* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pharmacokinetic & Pharmacodynamic of Ketamine in Pediatric
Survey
Document related concepts
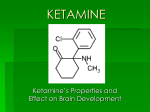
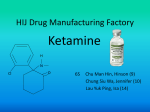
Transcript
Pharmacokinetic & Pharmacodynamic of Ketamine in Pediatric Patients Prepared by Nissreen A. Al Thaqafi M.Sc candidate Supervised by Iman Zaghloul Ph.D Abdulatif Al Dwailie Ph.D Hala Al Alem Ped. intensive Consultant Tuesday, June 1,2004 1 Outline Background Objective Methodology Study design Inclusion criteria and Exclusion criteria Procedure Work plan 2 Background of the study Pediatric patient frequently require procedural intervention which are uncomfortable and emotionally disturbing for children, and require substantial immobilization for optimal performance. 3 Background, cont’d Ketamine has been used in King Abdulaziz Medical City/King Fahad National Guard Hospital/PICU (KAMC/KFNGH) since June 2002 as a part of a regimen consisted of AtropineMidazolam and Ketamine (AMK). 4 ketamine 2-(o-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino) cyclohexanone 5 Rotatable 3D model S-(+)-ketamine R-(-)-ketamine 6 Background Phencyclidine derivatives Used as dissociative anesthetic It is commercially available as racemic mixture of two enantiomers R(-)ketamine and S(+)-ketamine. 7 1970: Ketamine officially released for clinical use in U.S. 1999: Ketamine becomes a schedule III substance under the CSA 8 Background Disadvantage: Emergence phenomena Increased cerebral blood flow Sympathomimetic cardiovascular effects Cholinergic salivary and bronchial gland secretion Advantage: No cardio-respiratory depressant effects produce significant analgesia 9 Background, cont’d Mechanism of action Non competitive NMDA glutamate receptor antagonism (functional and electro-physiologic dissociation between thalamus & limbic system) It antagonizes acetyl choline receptors It has a weak affinity for opioid receptors and possibly GABA receptors (The analgesic effect) 10 Background (cont.) It inhibits serotonin and dopamine reuptake. Inhibition of nerve growth factor and of voltage gated Na and K channels. 11 Pharmacokinetics of ketamine Three compartment open model t1/2α = 11 - 16 minutes t1/2β = 2 - 3 hours Vd ss = 3 L/kg Therapeutic range 0.7-2.2 ㎍/ml. Awakening occurs below 0.5 ㎍/ml. 12 Pharmacokinetics of ketamine Metabolism Metabolized by the hepatic microsomal system (CYP3A4, CYP2C9 and CYP2B6). N-demethylation ketamine norketamine (metabolite I) 13 Norketamine (NK) has 20-30% of the ketamine activity NK hydroxlyated to Hydoxynorketamine, conjugated with glucuronate and excreted in the urine. 14 Doses, Routes of Administration 15 Objectives Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ketamine in pediatric patients who requires sedation for short procedures at KAMC/KFNGH. Determination of the duration of analgesia which will be correlated to the measured concentrations in order to determine the minimum analgesic range. 16 Methodology 17 Study design Prospective cross sectional study of pediatric population undergo short stressful and/or painful procedure admitted to KAMC/KFNGH A total of 25 pediatric patients will be enrolled in the current study 18 Inclusion criteria 1. Age between 3 month and 12 years old. 2. Clinically and hemodynamically stable patients (ASA Physical Status ClassⅠ& ClassⅡ) 19 Exclusion criteria 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Known increased intracranial pressure Tumors of the CNS Severe pre-existing hypertension Hypersensitivity to any component of sedation regimen. Evidence of pulmonary disease Evidence of heart disease. ASA Physical Status Class III , Class IV and Class V Refuse to consent 20 Procedure A. Informed consent form B. NPO 4-6 hours before procedure. C. IV-access 21 Procedure D. Base line data A. B. C. D. E. Demographic data Past and present medical illness History of previous anesthesia Procedure indication and physical assessment Laboratory data will be collected before and 24 hours after the procedure: CBC, AST, ALT, and serum creatinine 22 Procedure E. Drug dose, administration F. Collection of blood sample At 0, 5, 30 minutes, 2, 6,10 hours following Ketamine administration in heparinized tube. 23 Procedure G.Hemodynamic measurement Cardiorespiratory Monitor, Pulse oxymetry will be connected to the patient. • • • • • • • Systolic blood pressure (SBP) Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) Heart rate (HR) Respiratory rate (RR) O2 saturation will be measured Patient responsiveness Adverse events (Will be observed and measured in 5 minutes interval until discharge from PICU, and 30 minutes after upto 24 hrs) 24 Procedure H. Efficacy end point: Onset of sedation Observed patient sedation score 1. Patient sedation during the surgery scored from 0-2 as follows: 0 = drowsy or sleep but easily to arouse by verbal stimulus. 1 = sleep and difficult to arouse or by verbal stimulus (considered over sedated) 2 = awake and anxious or disturbed (considered inadequately sedated) 25 Procedure H. Efficacy end point:Cont’d 2. Patient movement during procedure scored from 0-3 as follows: ▰0 = none ▰2 = moderate ▰1 = mild ▰3 = severe Recovery time: 1. Time to voice arousal 2. Time to speak 3. Time to sit up 4. Time to meet criteria for removal of monitoring devices 5. Time to meet criteria for discharge. 26 Procedure H. Efficacy end point:cont’d Duration of analgesia will be evaluated by “FACES PAIN RATING SCALE” every 30 minute- 1 hour during and post procedure for 24 hours or until the 1st dose of any analgesic drug given. 27 Procedure I. Ketamine assay Ketamine will be analyzed by HPLC (high pressure liquid chromatography) according to Bolze S et al. 28 Data analysis 1. Pharmacokinetic analysis Compartmental and Non-Compartmental analysis of the plasma concentrations of Ketamine will be conducted using WinNONLIN program. 29 2. Statistical analysis SPSS program will be used for statistical evaluation of the data. Paired t-test will be used to compare the maximal change in hemodynamic variables during Ketamine administration with baseline values. 30 Statistical analysis-cont. ANOVA test will be used for comparison of hemodynamic variables at different time intervals. The non-parametric Spearman's rank correlation test to study the correlation between pharmacokinetic variable and pathological variables (age, body weight, creatinine clearance) 31 Work plan Date Activity April 2004 Literatures review May 2004 Writing the proposal and preparing the data collection form KAMC research committee approval May 2004 June-August Collecting blood samples and patient data SeptemberOctober Analysis of Ketamine by HPLC November Pharmacokinetic of data and writing the data 32 33