* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antiretroviral Agents presentation
Tablet (pharmacy) wikipedia , lookup
MTOR inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of HIV-protease inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
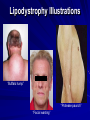
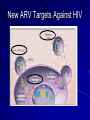
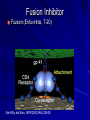
Antiretroviral Pharmacology Dr Njagi Lilian, M.B.Ch.B, MSc. TID 2009 UON INTRODUCTION Retroviruses; A retrovirus is an RNA virus that is replicated in a host cell via the enzyme reverse transcriptase to produce DNA from its RNA genome. The DNA is then incorporated into the host's genome by an integrase enzyme. The virus thereafter replicates as part of the host cell's DNA. Retroviruses are enveloped viruses that belong to the viral family Retroviridae. General characteristics; Envelope: RNA: Two single-strand linear RNA molecules per virion Proteins: gag, protease(PR), pol and env. Reverse transcriptase (RNA to DNA); Virus classification Group: Group VI (ssRNA-RT) Family: Retroviridae Genera Subfamily: Orthoretrovirinae Alpharetrovirus Betaretrovirus Gammaretrovirus Deltaretrovirus Epsilonretrovirus Lentivirus Subfamily: Spumaretrovirinae Spumavirus Antiretroviral Classes NRTIs (Nucleoside OR Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors) Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors) Nucleoside PIs (Protease Inhibitors) Fusion Inhibitors Chemokine Receptor Antagonists Integrase Inhibitors NNRTIs (Non- Mechanism of Action of ARVs Integrase Inhibitor Fusion Inhibitor & Chemokine Receptor Antagonist NNRTI NRTI Illustration by David Klemm Protease Inhibitor Antiretroviral Drug Approval: Maraviroc 1987 - 2007 FPV DRVRaltegravir FTC ATV TPV T-20 20 15 RTV IDV NVP 3TC SQV 10 EFV TDF LPV/r ABC NFV APV DLV d4T 5 AZT ddI ddC 0 1987 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2006 NRTIs Mechanism of Action Nucleoside analogs (like AZT below) Analog of thymidine, cytosine, adenine, or guanine Triphosphorylated inside lymphocytes to active compound Incorporate into the growing HIV viral DNA strand by reverse transcriptase(competitively inhibits reverse transcriptase). Nucleotide analog Currently only tenofovir (TDF) Does NOT need to be tri-phosphorylated only di-phosphorylated to active compound After incorporation of the NRTI, viral DNA synthesis will be terminated. NRTI Class Toxicities Lactic Acidosis – Damage to mitochondria in cells – Elevated lactate, low pH/bicarbonate, N/V, shortness of breath, if untreated can lead to death Hepatomegaly with Steatosis – Build up of fat droplets inside liver cells – Enlarged liver NRTIs Drug Standard Dose* Dosage forms Common Side Effects Metabolism/ Elimination Zidovudine (ZDV/AZT) Retrovir 300mg bid* 300mg tab, 100mg cap, iv, oral soln Fatigue, malaise, HA myalgia, anemia, GI Renal Lamivudine (3TC) Epivir 150mg bid* or 300mg qd 150, 300mg tab, oral soln Well tolerated Renal Emtricitabine (FTC) Emtriva 200mg qd* 200mg cap Well tolerated Renal Didanosine (ddI) Videx 400mg EC qd ( 60kg) 250mg EC qd (<60kg)* 125,200,250, 400mg cap, pwdr for soln Pancreatitis, peripheral neuropathy, LA/HS Renal •Note: Lactic acidosis can occur with any NRTIs *dose reduce for renal dysfunction NRTIs Drug Standard Dose* Dosage forms Common Side Effects Stavudine (d4T) Zerit IR 40mg bid ( 60kg) 