* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medication Administration
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
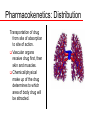
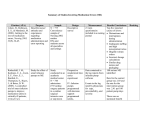
Medication Administration Unit VI Part 2 (lecture) Keith Rischer, RN, MA, CEN, CCRN Today’s Objectives… Differentiate the various effects of drugs on the body Explain how age, illness, time of administration, & absorption affect drug action Describe the relationship between mechanism of action of most commonly used drugs and nursing assessment and implications for the nurse Minnesota Nurse Practice Act Legal aspects r/t the nurse (6) Engaging in unprofessional conduct, including, but not limited to, a departure from or failure to conform to board rules of professional or practical nursing practice … to the minimal standards of acceptable and prevailing professional or practical nursing practice, or any nursing practice that may create unnecessary danger to a patient's life, health, or safety. Actual injury to a patient need not be established under this clause. Laws and Regulations Drug legislation in the U.S. Pure Food and Drug Act - 1906 Harrison Narcotic law of 1914 – defined narcotic Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetics Act of 1938 established the FDA, set standards r/t safety, potency, efficacy. Durkham-Humphrey Amendment of 1952 differentiates between prescription and nonprescription drugs. Laws and Regulations Controlled Substance Act 1970 Categorizes controlled substances Limits refills Established programs to prevent and treat drug dependence FDA instituted the MedWatch program in 1993 Consumer Rights Drugs are safe, pure, effective and reliable Clients have the right to quality health information r/t drugs and medications Name, of drug, purpose, action, possible adverse side effects. Consumer Rights Patients have a right to: To refuse any medications To have qualified person assess medication history including allergies Not to be given unnecessary medications Safety The Joint Commission Oxycontin vs. Oxycodone Hydromorphone vs. Morphine Ephedrine vs. Epinephrine Hydralazine vs. Hydroxyzine ISMP Institute for Safe Medication Practices http://www.ismp.org Schedule of Controlled Substances Schedule I: High potential for abuse No medical use exists Heroin Schedule II: Potential for abuse, physical and psychological dependence Has accepted medical use No refills Methadone, Morphine, Fentanyl, Oxycontin, Percocet Schedule of Controlled Substances Schedule III: intermediate potential for abuse Has accepted medical use May Refill 5 times Vicodin, Tyl. #3 Schedule IV: Less abuse potential. May refill 6 times within 6 months Benzodiazepines, Ambien Schedule V: Minimal abuse potential Cough suppressants with codeine Controlled Substances Drugs kept in locked drawer Forms for recording the use of these drugs Nurse verifies the number of a specific drug available If drug wasted, second nurse acts as a witness Drugs are counted each shift with 2 RNs Pharmacokenetics Study of action of drugs within the body Must consider before administering meds Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Pharmacokenetics: Absorption Process by which drug passes into the bloodstream better the blood supply faster the absorption GI tract: variable IV: immediate Subcutaneous: depends on local blood flow Intramuscular: depends on local blood flow Topical: slow, incomplete Inhalation: rapid Rectal: may be erratic Pharmacokenetics: Absorption Factors influencing absorption Dose form and route Influence of pH Blood flow to site Solubility of drug Time Action Profile Onset Peak Duration Pharmacokenetics: Distribution Transportation of drug from site of absorption to site of action. Vascular organs receive drug first, then skin and muscles. Chemical/physical make up of the drug determines to which area of body drug will be attracted. Pharmacokenetics: Metabolism The process of altering or changing the drug into a less active form. Caution: this process may be impaired in the elderly or in someone with liver disease Biotransformation Pharmacokenetics: Excretion Process by which drug is eliminated from the body. Caution: since the kidneys/liver of older adults are less efficient, they may require smaller doses of a drug. Promote adequate fluid intake Medication Pharmokinetics Morphine Tylenol Ibuprofen Atenolol Coumadin Why is pharmokinetics relevant if your patient has renal or liver disease? Special Dosing Considerations Renal Disease Chronic renal insufficiency Diabetes CKD-dialysis dependant Labs – GFR – Creatinine Special Dosing Considerations Liver Disease Cirrhosis Hepatitis ETOH Labs – – – – AST ALT Bili Albumin Special Dosing Considerations Heart failure CHF Diastolic Systolic Cardiomyopathy Body size Underweight/pediatric calculated by weight or body surface area Obese Normal Developmental Factors/drug action Developmental factors: Pregnancy Infants Older adults Diet Food alters drug absorption rate, metabolism Nutrition can affect the action of a drug Ex: Vitamin K – found in green leafy vegetables can counteract the effect of an anticoagulant – Coumadin Factors affecting drug action: Elderly Use w/caution Digoxin Nifedipine Benzodiazepines Alprazolam Diazepam Increased fall risk ACE inhibitors Beta blockers Ca++ channel blockers Vasodilators Diuretics Opiod narcotics Anti-depressants Benzodiazepines Factors affecting drug action Environmental Time of administration Stress Exposure to heat and cold Cultural, ethnic, genetic Ethnopharmacy Cultural factors and practices Mechanism…Nursing Implications Analgesics Morphine, Dilaudid, Percocet, Vicodin Mechanism: Binds to opiate receptors in CNS Produces generalized CNS depression Opiate effects cause vasodilation, decreased peristalsis Nsg. Implications… Classifications/Nursing Implications Analgesics Mild Tylenol NSAIDS Ibuprofen, Aspirin Moderate Opiod Narcotics po – Tylenol #3, Vicodin, Percocet Severe Opiod Narcotics IV – Morphine, Dilaudid, Fentanyl Anticoagulants Warfarin (Coumadin) Mech of Action Uses Nursing implications INR (0.9-1.2)…11-13 seconds clotting time 2-3 therapeutic Heparin Mech of action Vitamin K clotting factors Prevents conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin Uses Nursing implications Aspirin Mech of action Uses Nursing implications Mechanism…Nursing Implications Calcium Channel Blockers Diltiazem Mechanism: Inhibits transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells during the cardiac action potential phase. Causes systemic vasodilation and coronary artery vasodilation as well as slowing AV node conduction and decreased cardiac contractility Nsg. Implications… Mechanism…Nursing Implications Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Lisinopril, Enalapril Mechanism: Blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. Net effect: systemic vasodilation Nsg. Implications… Classifications/Nursing Implications Loop Diuretics Mechanism: Furosemide (Lasix) Inhibits the reapsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule Increases renal excretion of water, Na+, Cl-, Mg+, and K+ causing loss of excess fluid and drop in BP Nsg. Implications… Medication interactions When one medication modifies the action of another, this can occur Synergistic effect: effect of 2 drugs when combined is greater than when meds given separately. Beneficial: give Tylenol with oxycodone to reduce the total amount of narcotic needed.(additive effect) Harmful: Alcohol taken with antihistamines, antidepressants, barbiturates and narcotic analgesics Medication interactions Iatrogenic disease: disease caused unintentionally by medical therapy Ex: liver failure after prolonged use of Tylenol Amiodarone and pulmonary fibrosis Pregnant woman takes medication that results in malformations in the fetus. Nursing implications What can nursing do to enhance desired effect/decrease adverse effects and ensure safety?? History Allergies Shellfish…Iodine Med data Clients condition Clients knowledge/learning needs Drug Medication Systems Stock Supply Unit-Dose Automated Medication Dispensing (Pyxis) Bar Code Medication – use of scanner Self-administered PCA, Inhalers, ointments etc