* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Fatty Acids
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
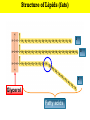
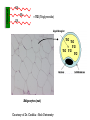
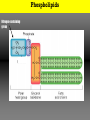
Lipids (fats) Main Function: long-term energy storage 2 Fats/ oils Which are made of Special Feature: contain more energy per gram than 3 4 any other biological molecule (9 cal/g) Nucleic acids Groupings: Mostly C and H Proteins atoms (hydrocarbons) (e.g., DNA/RNA) Which made of Types: 1.are Fats and Glycerol & 3 Fatty Acids which contain Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen main function ENERGY STORAGE long-term Which are made of oils 3. Steroids 2. Phospholipids Nucleotides which contain Carbon, hydrogen oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus main function Amino Acids which contain Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, main function CATALYSIS ENCODING & HEREDITARY STRUCTURE Plant oils (liquid @ room temp INFORMATION /SUPPORT Animal fat (solid @ room temp) Structure of Lipids (fats) 1 2 3 Glycerol Fatty acids Glycerol FA FA FA = TG (Triglyceride) Lipid droplet TG TG TG TG TG TG Adipocytes (rat) Courtesy of Dr. Ceddia – York University Making and Breaking Lipids (fats) Fats and oils are called triglycerides because of their structure What functional groups are present on the glycerol and fatty acid molecules? Ester linkage Hydrolysis Condensation Synthesis + 3 H2O Saturated Unsaturated Polyunsaturated # of double bonds between carbons Orientation State at Room Temp. Origin Which are better for you? Example Types of Fatty Acids Types of Fatty Acids Poly Saturated Unsaturated unsaturated # of Double Bonds between Carbons None (contains maximum # of H atoms) At least one double bond between carbon atoms Several double bonds Types of Fatty Acids Fewer hydrogens – “unsaturated” Types of Fatty Acids Poly Saturated Unsaturated unsaturated Orientation Straight of Fatty chains Acids Kinks / Kinks / bends at bends at the double the double bonds bonds Types of Fatty Acids CH2-CH BEND DUE TO DOUBLE BOND Types of Fatty Acids Poly Saturated Unsaturated unsaturated Examples butter, lard olive oil, vegetable oil, peanut oil, canola oil Types of Fatty Acids Trans Fat Taking a perfectly good fat and making it bad! Addition of hydrogen atoms to the acid, causing double bonds to become single ones. (unsaturated becomes saturated) LDL HDL Phospholipids Fat derivatives in which one fatty acid has been replaced by a phosphate group and one of several nitrogencontaining molecules. an important part of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) Phospholipids Nitrogen-containing group Phospholipids The phospholipid can also be represented as: Polar Head – hydrophilic (water-loving) Non-Polar Tails (fatty acids) – hydrophobic (water-hating) Steroids Steroids consist of 4 fused carbon rings Testosterone Cholesterol • Precursor for other steroids • Component of animal cell membranes • Contributes to atherosclerosis