30mg bid (<60kg) * 15,20,30,40 mg cap,oral soln Peripheral neuropathy, Pancreatitis, LA/HS, Lipoatrophy, facial wasting Abacavir (ABC) Ziagen 300mg bid, 600mg qd 300mg tabs, oral soln hypersensitivity Hepatic by alcohol dehydrogenase and glucuronyl transferase Tenofovir (TDF) Viread 300mg qd* 300mg tabs Few SEs, renal toxicity Renal *dose reduce for renal dysfunction Metabolism/ Elimination Renal NRTI Combinations Drug Standard Dose* Dosage forms Lamivudine/ Zidovudine (COM) Combivir 1 Tablet bid * 150/300mg tabs Abacavir/Lamivudine/Zidovudine (TZV) Trizivir 1 Tablet bid* 300/150/300mg tabs Tenofovir/Emtricitabine Truvada 1 Tablet qd* 300/200mg tabs Abacavir/Lamivudine Epzicom 1 Tablet qd* 600/300mg tabs Tenofovir/Emtricitabine/Efavirenz Atripla 1 Tablet qd* 300/200/600 mg tabs *dose reduce for renal dysfunction Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) These agents directly bind to reverse transcriptase to inhibit transcription NNRTIs do not require phosphorylation to be active RT NNRTIs Drug Standard Dose Dosage forms Common AEs Metabolism Delavirdine (DLV) Rescriptor 400 mg tid 100mg tab, 200mg cap Rash Potent CYP3A inhibitor; 3A4 substrate Nevirapine (NVP) Viramune 200 mg qd x 14 d then 200 mg bid 200mg tabs, Oral susp Rash (SJ), hepatotoxicity CYP3A inducer, auto inducer; 3A4, 2B6 substrate 50, 100, 200mg cap, 600mg tab Vivid dreams, drowsiness or insomnia, rash (SJ), hyperlipidemia CYP3A, 2B6 inducer; 2B6, 3A4 substrate Efavirenz* 600 mg qhs (EFV) Sustiva *Pregnancy Class D Second Generation NNRTIs ETRAVIRINE (ETR) Diaminopyrimidine (DAPY) compound; flexible chemical structure In vitro EC50 1.4-4.8 nM (wild-type HIV-1); 3.5 uM (HIV2) In vitro activity against NNRTI-resistant virus Metabolism: inducer + substrate of CYP 3A4 and others Drug interactions: do NOT use with other NNRTI, unboosted PI, ATV/r, FPV/r, TPV/r, RIF, antisz meds; use with caution LPV/r; OK with DRV/r, SQV/r, methadone Package Insert 2008 FDA approved 1/08 Progress on 2ng gen NNRTI (11/08/08 xvii international Aids conference) TMC278 (rilpivirine; Tibotec),Most advanced stage of development(phase2b). Very few patients experienced virologic failure with resistance-associated mutations.Most commonly observed mutations were 184V and 134k but not sure how many mutations are sufficient to confer resistance to TMC287. IDX899 ; Potent in vitro activity for both wild-type and NNRTI-resistant HIV-1, has a high barrier to resistance. RDEA806 phase 2a data presented on this NNRTI with an in vitro high barrier to resistance and activity against isolates resistant to current NNRTIs. It may be important that its metabolic pathway does not appear to have any significant effect on other drugs. Previous work in healthy volunteers had shown good bioavailability and tolerability. Protease Inhibitors (PIs): Mechanism of Action Protease enzyme cleaves HIV-1 Protease HIV precursor proteins (gag/pol polyproteins) into active proteins that are needed to assemble a new, mature HIV virus. PIs bind to protease preventing the cleavage and inhibiting the assembly of new HIV viruses PI X HIV Lipids, Insulin Resistance (Lypodystrophy) Hypercholesterolemia – Usually hypertriglyceridemia, can have increased LDL and decreased HDL – Treat with Fibric acid derivatives and certain HMGCoA reductase inhibitors Insulin Resistance – Treat with