulatio n of small changes =Sympatric Speciation GRADUALISM Polyploidy TEMPO 2N of evolutio n 4N =Sympatric Speciation Polyploidy Big changes 2N as it “buds” from parent species, few changes after that 4N =Sympatric Speciation Stephen J. Gould how did we differentiate ???????? change in rate & timing of developmental events in various parts of the body how did we differentiate ???????? If these genes are altered, the timing of development and rate will be altered within the species change in rate & timing of developmental events in various parts of the body change in rate & timing of developmental events in various parts of the body how did we differentiate ???????? If these genes are altered, the timing of development and rate will be altered within the species QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Clusters of genes, involved in the regulation of development of animals, 1983 -Dr. Thomas Kaufman Indiana University discovered QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Evolved in the paleozoic era If mutated… OOPS QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. antennapedia, a mutation of the Hox Gene that turns the antenna of a fly into a leg. Clusters of genes, that determine where limbs and other body segments will grow in a developing fetus When these genes are altered, positioning varies Clusters of genes, provide positional info in the embryo When these genes are altered, positioning varies Clusters of genes, provide positional info in the embryo So, if we are connected, how did we different iate ??? Evolution is not the survival of the fittest. Rather it is the survival of the just good enough. What drove Human Evolution? QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=124906102 Summary Be able to discuss the main theories of what is a “species”. Know various reproductive barriers and examples. Summary Know allopatric and sympatric speciation. Be able to discuss gradualism and punctuated equilibrium theories. Summary Recognize various ideas about the origin of evolutionary novelties.