* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Child Development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
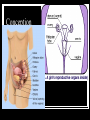
Child Development Chapter 5: Prenatal Development Section 5-1 The Developing Baby Pipe Cleaners With your pipe cleaner, make something to represent your feelings about learning about sexuality and conception in class. Bell Work Read p. 141 Answer these questions on your own paper: Why would hearing the baby’s heartbeat be significant for both parents? What other experience of the baby would be exciting to them? Why might hearing the heartbeat be especially moving for the father? Objectives Distinguish among the three stages of pregnancy Describe the prenatal development during each stage of pregnancy Explain what changes affect a woman during each stage of pregnancy Conception TPS Why is it important to understand how conception takes place? Period of the Zygote Lasts about 2 weeks Zygote- fertilized egg Zygote travel down fallopian tube Attaches itself to the lining of the uterus Lining provides nourishment At the end of this period the zygote is only the size of a pin head Period of the Embryo 3rd-8th weeks of pregnancy Embryo: the developing baby Grows rapidly The mass of cells develop into all the major systems of the human body Brain begins to take control of these systems Amniotic Fluid forms Placenta develops Umbilical Cord forms Bell Work p. 144- Health Tip Answer questions on own paper to turn in Period of the Fetus 8th week until birth- about 40 weeks 4th-5th month mother begins to feel baby movesensations are called “quickening” Fluid grows as fetus grows until just before birth when fluid begins decreasing Baby is swallowing it 7th month- baby capable of living outside womb but only with great medical help 8th and 9th month- organs become ready to survive on their own Fetus can- suck its thumb, cough, sneez, yawn, hiccup, and even cry Preparing for Birth Baby’s weight begins to shift down in 9th month- “lightening” Fetus is turned upside down in mother’s pelvis Less active Muscles of the uterus and abdomen can be stretched up to 60 times their original size! Return to original size in about 6 weeks after pregnancy. Section 5-2 A closer Look at Conception Genetic Package Each person inherits characteristics from parents Chromosomes: tiny threadlike particles in the nucleus of every cell Human babies receive 46 at conception- 23 pairs Each chromosomes has thousands of genes: the units that determine inherited characteristics For every inherited characteristic a person receives two copies of a gene- mother and father Dominant Gene: stronger Recessive Gene: weaker Making a Unique Person Family often times look alike because of the gene combinations Sex of a child is also determined at conception Two types of sex chromosome: X and Y Egg cells contain X Sperm cells contain wither X or Y Multiple Births Identical Twins: Fertilized egg divides into two separate babies Fraternal Twins: two eggs are released at the same time and both are fertilized 2.5% of births are multiple births More than 2 babies is even more rare Most of the time multiple births (more than 2) results from treatment of infertility: the inability to become pregnant Infertility Not all people are able to become pregnant 1st step: Doctor evaluates both parent’s help to determine cause Fertility drugs may be prescribed if the cause is eggs are not released every month Several drawbacks: serious side effects, multiple births, etc Options for Infertility After treatment for infertility some people are still not able to conceive Some options: Adoption Artificial Insemination: sperm injected into woman’s uterus In vitro Fertilization: Egg is fertilized outside body and then placed in the woman’s uterus Ovum Transfer: egg from female donor then fertilized Surrogate Mother