diet/exercise, metformin, TZDs, insulin, sulfonylureas Lipodystrophy Illustrations “Buffalo hump” “Protease paunch” “Facial wasting” Use of Ritonavir as a P450 Inhibitor with PIs Protease Inhibitors Standard Dose Dosage Forms Metabolism Common AEs** Saquinavir (Invirase) (1) 1000/ rtv 100 bid or 1600/ rtv 100 qd 200mg caps, 500mg tabs 3A, Pgp substrate; weak 3A inhibitor GI intolerance Nelfinavir (Viracept) (1) 1250 bid, 750mg tid 250mg, 625mg tabs, 50mg/g oral pwdr 2C19 (M83A) substrate; weak 3A inhibitor Diarrhea Lopinavir/ 400/100 bid ritonavir (Kaletra) (1,2) 200/50 mg tabs, 80/20mg/5mL soln 3A, Pgp substrate; 3A inhibitor; 2C9, 2C19 inducer Dyspepsia, Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence Indinavir 800/ rtv 100 bid, (Crixivan) 800mg tid (1-when taken with rtv) 100, 200, 333, 400mg caps 3A, Pgp substrate; weak 3A inhibitor Nephrolithiasis Drink 7-8 glasses of water per day; hyperbilirubinemia (1) Take with Food (2) Must be refrigerated ** All PIs except atazanavir can increase lipids and cause insulin resistance Protease Inhibitors Standard Dose Dosage Forms Metabolism Atazanavir (Reyataz) (1) 400qd or 300/ rtv 100qd 100, 150, 200mg caps 3A substrate; 3A and UGT1A1 inhibitor Hyperbilirubinemia, PR prolongation Fosamprenavir (Lexiva) (1) 1400mg bid; 700/100 RTV mg bid; 1400/200 RTV mg qd 700mg tabs (Agenerase-APV liq available) 3A4, Pgp substrate; 3A4 inducer/ Inhibitor Rash, GI intolerance, caution with sulfur allergy Tipranavir (Aptivus) (1,2) 500/200 RTV mg bid 250mg caps 3A4, Pgp substrate; 3A4, inducer/ inhibitor??; Pgp inducer Hepatotoxicity, Increased bleeding caution with sulfur allergy Darunavir (Prezista) (1) 600/100 RTV mg bid 300mg tabs 3A4 substrate; 3A4 inhibitors Diarrhea, nausea, HA, nasopharyngitis Ritonavir (Norvir) (1,2) Used as a PK booster 100-200mg 100mg caps; 80mg/mL 2D6, 3A4, Pgp substrate; 3A4, Pgp inhibitor Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, GI upset (1) Take with Food (2) Must be refrigerated ** All PIs except atazanavir can increase lipids and cause insulin resistance Common AEs** Dose adjustments to consider Renally-eliminated NRTIs (except Abacavir) Adjust for CrCl <50 ml/min or dialysis Didanosine Emtricitabine Lamivudine Stavudine Tenofovir Zidovudine Hepatic Metabolism NNRTIs PIs Adjust for certain inducers, substrates, or inhibitors of P450 system Adjust for insufficiency Indinavir Fosamprenavir Atazanavir Avoid Amprenavir oral soln Foasmprenavir (+/- ritonavir) Tipranavir New ARV Targets Against HIV Fusion Inhibitor Fuzeon (Enfuvirtide, T-20) See Kilby and Eron, NEJM 2003;348:2228-38 Fuzeon : Enfuvirtide (T-20) FDA-approved fusion inhibitor; 36 AA peptide – Requires 106 steps to manufacture Dose: 90 mg sq bid side effects: – injection site rxn, hypersensitivity (rare) resistance: changes in gp41 (cell surface protein) HIV Tropism Chemokine Receptor Antagonists Marviroc (Selzentry®) CCR5 or CXCR4 receptors on cell surface Virus will bind to one of the 2 receptors – Some patients’ virus will bind to either receptor Marviroc blocks viral entry at CCR5 Dosed 300mg BID – 150mg BID with P450 inhibitors – 600mg BID with P450 inducers Integrase Inhibitors Raltegravir (Isentress™) Dosed 400mg BID (1 tab BID) No induction or inhibition on CYP450 enzymes or Pgp Metabolized by UGT1A1 (glucuronidation) – Only affected by drugs that inhibit or induce UGTs (ie, rifampin) Drug Interactions Antiretroviral Metabolism, Induction, and Inhibition Drug Substrate Inhibits Efavirenz 2B6, 3A4 Nevirapine 3A4, 2B6 Ritonavir 2D6, 3A4, Pgp 3A4, 2D6, Pgp Saquinavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4 Nelfinavir 2C19 (M83A4) 3A4 Amprenavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4 (in vitro) 3A4 (in vivo) Fosamprenavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4 (in vitro) 3A4 (in vivo) 3A4 2C9, 2C19, 1A2 Lopinavir/ritonavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4 Induces 3A4, 2B6 3A4 Atazanavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4, UGT, 1A2 Tipranavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4 Darunavir 3A4, Pgp 3A4 Maraviroc 3A4, Pgp 2D6 (at high doses only) Other enzymes Cytochrome P450: Non-Antiretrovirals Substrate Inhibitor Inducer 3A4 Macrolides,cyclosporine, CCB, statins, azoles, PDE5 inhibitors, aprepitant, midazolam, triazolam Cimetidine, Macrolides, FQs, SSRIs, CCB, azoles, aprepitant rifamycins, phenytoin, carbamazepine, St. John’s wort, aprepitant, garlic 2D6 Opiates, nortriptyline, amitriptyline, tramadol, trazodone, paroxetine, metoprolol, propranolol, carvedilol Haldol, SSRIs, cimetidine, amiodarone rifamycins, phenytoin, CBZ, St. John’s wort 1A2 Amitriptyline, clozapine, caffeine, clozapine, imipramine, R-warfarin, theophylline, proprnaolol FQs, azoles, macrolides, rifamycins, phenytoin, CBZ, smoking, St. John’s wort SSRIs, azoles, fluvastatin, omeprazole, topiramate rifamycins, CBZ, phenytoin 2C19 Omeprazole, phenytoin 2C9 S-warfarin, Amiodarone, SSRIs, sulfonylureas, phenytoin, azoles, amiodarone carvedilol Phenytoin, CBZ, rifammycins, aprepitant Protease Inhibitors and Acid Suppression Do Not combine Atazanavir and Proton Pump Inhibitors – May Combine ATV and Famotidine but dose adjustments are REQUIRED May use Indinavir with PPIs but ONLY if coadministered with RTV May use Fosamprenavir with Esomeprazole – Separate FPV from H2 blockers if used concomitantly Dose Adjustments Between ARVs Drug A Drug B Recommendation Tenofovir Didanosine Dose ddI as 250mg QD with TDF 300mg QD Tenofovir Atazanavir Use RTV 100mg QD with ATV + TDF Efavirenz (Nevirapine) Atazanavir Use RTV 100mg QD with ATV + EFV Efavirenz (Nevirapine) Fosamprenavir Use RTV with FPV Efavirenz (Nevirapine) Lopinavir/ritonavir Increase LPV/RTV to 3 tabs BID Important Drug Interactions Do NOT use Simvastatin, Lovastatin, Antiarrthymics, Midazolam, Triazolam, Ergot derivatives, Rifamin, St. Johns Wort, or Garlic with most PIs or DLV Do NOT combine Rifampin with PIs – LPV/RTV may be dose increased and combined with Rifampin – Conflicting data with EFV and NVP Use other P450 inducers with CAUTION when combining with PIs and NNRTIs Do NOT use Fluticasone or Alfuzosin with Ritonavir Caution with Azoles, Clarithromycin, Oral Contraceptives, Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Phenobarbital, Methadone, PDE5 inhibitors, Atorvastatin, Beta blockers, when combined with PIs Avoid Herbal Products with Known or Suspected Interactions When combining Protease Inhibitors, Often Dose Adjustments are Necessary Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Not widely used in the US Recommended in certain situations for PIs and NNRTIs What makes a drug a good candidate for TDM? When should TDM be performed for antiretrovirals?