* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
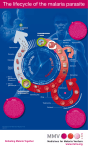
Eradication of Malaria • So why did the campaign fail? • 1) Insecticides (DDT) – Environmental damage! Pesticide Resistance • Rapid Reproduction • Selection DDT Pesticide Resistance • Rapid Reproduction • Selection DDT Eradication of Malaria • 2) Plasmodium – Wide use of chloroquine has led to drug resistant strains! Eradication of Malaria • 3) Social/Political Reasons – Emerging nations in Africa were trying to be free from external (Western European nations) domination; much of the monetary resources stopped flowing in! There are some general genotypes that are resistant to malaria • Genetic resistance to Plasmodium • 2 examples Duffy Blood Group • Noticed in military groups in Vietnam. • African Americans had less severe cases or no cases of malaria! Genetic Resistance • Plasmodium vivax • Duffy blood groups – Proteins on cell surface – 3 alleles • A Dominant • B Dominant • y recessive A= B= y = no proteins Genetic Resistance • Plasmodium vivax • Duffy blood groups – Proteins on cell surface – 3 alleles A= B= y = no proteins By • A Dominant • B Dominant • y recessive AA BB AB Ay yy Genetic Resistance • yy genotype has advantage – P. vivax malaria resistance – Only advantageous if P. vivax malaria endemic • 40% people of W. African decent • 0.1% people of non-African decent • P. vivax keeps the allele common in Africa. Genetic Resistance • Sickle celled anemia • Codominant trait (Allele “A” and “B”) – AA have sickle celled anemia – AB have both types of cells • Sickle cells don’t support species of Plasmodium well. • Resistance to infection Genetic Resistance • AA selected against – Sickle celled anemia • AB selected for – Both sickle and normal cells • BB selected against – Normal cells • If malaria not endemic, what alleles will be selected for? Against? • Allele for sickle cells maintained in the population even though strongly disadvantageous to have both alleles. Genetic Resistance Sickle Celled Anemia • In the US, 10% of African Americans have this allele! Other forms of Resistance to Malaria • Babies get antibodies from their moms breast milk; they are protected until weaned. • Once weaned becomes susceptible again! • What you need to have malaria spread within a population! Epidemiological Models Habitat Behavior Infected People contact Mosquitoes contact Source of Plasmodium Uninfected People Source of New Hosts Climate Habitat Food Breaking the Chain Habitat Behavior Infected People contact Mosquitoes contact Source of Plasmodium Uninfected People Source of New Hosts Climate Habitat Food Eliminating Mosquitoes • Mosquito Life Cycle Eliminating Mosquitoes Eliminating Mosquitoes • Destroy habitat • Insecticides • Biological control Eliminating Mosquitoes • • • • Destroy habitat Insecticides Biological control Why don’t these methods work? Pesticide Resistance • Rapid Reproduction • Natural selection Getting rid of the source of Plasmodium Getting rid of the source of Plasmodium • Drug treatment • Transgenic mosquitoes Getting rid of the source of Plasmodium • Drug treatment • Transgenic mosquitoes • Why don’t these work? Getting rid of the source of Plasmodium • Drug treatment • Transgenic mosquitoes • Why don’t these work? – Availability of drugs • Money • Medical staff – – – – – Recrudescense Drug resistance Reservoir hosts? Transgenic mosquitoes not a reality Expensive How can we protect the uninfected population? • Vaccines • Prophylactic drugs How can we protect the uninfected population? • Vaccines • Prophylactic drugs • Why don’t these work? How can we protect the uninfected population? • Vaccines • Prophylactic drugs • Why don’t these work? – Vaccines unsuccessful – Prophylactic drugs expensive – Prophylactic drugs unpleasant How can we prevent contact between people and mosquitoes? • • • • • Insecticides Mosquito nets Long clothing Behavior Avoid mosquito habitat • Screens on houses How can we prevent contact between people and mosquitoes? • • • • • Insecticides Mosquito nets Long clothing Behavior Avoid mosquito habitat • Screens on houses • Why don’t these work? How can we prevent contact between people and mosquitoes? • • • • • Insecticides Mosquito nets Long clothing Behavior Avoid mosquito habitat • Screens on houses • Why don’t these work? – Money – Availability of materials – Human behavior difficult to change • "Everything about malaria is so molded by local conditions that it becomes a thousand epidemiological puzzles." Hackett (1937) Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment • Prevention – insecticide-treated materials – vector control measures • indoor spraying • larvicide • environmental management Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment • Prevention – insecticide-treated materials – vector control measures • indoor spraying • larvicide • environmental management • Prevention of malaria in pregnancy Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment • Prevention – insecticide-treated materials – vector control measures • indoor spraying • larvicide • environmental management • Prevention of malaria in pregnancy • Monitoring for epidemics – Rapid response Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment • Prevention – insecticide-treated materials – vector control measures • indoor spraying • larvicide • environmental management • Prevention of malaria in pregnancy • Monitoring for epidemics – Rapid response • New methods and tools Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment • Prevention – insecticide-treated materials – vector control measures • indoor spraying • larvicide • environmental management • Prevention of malaria in pregnancy • Monitoring for epidemics – Rapid response • New methods and tools • Improvement in existing tools through research and development Roll Back Malaria (RBM) Strategy • Early diagnosis and prompt treatment • Prevention – insecticide-treated materials – vector control measures • indoor spraying • larvicide • environmental management • Prevention of malaria in pregnancy • Monitoring for epidemics – Rapid response • New methods and tools • Improvement in existing tools through research and development • Coordinated action through establishing partnerships that utilize an optimal mix of measures adapted to local situations.