* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
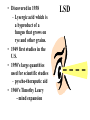
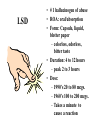
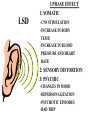
Hallucinogens • Any of several drugs called psychedelics, that produce sensations such as distortions of time, space, sound, color, and other bizarre effects. • LSD • Mescaline • Psilocybin (mushrooms) • MDMA (Ecstasy) • Discovered in 1938 – Lysergic acid which is a byproduct of a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. • 1949 first studies in the U.S. • 1950’s large quantities used for scientific studies – pyscho-theraputic aid • 1960’s Timothy Leary - mind expansion LSD LSD • # 1 hallucinogen of abuse • ROA: oral/absorption • Form: Capsule, liquid, blotter paper – colorless, odorless, bitter taste • Duration: 4 to 12 hours – peak 2 to 3 hours • Dose: – 1990’s 20 to 80 mcgs. – 1960’s 100 to 200 mcgs. – Takes a minute to cause a reaction • • • • • EFFECTS UNPREDICTABLE DEPEND ON DOSE, USER’S PERSONALITY, AND SETTING RAPID MOOD SWINGS HALLUCINATIONS MIS-PERCEPTIONS OF STIMULI – HEARING COLORSSEEING SOUNDS LSD 3 PHASE EFFECT 1: SOMATIC LSD -CNS STIMULATION -INCREASE IN BODY TEMP. -INCREASE IN BLOOD PRESSURE AND HEART RATE 2: SENSORY DISTORTION 3: PSYCHIC -CHANGES IN MOOD -DEPERSONALIZATION -PSYCHOTIC EPISODES -BAD TRIP LSD FLASHBACKS: Caused by a similar stimulus NOT a latent chemical reaction. DRUG TESTIING: Difficult to detectpasses out of system within 30 hours. TOLERANCE: Develops quickly, decreases if use is discontinued. LSD: Long Term Use • Psychiatric Illness • Disruption of personality LSD reduces the normal person’s ability to control emotional reactions-drug induced alterations of perception can be so intense, they overwhelm the individual’s ability to cope. Psilocybin Source: Mushrooms 1/200 as potent as LSD ROA: Oral Duration: 6 to 10 hours Effects: Similar to LSD Dose: Varies based on mushrooms and quantity consumed. Ketamine Rapid acting anesthetic -used in pediatric burn cases; dentistry -animal tranquilizer ROA: oral/inject/smoke/snorted Duration: 1 to 6 hours, 24 hours for full recovery Effects: numbness, respiratory depression, exaggerated sense of strength, sense of invulnerability, hallucinogen effects, paranoia, disassociative state PCP Rapid acting anesthetic used for animals ROA: smoke/oral/snort/inject Duration: Smoke-peak effect 15 minutes; Oral peak effect 2 hours Effects: bizarre and violent psychiatric reactions, agitation, disorganized thought, seizures, psychotic episodes, suicide. Only hallucinogen that elicits cravings Mescaline • From Peyote Cactus • Used by Native American Church • ROA: Oral • Duration: 10 hours – Peak effect 30 to 90 min. • Effects: – visual hallucinations – anxiety – stress reactions MDMA: Ecstacy Synthetic Hallucinogen/Amphetamine Similar to mescaline/methamphetamine ROA: Oral/inject/smoke Duration: 6 to 8 hours Effects: Confusion, depression, anxiety, sleep problems, muscle tension, increase body temperature MDMA: Ecstacy MDMA destroys seratonin receptors which are responsible for regulation of mood, aggression, sexual activity, and sleep. Prolonged use results in irreversible Parkinson disease like symptoms