* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hydrogen Bonds
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
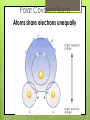
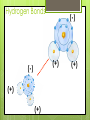
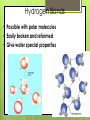
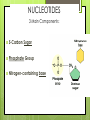
Chemistry of Life How small is an atom? Placed side by side, 100 million atoms would make a row only about 1 centimeter long About the width of your little finger Atoms- basic unit of matter Smallest particles of elements Protons: Neutrons: Electrons: Charge + none - Weight Yes Yes No Location Nucleus Nucleus Orbitals Elements Cannot be reduced to simpler components Isotopes Atoms of the same element that differ in their numbers of neutrons All isotopes of that element still have the same properties When will atoms react? To gain Electrons To lose Electrons To share electrons Molecules 1. Combinations of atoms 2. Joined by chemical bonds - covalent Types of Chemical Bonds Ionic Bonds – gain or lose e- Covalent Bonds – share e- Polar Non-polar Hydrogen Bonds - general attraction between partial charges of two different molecules Ionic Bonds : Losing or Gaining NaCl e- Covalent Bonds: Share Electrons Non-Polar Covalent: neither nucleus exerts more pull on shared electrons Polar Covalent Bond Atoms share electrons unequally Hydrogen Bonds (-) (+) (-) (+) (+) (+) Hydrogen Bonds • Possible with polar molecules • Easily broken and reformed • Give water special properties Cohesion vs. Adhesion Cohesion – the attraction between molecules of the same substance Adhesion – attraction between molecules of different substances Cohesion Water is extremely cohesive b/c of H bonding Adhesion Water – More… Found to be part of a solution – where one or more substances are evenly distributed in another substance Solute – the substance that is dissolved Solvent – the substance in which the solute is dissolved Still more about H2O Acids, Bases, and pH pH – determined by the concentration of H+ ions H2O H+ + OH - A water molecule can react to form ions pH Acid Solutions – contain more H+ ions (pH < 7) Base Solutions – contain more OH- ions (pH>7) Organic Compounds (C) Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Proteins Acids Group Name Chemical Composition Carbohydrate s C:H:O 1:2:1 ratio Examples Function in Living Things Monosaccharide s- glucose, fructose Disaccharide – sugar Polysaccharide – starch, cellulose Storing energy Structure in plants Lipids 3 fatty acids 1 glycerol Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Store energy Pigments Cell Membrane Messages in body Proteins Amino acids Enzymes Collagen Antibodies Structural component Chemical reactions Nucleic acids Nucleotides DNA RNA Hereditary info Enzymes and messages Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fats NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids include RNA and DNA RNA- Ribonucleic Acid DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid Polymers made up of repeating monomers called nucleotides. NUCLEOTIDES 3 Main Components: 5-Carbon Sugar Phosphate Group Nitrogen-containing base Nucleotides: Important Energy Storage Molecules ATP: acts like cell’s battery, providing energy for most activities.