* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
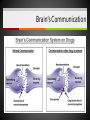
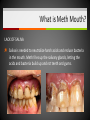
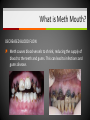
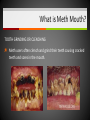
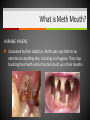
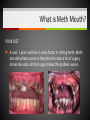
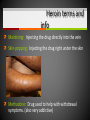
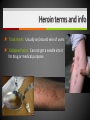
Unit 5 – Drugs & Drug Abuse Ms. Snyder How Drugs Affect the Brain FRONTAL LOBE Problem solving, planning, reasoning, organizing, attention, judgment, emotional responses, memory TEMPORAL LOBE Hearing, long-term memory PARIETAL LOBES Senses, perception, cognition, visual perception OCCIPITAL LOBES Visual processing, color recognition CEREBELLUM Balance, coordination, speech The most development of the frontal lobe is between the ages 15 and 22. Are you allowing drugs to hinder this important development?? A teen that uses drugs changes his or her brain, and that in turn changes their emotions, personality and values! Definitions Drug Addiction – A chronic, relapsing brain disease that is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences. It is considered a brain disease because drugs change the brain. They change its structure and how it works. Physical Dependence – body adapts to the drug and develops a tolerance. Your body becomes dependent on a substance or drug your cells cannot function without it. Definitions Psychological Dependence – is all in the mind. This is when you think you need the drug and cannot live without it. Your whole life revolves around getting the next dose. Withdrawal – drug specific physical or mental symptoms if drug use is abruptly ceased. Nausea, vomiting, headaches are the body telling you it needs more of the substances to return to its new (artificial) state of normalcy. Tolerance – requiring more of a drug to achieve certain effects. Brain’s Communication What is dopamine?? Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps control the brain’s reward and pleasure centers. Using addictive drugs flood the brain with dopamine as much as 10 times the normal level. The brain’s motivational center becomes reorganized. The priorities are shuffled and now the top priority is to find and use that substance. In this sense, the drug has essentially taken over the brain, and the addict is no longer in control of their behavior. What is dopamine?? Over time, the brain adjusts to the excess dopamine and decreases the amount of dopamine in the brain. This is why abusers eventually feel flat, lifeless, depressed, and are unable to enjoy things that previously brought them pleasure. Users must use more and more of the drug to achieve the same “high” and bring their dopamine function back to normal, an effect known as tolerance. ** However, addicts can recover. The brain has a remarkable ability to mend from drug use. Drug Scheduling Schedule I – Most dangerous with a high potential for abuse with potentially severe psychological or physical dependence. Heroin, LSD, Marijuana, Ecstasy, Peyote, Mescaline, Psilocybin, GHB Schedule II – High potential for abuse, less abuse potential than Schedule I drugs. Potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. Vicodin, Cocaine, Meth, Methadone, Oxycodone, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin, Codeine, Morphine, PCP Schedule III – Moderate to low potential Ketamine, Anabolic Steroids for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule IV – Low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Xanax, Valium, Ambien, Darvon Schedule V – Lower potential for abuse and Cough preparations with less than 200 contain limited quantities of certain milligrams of codeine or 100 milliliters narcotics. (Robitussin AC), Lyrica Definitions Paranoia: • An irrational fear or distrust of others – often drug induced Euphoria: • A feeling of intense well-being that may be followed by a “crash” or letdown. Flashbacks: a similar recurrence of the effects of a hallucinogenic drug • Flashbacks can happen at any time without warning – long after the drug use ends! Stimulants Stimulants - speed up the Central Nervous System (CNS) Examples: • Methamphetamines • Nicotine • Caffeine • Cocaine/Crack • Amphetamines What do stimulants do? Increases alertness and endurance Keep people awake Decrease appetite Produce feeling of well-being and euphoria Cocaine Cocaine is a white powder made from coca bush. The high feels so intense increase heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature seizures cardiac arrest death Then the crash feels so bad, that the person wants to use it again. Overtime it will change the way your brain works, teaching you to repeat the behavior. Crack A form of cocaine that has been processed to make a rock crystal that people smoke. The term “crack” refers to the crackling sound the rocks make when they are heated. Cocaine in its different forms A pile of Cocaine hydrochloride A pile of crack cocaine ‘rocks’. Bricks of cocaine, a form in which it is commonly transported. Interesting Facts Was Cocaine originally used in the making of Coca-Cola?? • The only known measure of the amount of cocaine in Coca-Cola was determined in 1902 as being as little as 1/400 of a grain (0.2 mg) per ounce of syrup. The actual amount of cocaine that Coca-Cola contained during the first twenty years of its production is practically impossible to determine. Today, Coca-Cola contains only caffeine and clinical cocaine use is restricted to a few surgical procedures. In 1914 the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act outlawed the use of cocaine in the United States. This law incorrectly referred to cocaine as a narcotic, and the misclassification passed into popular culture. As stated above, cocaine is a stimulant, not a narcotic. Methamphetamine A highly addictive drug. Meth provides a short-term feeling of euphoria and often leads to feeling of depression, paranoia, and delusions. Cooked with over-the-counter drugs in “meth labs”. Meth Labs Meth Lab Explosions What is Meth Mouth? LACK OF SALIVA Saliva is needed to neutralize harsh acids and reduce bacteria in the mouth. Meth fries up the salivary glands, letting the acids and bacteria build up and rot teeth and gums. What is Meth Mouth? DECREASED BLOOD FLOW Meth causes blood vessels to shrink, reducing the supply of blood to the teeth and gums. This can lead to infections and gums disease. What is Meth Mouth? TOOTH GRINDING OR CLENCHING Meth users often clench and grind their teeth causing cracked teeth and sores in the mouth. What is Meth Mouth? HORRIBLE HYGIENE Consumed by their addiction, Meth users pay little to no attention to anything else, including oral hygiene. They stop brushing their teeth and let bacteria build up in their mouths. What is Meth Mouth? POOR DIET A user’s poor nutrition is a key factor in rotting teeth. Meth also dehydrates users so they tend to crave a lot of sugary drinks like soda. All that sugar makes the problem worse. Amphetamines (Speed) People use to increase activity, boost alertness, and energy. When prescribed by a doctor, they can be relatively safe and effective. Stimulants have been abused as an “academic performance enhancement”. However, studies have found that they do not increase learning or thinking ability who are not diagnosed with ADHD. Caffeine Addictive and can can result in withdrawal symptoms when discontinued. Depressants Slow down the CNS – suppresses breathing and heartbeat. Commonly abused Depressants are: • • • • • Alcohol Barbiturates Tranquilizers Rohypnol GHB Depressants do what to the body? Relax muscles Relieve feelings of tension / worry Bring on sleep Slow down heart and breathing rates Lower blood pressure Alcohol The #1 most abused drug. Barbiturates Known as sedative-hypnotics, which generally describe their sleep-inducing anxiety-decreasing effects. • • • Small doses: the abuser feels drowsy, disinhibited, and intoxicated. Higher doses: the abuser is unable to be aroused (coma) and may stop breathing. Death is possible. Tranquilizers Minor tranquilizers: therapeutic treatment of anxiety disorders, alcohol withdrawal, seizures, insomnia, and muscle spasms (ex. Xanax, valium). Major tranquilizers: used to treat mental disorders, such as schizophrenia. Rohypnol (Roofies) Is referred to as the date rape drug. Slurred speech, muscle relaxation, loss of motor coordination. Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid (GHB) Also known as the date rape drug. Misused to cause amnesia. Hallucinogens Cause people to see images, hear sounds and feel sensations that seem real but are not, making it hard to communicate or think clearly. Hallucinations work by disrupting your nerve cells and neurotransmitter serotonin. By changing the normal, healthy structure of serotonin in the body hallucinogens twist and alter the way your brain processes your sense, feelings, and visual information, loosening your grip on reality. Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) Known as acid is one of the most potent mood-changing chemicals. Users often experience flashbacks, or recurrences of certain aspects of the drug experience. Often added to absorbent paper (blotter paper). LSD Blotter Paper and Stickers Phencyclidine (PCP) Distorts perceptions of sight and sound and produces feelings of detachment from the environment and self. Because the drug eliminates the sensation of pain, abusers may intentionally injure or even kill themselves. Symptoms: mimic schizophrenia, such as delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia. Psilocybin (Shrooms) A hallucinogenic chemical found in an edible mushroom. Causes severe anxiety and paranoia. DANGER: There is a similar looking mushroom that is deadly and often mistaken for Psilocybin. Ecstasy (MDMA) Acts as both a stimulant and psychedelic. Mainly affects brain cells that use the chemical serotonin. Interferes with the body’s