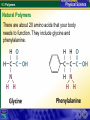
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9.3 Polymers - Central Lyon CSD
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Natural product wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup