* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Survivors - Dr. Ian Curtis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
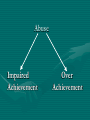
Psychiatric Impact of Childhood Sexual Abuse: Life on the Borderline Survivors of Abuse – Access to Justice Information Seminar, 14 May 2004 Ian Curtis MBBS FRANZCP FAChAM Borderland (author BV, with permission) The sand stings The Wind is Howling Of pain past. I know nothing The sand in my eyes Of pain present. I just exist Ask me who “I” am No answer. Gritting sand Prevents looking where The I is. Can’t be heard The Wind is Howling Lonely and worse. Isolate So as not to feel Contact causes hurt. The Wind is Howling When will I be Whole? (BV) Prevalence of Borderline Features • • • • General population Outpatient mental health clinics Psychiatric inpatient clinics Special Clinic Populations involving personality disorders 1-2% 10% 20% 30-60% The Damage Aetiology Early life Physical and Sexual Abuse, Neglect, Hostile Conflict, and early Parental Loss/Separation are more common in the Childhood histories. (Source: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual Mental Disorders, 4th Edition, p708) General Behaviours of the Borderline • • • • • Ambivalence Emptiness Anger Instability Impulsivity and Recklessness • Deliberate Self-Harm • Immaturity Frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment Ambivalence: alternating between extremes of idealisation and devaluation Pattern of unstable and intense interpersonal relationships alternating between extremes of idealisation and devaluation Identity disturbance: unstable self-image or sense of self Hopeless-Helpless: chronic feelings of emptiness Instability: affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood Anger Management Problems inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger Self-Harming: impulsivity in at least two areas that are potentially self-damaging (eg spending, sex, substance abuse etc) Suicidality: recurrent suicidal behaviour, gestures, threats, self-mutilating behaviour Psychotic Border: stress-related paranoid ideation or severe dissociative symptoms And Drug Abuse • • • • • • • Self-treating Fill emptiness Isolate interpersonally Pseudo-closeness “Control emotions” Obscure anger Self-harm Unique Difficulties Bipolarities Ambivalence Embraced Failure (Abandoned Hope) Abuse Impaired Achievement Over Achievement Vulnerability Transition to Adulthood Failed Stalled Over Compensated Adult Outcomes Serious Impairment Adult Success