* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Water Soluble Vitamins
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
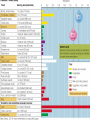
Water Soluble Vitamins The “supporting” cast Vitamins in general • • • • vital individual units assist enzymes with the release of energy measured in micrograms (ug) or milligrams (mg) • organic – can be destroyed by heat, UV, oxygen • available in food • bioavailability – quantity and • digestion efficiency • nutrition status • other foods • food preparation • source Solubility • water soluble – 8 B vitamins – vitamin C • fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K Water Soluble Vitamins B, C • found in water parts of food • • • • – easily destroyed or minimized by certain cooking processes move directly to blood freely circulate excesses are removed by kidney – too many can overwhelm the system regular intake Fat Soluble • • • • • A, D, E, K found in fats and oils enter the lymph, then the blood held in fatty tissues remain in fat storage may reach toxic levels Essential and Harmful Too much: vitamin A – headaches, fatigue vitamin D – weakness, calcium in arteries vitamin E – increased cholesterol levels Blindness: vitamin A deficiency Pellagra: niacin (B vitamin) deficiency Rickets: vitamin D deficiency B Vitamins • thiamin (B1) – coenzyme in energy metabolism – whole grains • riboflavin (B2) – energy metabolism – milk producst Enzyme Coenzyme Vitamin CD A Vitamin Coenzyme Enzyme B Vitamins • niacin – energy metabolism – milk, eggs, meat, fish • biotin – fat synthesis, amino acid metabolism, glycogen synthesis – widespread in food B Vitamins • pantothenic acid • • – energy metabolism – widespread in food vitamin B6 – amino acid and fatty acid metabolism – meat, fish, potatoes folate – folic acid – DNA synthesis and new cell formation – fortified grains, leafy vegetables B Vitamins • Vitamin B12 – closely related to folate • nerve cell maintanence – each are dependent on each other – animal products B Vitamins • work together in energy metabolism – energy releasing reaction – build cells – dependent on each other Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Vitamin C: Ascorbic Acid • antioxidant – defends against free radicals • unstable and reactive (free electron) • vitamin C sacrifices an electron, making substance stable • cofactor – in collagen formation • structural protein Vitamin C • cure for the common cold – controversial – does deactivate histamine • may help in preventing cancer, heart disease, cataracts – difficult to study Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Vitamin B and C Recommendations VITAMIN RDA UPPER LEVEL thiamin (B1) riboflavin (B2) niacin biotin pantothenic acid vitamin B6 folate (folic acid) vitamin B12 vitamin C smokers 1.1-1.2 mg 1.1-1.3 mg 14-16 mg 30ug 5 mg 1.3 mg 400 ug 2.4 ug 75-90 mg + 35 mg none none 35 mg none none 100 mg 1000 ug none 2000 mg