ability to regulate temperature resulting in cardiovascular system failure. You can never be sure what you are getting!! Ketamine Distorts perceptions of sight and sound and makes the user feel disconnected and not in control. Unconsciousness and amnesia could occur. Peyote and Mescaline Peyote is a small, spineless cactus and the ingredient is the hallucinogen mescaline. K2/Spice A mixture of herbs and spices sprayed with a synthetic compound chemically similar to THC. Psychological effects include paranoia and panic attacks. It appears to be stored in the body for long periods of time and therefore the long-term effects on humans are not fully known. Narcotics (Opioids) Dulls the senses and relieves pain. Produces a well-being by reducing tension, anxiety, and aggression. Highly addictive because they change the chemistry of the brain; they decrease the perception of pain and alter the body’s reaction to pain. Narcotics (Opioids) Includes: oxycodone (oxycontin), morphine, heroin, hydrocodone (vicodin), codeine, percocet, methadone, opium, and more. THESE DRUGS ARE NOT MEANT TO BE TAKEN WITHOUT A DOCTOR’S PERMISSION AND MONITORING! Side Effects: Nausea, track marks, unconsciousness, confusion, addiction, death. Drugs Terms & Info Continued… When injecting substances through a needle a person is at risk of contracting: • • Hepatitis B HIV Heroin terms and info Mainlining: Injecting the drug directly into the vein Skin-popping: Injecting the drug right under the skin Methadone: Drug used to help with withdrawal symptoms. (also very addictive) Heroin terms and info Track marks: Usually on/around vein of users Collapsed Veins: Can not get a needle into it for drug or medical purposes Inhalants Substances that produce chemical vapors that induce psychoactive or mild-altering effects. • “Huffing” “Sniffing” or “Chroming” Side Effects: Dizziness, nosebleeds, euphoria, nausea, hearing loss, slurred speech, lack of coordination Inhalants cause brain damage by cutting off oxygen flow to the brain. Inhalants The hippocampus is a part of the brain that is responsible for memory. Someone who repeatedly uses inhalants may lose the ability to learn new things or carry on a simple conversation. Inhalants can kill you the first time you use them!! It can take up to 2 weeks for the chemical to completely pass from the body. 22% of inhalant users will die from Sudden Sniffing Death. Common Inhalants Aerosol sprays Correction fluid Adhesives and cements (rubber cement, plastic cement, etc.) Gasoline Insecticide Nail polish remover (acetone or similar chemicals) Paint or spray paint Paint thinner (turpentine similar chemicals) Air freshener Butane Canned air (compressed hydrofluorocarbons) Cassette player head cleaner Xylene markers Toluene Diethyl ether Freon Marijuana/Cannabis A mind altering (psychoactive) drug. THC is the main ingredient that produces the psychoactive effect. Short-term effects – changes in mood, impaired body movement Long-term effects – brain development, reduce thinking, memory, and learning functions Cannabis Facts and Info… Cannabis smoke contains more cancer causing chemicals than cigarettes smoke. Males who regularly use marijuana may experience • Lower levels of testosterone • Lower sperm productivity Females who regularly use marijuana may experience • • • Still births Low birth weights Similar condition to F.A.S. Marijuana Did You Know? Smoking one marijuana cigarette deposits approximately four times the amount of tar into the lungs than a filtered tobacco cigarette. Marijuana is considered a "gateway" drug, because it often leads to the use of other illegal drugs such as cocaine and heroin. Being in a room with marijuana smoke can cause a "contact high" from just breathing. Anabolic Steroids Synthetic male hormones (testosterone) used to build muscle and enhance performance. Addiction to steroids is different compared to other drugs of abuse, because users don’t become high when using. People who become addicted keep using despite bad effects on their bodies and lives. Anabolic Steroid Side Effects Both - Severe acne - Fluid retention - Weight gain Males - Shrinking of testicles - Reduced sperm count - Development of breasts Females - Facial hair Male-pattern baldness Deepened voice Change in menstrual cycle ** Enlarged heart, heart attack, stroke, kidney failure problems Resources At West Campus: Mrs. Disselhorst, Mrs. Reid, Mrs. Cooper At East Campus: Mrs. Eggert, Mr. Popovich At Both Campuses: Any of your teachers, school counselors, assistant principals, Officer Rewiako Resource in our town: Rosecrance 815-363-6132 National Institute on Drug Abuse: Get more facts about the science behind drugs and addiction Things to remember: Never let anyone buy you a drink unless you get it with them! Never let anyone prepare a drink for you unless you are there to watch them! Never leave your drink unattended/Bring it with you! You never know who could be watching! THE END!!