* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Excretory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
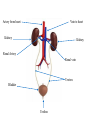
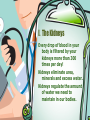
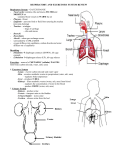
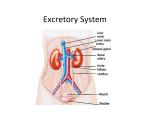
How Our Body Eliminates Cellular Wastes Excretion When proteins are broken down into amino acids, during digestion, they travel to the liver to be stored. Excess amino acids are converted to glucose, glycogen, or fat. This conversion produces a toxic substance called ammonia, which when combined with CO2, forms urea. Although Urea is safe to travel in the blood stream, it still needs to be expelled from the body (a build up of urea in the body can be toxic). Excretion It is the role of the excretory system to remove urea and other waste products, such as; water and CO2 (products of cellular respiration). The removal of waste products from the body is referred to as EXCRETION. Excretory System – removes excess water, H2O, urea, carbon dioxide, CO2, and other wastes from our blood. Kidneys – filter out excess water and urea Lungs – filter out carbon dioxide, CO2, from the blood. Skin – excretes water, as sweat, which contains some trace chemical wastes, including urea. Vein to heart Artery from heart Kidney Kidney Renal Artery Renal vein Ureters Bladder Urethra Kidneys – filter wastes and excess water from the blood. Ureters – tubes that take urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. Urinary Bladder – a sack that stores urine. Urethra – small tube that leads urine out of the body. I. The Kidneys Every drop of blood in your body is filtered by your kidneys more than 300 times per day! Kidneys eliminate urea, minerals and excess water. Kidneys regulate the amount of water we need to maintain in our bodies.